
Mauritania, a country in the western region of the continent of Africa, is generally flat, its 1,030,700 square kilometres forming vast, arid plains broken by occasional ridges and clifflike outcroppings. Mauritania is the world’s largest country lying entirely below an altitude of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). It borders the North Atlantic Ocean, between Senegal and Western Sahara, Mali and Algeria. It is considered part of both the Sahel and the Maghreb. A series of scarps face southwest, longitudinally bisecting these plains in the center of the country. The scarps also separate a series of sandstone plateaus, the highest of which is the Adrar Plateau, reaching an elevation of 500 metres or 1,640 feet. Spring-fed oases lie at the foot of some of the scarps. Isolated peaks, often rich in minerals, rise above the plateaus; the smaller peaks are called Guelbs and the larger ones Kedias. The concentric Guelb er Richat is a prominent feature of the north-central region. Kediet ej Jill, near the city of Zouîrât, has an elevation of 915 metres or 3,002 feet and is the highest peak.

The Mauritania national football team, nicknamed Al-Murabitun in reference to Almoravid dynasty, represents Mauritania in men's international football. It is controlled by the Fédération de Football de la République Islamique de Mauritanie, and is a member of the Confederation of African Football. They have not qualified for the FIFA World Cup. However, in the Amílcar Cabral Cup, a regional tournament for West Africa, Mauritania came fourth in 1980 on hosting the competition. The national football team of Mauritania were later runners-up in 1995, losing on penalties to Sierra Leone after the final finished 0–0.
João Fernandes was a Portuguese explorer of the 15th century. He was perhaps the earliest of modern explorers in the upland of West Africa, and a pioneer of the European slave and gold trade of Guinea.
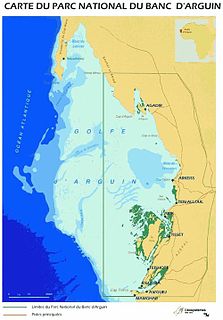
The Banc d'Arguin National Park of Bay of Arguin lies in Western Africa on the west coast of Mauritania between Nouakchott and Nouadhibou. The World Heritage Site is a major site for migratory birds and breeding birds, including flamingos, pelicans and terns. Much of the breeding is on sand banks including the islands of Tidra, Niroumi, Nair, Kijji and Arguim. The surrounding waters are some of the richest fishing waters in western Africa and serve as nesting grounds for the entire western region.

Ras Nouadhibou is a 60-kilometre (37 mi) peninsula or headland divided by the border between Mauritania and Western Sahara on the African coast of the Atlantic Ocean. It is internationally known as Cabo Blanco in Spanish or Cap Blanc in French.

The Mormyridae, sometimes called "elephantfish", are a family of weakly electric freshwater fish in the order Osteoglossiformes native to Africa. It is by far the largest family in the order with around 200 species. Members of the family can be popular, if challenging, aquarium species. These fish are also known for having large brain size and unusually high intelligence.

The milk shark is a species of requiem shark, and part of the family Carcharhinidae, whose common name comes from an Indian belief that consumption of its meat promotes lactation. The largest and most widely distributed member of its genus, the milk shark typically measures 1.1 m (3.6 ft) long, and can be found in coastal tropical waters throughout the eastern Atlantic and the Indo-Pacific regions. Occurring from the surface to a depth of 200 m (660 ft), this species is common near beaches and in estuaries, and has been recorded swimming up rivers in Cambodia. Juveniles are known to inhabit tidal pools and seagrass meadows. The milk shark has a slender body with a long, pointed snout and large eyes, and is a nondescript gray above and white below. This shark can be distinguished from similar species in its range by the long furrows at the corners of its mouth, and seven to 15 enlarged pores just above them.
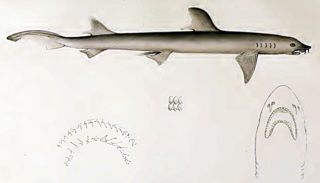
The barbeled houndshark is a species of ground shark and the only member of the family Leptochariidae. This demersal species is found in the coastal waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean from Mauritania to Angola, at depths of 10–75 m (33–246 ft). It favors muddy habitats, particularly around river mouths. The barbeled houndshark is characterized by a very slender body, nasal barbels, long furrows at the corners of the mouth, and sexually dimorphic teeth. Its maximum known length is 82 cm (32 in).

The smoothback angelshark is an angelshark of the family Squatinidae found in the eastern Atlantic.

The Canal de São Vicente is a strait of the Atlantic Ocean separating the islands of Santo Antão and São Vicente, Cape Verde. At its narrowest point, it is 11 km (7 mi) wide. The ferry route between the ports of Porto Novo on Santo Antão and Mindelo on São Vicente crosses the canal. The channel begins in São Vicente's northwesternmost cape near Monte Cara up to the headland Ponta de João d'Évora in the northeast.
Mauretania's wildlife has two main influences as the country lies in two Biogeographic realms, the north sits in the Palearctic which extends south from the Sahara to roughly 19° North and the south in the Afrotropic realms. Additionally Mauritania is important for numerous birds which migrate from the Palearctic to winter there.

The winding cisticola is a species of bird in the family Cisticolidae. It has a scattered distribution across Africa south of the Sahara, and north of 11°S.

The Senegal jack, also known as the African jack, is a species of large marine fish classified in the jack family Carangidae. The species is distributed through the tropical waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean, ranging along the west African coast from Angola in the south to Mauritania in the north. It can be distinguished from co-occurring relatives by its longer dorsal fin lobe, as well as a host of other anatomical features. The Senegal jack grows to a known maximum length of 1 m. It is a coastal species, known to live semi-pelagically, inhabiting both the sea floor and surface waters to depths of around 200 m. The Senegal jack is a predatory species, taking fish, crabs and shrimps as its main prey items. The species reaches sexual maturity at 21 cm in females and 24 cm in males, with spawning occurring in two periods; February to April and September to November. The species is of minor importance to fisheries, and is not discriminated from other jacks in catch statistics. It is taken by trawls, seines and hook and line, and sold fresh or preserved.

The West African crocodile, desert crocodile, or sacred crocodile is a species of crocodile related to – and often confused with – the larger and more aggressive Nile crocodile.

Amphilectus strepsichelifer is a species of demosponges found in the Atlantic waters around Cape Verde, western Africa. The species name is a combination of the Latin strepsis = twisted, and chelifer = bearing chelae, reflecting the twisted condition of the chelae.
Amphilectus is a genus of demosponges, comprising around 20 species found in oceans around the world.
Sepia hierredda, the giant African cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish from the family Sepiidae, which was previously considered conspecific with the common cuttlefish Sepia officinalis. It is found along the western coast of Africa and is an important species to fisheries.

The grooved mullet is a species of ray-finned fish, a grey mullet from the family Mugilidae. It is found in the coastal waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean off the western coast of Africa, as far north as Mauritania, and into the western Indian Ocean.
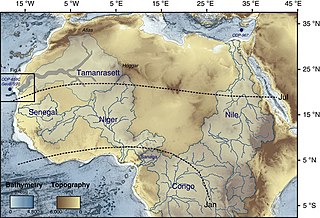
The Tamanrasset River is an enormous palaeoriver believed to have flowed through West Africa as recently as 5000 years ago during the African humid period. The Tamanrasset River basin is thought to have been comparable with the present-day Ganges-Brahmaputra river basin in Asia.
Neolithodes asperrimus is a species of king crab native to the coast of Africa. It has been found in South Africa and Mauritania at depths of 997–1,862 metres (3,271–6,109 ft), and Neolithodes aff. asperrimus has been found in Madagascar, Réunion, and the South Region of Brazil.















