
Egyptian hieroglyphs were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt, used for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with a total of some 1,000 distinct characters. Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Through the Phoenician alphabet's major child systems, the Egyptian hieroglyphic script is ancestral to the majority of scripts in modern use, most prominently the Latin and Cyrillic scripts and the Arabic script and possibly Brahmic family of scripts

In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a cartouche is an oval with a line at one end tangent to the oval, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name. The first examples of the cartouche are associated with pharaohs at the end of the Third Dynasty, but the feature did not come into common use until the beginning of the Fourth Dynasty under Pharaoh Sneferu. While the cartouche is usually vertical with a horizontal line, if it makes the name fit better it can be horizontal, with a vertical line at the end. The ancient Egyptian word for cartouche was shenu, and the cartouche was essentially an expanded shen ring. Demotic script reduced the cartouche to a pair of brackets and a vertical line.

In Egyptian mythology, Hemen was a falcon–god.

A hieroglyph was a character of the ancient Egyptian writing system. Logographic scripts that are pictographic in form in a way reminiscent of ancient Egyptian are also sometimes called "hieroglyphs". In Neoplatonism, especially during the Renaissance, a "hieroglyph" was an artistic representation of an esoteric idea, which Neoplatonists believed actual Egyptian hieroglyphs to be. The word hieroglyphics refers to a hieroglyphic script.
Gardiner's Sign List is a list of common Egyptian hieroglyphs compiled by Sir Alan Gardiner. It is considered a standard reference in the study of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs.
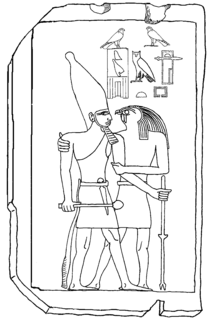
Qahedjet could be the Horus name of an ancient Egyptian king (pharaoh), who may have ruled during the 3rd Dynasty or could be a voluntarily archaistic representation of Thutmose III. Since the only artifact attesting to the ruler and his name is a small stela made of polished limestone of uncertain origin and authenticity, Egyptologists are discussing the chronological position and historical figure of Qahedjet.
This is a glossary of ancient Egypt artifacts.
The ancient Egyptian Papyrus stem hieroglyph is one of the oldest language hieroglyphs from Ancient Egypt. The papyrus stalk, was incorporated into designs of columns on buildings, also facades, and is also in the iconographic art portrayed in ancient Egyptian decorated scenes.
Reading Egyptian Art: A Hieroglyphic Guide to Ancient Egyptian Painting and Sculpture is a 1992 primer on Egyptian hieroglyphs written by English archaeologist Richard H. Wilkinson.The book was written from the viewpoint of seeing hieroglyphs in the context of their use in iconography of sculpture, monuments, reliefs, tomb reliefs, literature, specifically the corpus of The Book of the Dead versions for various deceased Egyptians, and other areas.
The pectorals of ancient Egypt were a form of jewelry, often represented as a brooch. These were mostly worn by richer people and the pharaoh.
The Paser Crossword Stela is an ancient Egyptian limestone stela that dates from the 20th Dynasty. It was constructed by Paser, ca. 1150 BC, during the reign of Pharaoh Ramesses VI.

The Stela of Tetisheri is a limestone donation stele erected by Pharaoh Ahmose I, founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. It sits in the construction of his mortuary complex that included a cenotaph to his grandmother Queen Tetisheri, Senakhtenre's Great Royal Wife and grandmother of both Ahmose and his Principal Wife, Ahmose-Nefertari.
The ancient Egyptian Branch hieroglyph, also called a Stick, is a member of the trees and plants hieroglyphs.

The ancient Egyptian Bone-with-meat hieroglyph represented: "ancestry, inherit", and phonetic isw, iw' ; a determinative for the femur, (iw'); and swt, for the tibia.
The Jubilee Festival for the Pharaoh, the Heb Sed is represented in hieroglyphs by a Jubilee Pavilion Hieroglyph. It is Gardiner Sign Listed as no. O23. However it often appears with other pavilion, or festival hieroglyphs: the Hall, no. O22,

The following outline is provided as an overview of a topical guide to ancient Egypt:
This page list topics related to ancient Egypt.

The ancient Egyptian Scribe equipment hieroglyph 𓏞, or its reversed form 𓏟, portrays the equipment of the scribe. Numerous scribes used the hieroglyph in stating their name, either on papyrus documents, but especially on statuary or tomb reliefs.
Nefer-Setekh is the name of an ancient Egyptian high official, who lived and worked either during the late midst of the 2nd or during the beginning of the 3rd dynasty. He became known by his name, which was addressed to the deity Seth.









