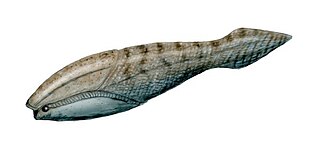
Arandaspida is a taxon of very early, jawless prehistoric fish which lived during the Ordovician period. Arandaspids represent the oldest known craniates, a proposed group of chordates that contain all chordates with a cartilage-derived skull, and hagfish. The group represents a subclass within the class Pteraspidomorphi, and contains only one order, the Arandaspidiformes. The oldest known genus of this group is Sacabambaspis found in South America.

Protaspididae is an extinct family of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathans. Fossils of the various genera are found in early Devonian-aged marine strata. Protaspidids were once thought to represent a transitional form between the Pteraspididae and the Psammosteida, bearing the broad head shield shape of the latter, due to a more benthic (bottom-dwelling) existence, but recent phylogenical comparisons demonstrate that the protaspidids are actually highly derived pteraspidids, and that the anchipteraspidids, the most primitive of pteraspidids, are the sister-group of the Psammosteids.

The class Osteostraci is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian.

Bothriolepis is a widespread, abundant and diverse genus of antiarch placoderms that lived during the Middle to Late Devonian period of the Paleozoic Era. Historically, Bothriolepis resided in an array of paleo-environments spread across every paleocontinent, including near shore marine and freshwater settings. Most species of Bothriolepis were characterized as relatively small, benthic, freshwater detritivores, averaging around 30 centimetres (12 in) in length. However, the largest species, B. maxima, had a carapace about 100 centimetres (39 in) in length. Although expansive with over 60 species found worldwide, comparatively Bothriolepis is not unusually more diverse than most modern bottom dwelling species around today.

Errivaspis is an extinct genus of pteraspid heterostracan agnathan vertebrate known from fossils at the Wayne Hereford Quarry, of Early Devonian England, and of Podolia, Early Devonian Ukraine. It was originally described by Dr. Errol Ivor White as one of five form-variants of Pteraspis rostrata, i.e., "Pteraspis rostrata var. waynesis. In 1984, Alain Blieck moved var. waynesis into its own genus, Errivaspis, which he named after Dr. White. Other later researchers would then mistakenly assume that Blieck synonymized the entire genus of Pteraspis into Errivaspis.

Pituriaspis doylei(Doyle's pituri shield) was one of two known species of jawless fish belonging to the Class Pituriaspida, and is the better known of the two. The species lived in estuaries during the Givetian epoch of the Middle Devonian, 390 million years ago in what is now the Georgina Basin of Western Queensland, Australia.

Neeyambaspis enigmatica is the lesser known of the two species of pituriaspid agnathans. The species lived in estuaries during the Middle Devonian, in what is now the Georgina Basin of Western Queensland, Australia.

Ctenaspis is an extinct genus of heterostracan cyathaspid agnathans from the early Devonian of Canada.

Furcacauda is a genus of thelodontid agnathan from the Lower Devonian of Canada, and is the type genus of the order Furcacaudiformes. Furcacaudiform thelodontids were deep water jawless vertebrates with symmetrical fork and lobed-finned tails and scales smaller than typical loganellid and nikoliviid thelodonti scales. Furcacaudiform thelodonts are noted as having a laterally compressed body, large anterior eyes, slightly posterior, lateral, and vertical to a small mouth, and a condensed curved row of branchial openings (gills) directly posterior to the eyes. Many but not all had laterally paired fins. Wilson and Caldwell also note the presence of a caudal peduncle and a long caudal fin made of two large lobes, one dorsal and one ventral separated by 8 to 14 smaller intermediate lobes, giving the appearance of a striated half-moon shaped tail resembling the tail of a heterostracan. A large square cavity within the gut connecting a small intestine to an anal opening lead many to believe that it is this genus that exhibits the first vertebrate stomach. According to Wilson and Caldwell their discovery, based on sediment infillings of fossils of the Furcacauda heintze, gives credence to the evolutionary development of stomach before jaws.
Protaspis is an extinct genus of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathan which lived during the Early Devonian of the United States, with fossils found in marine strata in what is now Utah, Wyoming and Idaho.

Traquairaspis is a genus of extinct heterostracan agnathan fish known from the Silurian and Early Devonian periods. It is predominantly known from Late Silurian fluvial deposits from Wales and England: some species were also found in shallow water marine environment in Canada and North America.
Palanasaspis chekhivensis is an extinct species of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathan which existed during the Pragian epoch of the early Devonian period in what is now Podolia, Ukraine. It is known primarily from a wide rostral plate, which is referenced in the generic name, a compound word combining the Latin words pala, "shovel," and nasus, "nose," with the Greek suffix aspis, "a small shield." Although the rostral plate clearly marks the creature as a pteraspidoid heterostracan, that literally nothing else of its anatomy is known forces researchers to leave it as incertae sedis.

Psammmosteida also called as Psammosteoidei is a suborder of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathans. The psammosteids had broad, flattened bodies, suggesting a predominantly benthic habit. The earliest unequivocal psammosteid is Drepanaspis of Early Devonian Germany, which is either included in the family Psammosteidae, or placed within its own family, Drepanaspididae. If the late Silurian/Early Devonian Weigeltaspis is a psammosteid, as opposed to being a traquairaspid, then that genus, instead, would be the oldest psammosteid. However, its placement within Heterostraci remains a matter of debate. Other notable psammosteids include Psammosteus, and Obruchevia, two genera of enormous species with dorsal shields around one meter in diameter. The Psammosteids were the only heterostracans to survive to the end of the Devonian, where they finally perish during the Hangenberg event.

Pteraspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan agnathan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Early Devonian strata of Europe and North America, and from Upper Silurian Canada.

Amphiaspidida is a taxon of extinct cyathaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. Some authorities treat it as a suborder of Cyathaspidiformes, while others treat it as an order in its own right as "Amphiaspidiformes." In life, they are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. Amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothorax armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked like a potpie or a hot waterbottle with a pair of small, or degenerated eyes sometimes flanked by preorbital openings, a pair of branchial openings for exhaling, and a simple, slit-like, or tube-like mouth.

Anglaspis is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Europe, from the late Silurian period until genus' extinction during the Early Devonian. As with other cyathaspidiforms, individuals of Anglaspis had dorsal and ventral plates covering the forebody, gill pouches, and nasal openings that lay on the roof of the oral cavity.

Traquairaspidiformes is an order of extinct heterostracan agnathan fish known from the Silurian and Early Devonian periods. It is predominantly known from Late Silurian fluvial deposits from Wales and England: some species were also found in shallow water marine environment in Canada and North America.

Lamiaspis longiripa is an extinct pteraspid heterostracan agnathan vertebrate found in marine strata of Early Devonian Nevada.

















