
The Neogene is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period 23.03 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period 2.58 million years ago. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868).
Tertiary is an obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene Epoch. The time span covered by the Tertiary has no exact equivalent in the current geologic time system, but it is essentially the merged Paleogene and Neogene periods, which are informally called the Early Tertiary and the Late Tertiary, respectively.

The Zanclean is the lowest stage or earliest age on the geologic time scale of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 5.332 ± 0.005 Ma and 3.6 ± 0.005 Ma. It is preceded by the Messinian Age of the Miocene Epoch, and followed by the Piacenzian Age.

The Cisuralian is the first series/epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the Pennsylvanian and followed by the Guadalupian. The Cisuralian Epoch is named after the western slopes of the Ural Mountains in Russia and Kazakhstan and dates between 298.9 ± 0.15 – 272.3 ± 0.5 Ma.
The Aquitanian is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy's (ICS) geologic timescale, the oldest age or lowest stage in the Miocene. It spans the time between 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma and 20.43 ± 0.05 Ma during the Early Miocene. It was a dry, cooling period. The Aquitanian succeeds the Chattian and precedes the Burdigalian.
The Burdigalian is, in the geologic timescale, an age or stage in the early Miocene. It spans the time between 20.43 ± 0.05 Ma and 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma. Preceded by the Aquitanian, the Burdigalian was the first and longest warming period of the Miocene and is succeeded by the Langhian.
The Messinian is in the geologic timescale the last age or uppermost stage of the Miocene. It spans the time between 7.246 ± 0.005 Ma and 5.333 ± 0.005 Ma. It follows the Tortonian and is followed by the Zanclean, the first age of the Pliocene.
The Serravallian is, in the geologic timescale, an age or a stage in the middle Miocene Epoch/Series, which spans the time between 13.82 Ma and 11.63 Ma. The Serravallian follows the Langhian and is followed by the Tortonian.
The Langhian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, an age or stage in the middle Miocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma and 13.65 ± 0.05 Ma during the Middle Miocene.
The Tortonian is in the geologic time scale an age or stage of the late Miocene that spans the time between 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma and 7.246 ± 0.005 Ma. It follows the Serravallian and is followed by the Messinian.
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between 27.82 and23.03 Ma. The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian.
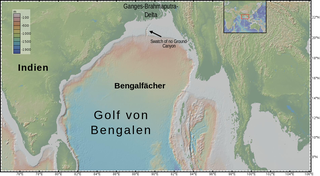
The Bengal Fan, also known as the Ganges Fan, is the largest submarine fan on Earth.
The Late Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma to 5.333 Ma.
The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is preceded by the Early Miocene.
The Early Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages.

The Paratethys sea, Paratethys ocean, Paratethys realm or just Paratethys was a large shallow inland sea that stretched from the region north of the Alps over Central Europe to the Aral Sea in Central Asia.
The Friasian age is a period of geologic time within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification of South America. It follows the Santacrucian and precedes the Colloncuran age.

The Pebas Formation is a lithostratigraphic unit of Miocene age, found in western Amazonia. The formation extends over 1,000,000 square kilometres (390,000 sq mi), including parts of Brazil, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia. It is interpreted as representing the deposits of a lake or series of lakes, formed within the foreland basin of the Andes mountain belt. It is known for its abundant fossil ostracods and molluscs and an unusually diverse group of crocodylians.
Caleta Herradura Formation is a geologic formation of Late Miocene (Montehermosan) age, cropping out on the Mejillones Peninsula in northern Chile. The erosion at the Coastal Cliff of northern Chile have created particularly good exposures of Caleta Herradura Formation. The formation deposited in a half graben within Mejillones Peninsula. The formation rests nonconformably on the Jorgino Formation.
Noriphoca is an extinct genus of phocid belonging to the subfamily Monachinae. It is known from the late Oligocene to early Miocene of Italy.







