
Agnatha is a paraphyletic infraphylum of non-gnathostome vertebrates, or jawless fish, in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both living (cyclostomes) and extinct. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes.
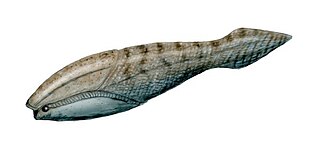
Arandaspida is a taxon of very early, jawless prehistoric fish which lived during the Ordovician period. Arandaspids represent some of the oldest known vertebrates. The group represents a subclass within the class Pteraspidomorphi, and contains only one order, the Arandaspidiformes. The oldest known genus of this group is Sacabambaspis found in South America.
Tolypelepidida is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates. These armored jawless fish superficially resemble their relatives, the cyathaspids, though, researchers place the tolypelepids as a sister group to the cyathaspids and the pteraspidids. A recent study by Lundgren and Blom in 2013 implies that the order is paraphyletic, with the type genus, Tolypelepis, being the sister taxon of Cyathaspidiformes. The typical tolypelepid had a carapace formed from dorsal and ventral plates, and a scaly tail.

Protaspididae is an extinct family of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathans. Fossils of the various genera are found in early Devonian-aged marine strata. Protaspidids were once thought to represent a transitional form between the Pteraspididae and the Psammosteida, bearing the broad head shield shape of the latter, due to a more benthic (bottom-dwelling) existence, but recent phylogenical comparisons demonstrate that the protaspidids are actually highly derived pteraspidids, and that the anchipteraspidids, the most primitive of pteraspidids, are the sister-group of the psammosteids.

Lepidaspis serrata is an extinct heterostracan jawless fish from Early Devonian Canada. Its scientific name refers to the fact that the armor is composed of hundreds of tiny scales with serrated edges.

Thelodonti is a class of extinct Palaeozoic jawless fishes with distinctive scales instead of large plates of armor.

Anaspida is an extinct group of jawless fish that existed from the early Silurian period to the late Devonian period. They were classically regarded as the ancestors of lampreys, but it is denied in recent phylogenetic analysis, although some analysis show these group would be at least related. Anaspids were small marine fish that lacked a heavy bony shield and paired fins, but were distinctively hypocercal.

Pteraspidomorphi is an extinct class of early jawless fish. They have long been regarded as closely related or even ancestral to jawed vertebrates, but the few characteristics they share with the latter are now considered as basal traits for all vertebrates.

Drepanaspis is an extinct genus of heterostracan armoured jawless fish from the Early Devonian. Drepanaspis are assumed to have lived primarily in marine environments and is most commonly characterized by their ray-like, heavily armoured bodies, along with their lack of paired fins and jaws.

Errivaspis is an extinct genus of pteraspid heterostracan agnathan vertebrate known from fossils at the Wayne Hereford Quarry, of Early Devonian England, and of Podolia, Early Devonian Ukraine. It was originally described by Dr. Errol Ivor White as one of five form-variants of Pteraspis rostrata, i.e., "Pteraspis rostrata var. waynesis. In 1984, Alain Blieck moved var. waynesis into its own genus, Errivaspis, which he named after Dr. White. Other later researchers would then mistakenly assume that Blieck synonymized the entire genus of Pteraspis into Errivaspis.

Astraspida, or astraspids, are a small group of extinct armored jawless vertebrates, which lived in the Late Ordovician in North America. They are placed among the Pteraspidomorphi because of the large dorsal and ventral shield of their head armor. They are represented by a single genus, Astraspis, including possibly two species, A. desiderata and A. splendens but their remains are fairly abundant in Ordovician sandstones of the USA and Canada (Quebec). The head armor of Astraspis is rather massive, with a series of ten gill openings lining the margin of the dorsal shield, and laterally placed eyes. The dorsal shield is ribbed by strong longitudinal crests, and the tail is covered with large, diamond-shaped scales. They are often grouped together with the Arandaspidida.

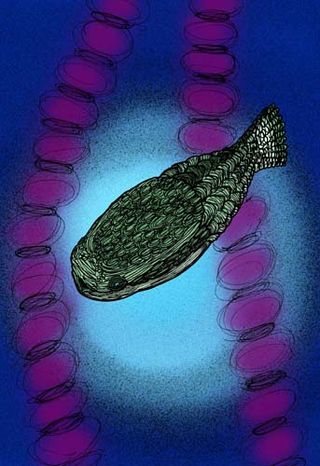
Furcacauda is a genus of thelodontid agnathan from the Lower Devonian of Canada, and is the type genus of the order Furcacaudiformes. Furcacaudiform thelodontids were deep water jawless vertebrates with symmetrical fork and lobed-finned tails and scales smaller than typical loganellid and nikoliviid thelodonti scales. Furcacaudiform thelodonts are noted as having a laterally compressed body, large anterior eyes, slightly posterior, lateral, and vertical to a small mouth, and a condensed curved row of branchial openings (gills) directly posterior to the eyes. Many but not all had laterally paired fins. Wilson and Caldwell also note the presence of a caudal peduncle and a long caudal fin made of two large lobes, one dorsal and one ventral separated by 8 to 14 smaller intermediate lobes, giving the appearance of a striated half-moon shaped tail resembling the tail of a heterostracan. A large square cavity within the gut connecting a small intestine to an anal opening lead many to believe that it is this genus that exhibits the first vertebrate stomach. According to Wilson and Caldwell their discovery, based on sediment infillings of fossils of the Furcacauda heintze, gives credence to the evolutionary development of stomach before jaws.

The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fish lineages belong to the Agnatha, or jawless fish. Early examples include Haikouichthys. During the late Cambrian, eel-like jawless fish called the conodonts, and small mostly armoured fish known as ostracoderms, first appeared. Most jawless fish are now extinct; but the extant lampreys may approximate ancient pre-jawed fish. Lampreys belong to the Cyclostomata, which includes the extant hagfish, and this group may have split early on from other agnathans.

Panamintaspis snowi is an extinct species of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathan which existed during the early Middle Devonian period of Death Valley, California. Fossils are found in Late Emsian-aged marine strata of the Lost Burro Formation. P. snowi strongly resembles Pteraspis, though while it was originally described as a member of the same family, Pteraspididae, a recent phylogenetic reassessment of the order Pteraspidiformes places P. snowi within the paraphyletic family "Protopeteraspidae," as the sister taxon of the suborder Pteraspidoidei.

Pteraspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan agnathan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Early Devonian strata of Europe and North America, and from Upper Silurian Canada.

Cyathaspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Silurian to Early Devonian strata of Europe, and North America, and from Early Devonian marine strata of Siberia.

Anglaspis is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Europe, from the late Silurian period until the genus' extinction during the Early Devonian. As with other cyathaspidiforms, individuals of Anglaspis had dorsal and ventral plates covering the forebody, gill pouches, and nasal openings that lay on the roof of the oral cavity.

Protopteraspididae is an extinct family of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathans. Fossils of the various genera are found in early Devonian-aged marine strata. Protopteraspidids were once thought to represent a taxon of basal pteraspidids but recent evaluations demonstrate that Protopteraspididae is a paraphyletic group of various transitional forms representing a gradual transition between the more advanced Pteraspoidei, and the anchipteraspidids and the Psammosteids.

Furcacaudidae, the "'fork-tailed' agnathans," is an extinct family of thelodontid agnathans from the Lochkovian stage of the Early Devonian epoch and Wenlockian epoch of the Silurian, known from fossils found in Northern Canada. It is the type family of the order Furcacaudiformes, and itself currently includes 6 known species. It was officially described in 1998 by Mark V. H. Wilson and Michael W. Caldwell.

Archipelepidiformes is an order of extinct jawless fishes in the class Thelodonti.




















