
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
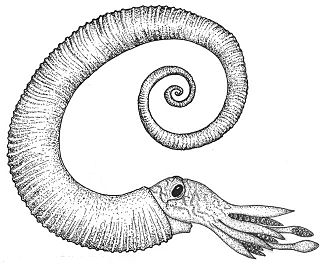
The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved during the Late Jurassic but were not very common until the Cretaceous period, when they rapidly diversified and became one of the most distinctive components of Cretaceous marine faunas. They have been recorded from every continent and many are used as zonal or index fossils. The most distinctive feature of the majority of the Ancyloceratina is the tendency for most of them to have shells that are not regular spirals like most other ammonites. These irregularly-coiled ammonites are called heteromorph ammonites, in contrast to regularly coiled ammonites, which are called homomorph ammonites.

Allocrioceras is an ammonoid cephalopod from the Turonian to Santonian stages of the Late Cretaceous, included in the turrilitoid family Anisoceratidae. Its shell is strongly ribbed and is in the form of a widely open spiral.
Aspinoceras is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonites that lived during the Early Cretaceous. The shell small; starts off with a few loosely wound whorls not in contact followed by a short moderately curved shaft ending in a broad hook. Surface covered with mostly fine, close spaced ribs, with periodic larger ribs. In general form it resembles Ancyloceras.
Astreptoceras is an extinct upper Cretaceous ammonoid cephalopod named by Henderson in 1970. Fossils belonging to this genera have been found in Antarctica and New Zealand.

Annuloceras is an extinct genus of ammonite cephalopod. Its fossils are found in Lower Barremian sediments from California. The genus is currently placed in the family Aegocrioceratidae.
Balearites is an extinct ancyloceratin genus included in the family Crioceratitidae, subclass Ammonoidea, from the Upper Hauterivian.

Nipponites is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonites. The shells of Nipponites form "ox-bow" bends, resulting in some of the most bizarre shapes seen among ammonites.

Bostrychoceras is a genus of heteromorph ammonite from the family Nostoceratidae. Fossils have been found in Late Cretaceous sediments in Europe and North America.

Crioceratites is an ammonite genus from the Early Cretaceous belonging to the Ancyloceratoidea.

Exiteloceras is an ammonite genus from the Late Cretaceous.

Nostoceras is an extinct genus of ammonites. The etymology of the name Nostoceras comes from "nostos" meaning return and "ceros" meaning horn, named as such by Alpheus Hyatt because it bends back on itself.

Phylloceras is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the family Phylloceratidae. These nektonic carnivores lived from Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous.

Eubostrychoceras is a genus of helically wound, corkscrew form, heteromorph ammonite which lived during the Upper Cretaceous. The genus is included in the ancycleratid family Nostoceratidae.
Sabaudiella is a genus of ammonites. It was described by Vasicek and Hoedemaeker in 2003, and the type species is S. sabaudianus, which was originally assigned to the genus Ancyloceras by Pictet and de Loriol in 1858. A new species, S. riverorum, which existed during the early Barremian of what is now Argentina, was described by Beatriz Aguirre-Urreta and Peter F. Rawson in 2012.

Macroscaphites is an extinct cephalopod genus included in the Ammonoidea that lived during the Barremian and Aptian stages of the Early Cretaceous. Its fossils have been found throughout most of Europe and North Africa.

Phyllopachyceras is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the family Phylloceratidae. These nektonic carnivores lived in the Cretaceous, from Hauterivian to Maastrichtian to age.

Pseudothurmannia is a genus of extinct cephalopods belonging to the subclass Ammonoidea and included in the family Crioceratitidae of the ammonitid superfamily Ancylocerataceae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived in the Cretaceous period, from Hauterivian age to Barremian age.
Antarcticoceras is a genus of crioconic ammonites in the family Shasticrioceratidae. It lived during the Early Cretaceous Period. Antarcticioceras fossils can be found in the Cretaceous rocks of Antarctica and South America.

Macroscaphitidae is an extinct family of ptychoceratoid cephalopods from the subclass Ammonoidea that lived from the Lower Barremian to the Lower Cenomanian stages of the Cretaceous. Fossils of Macroscaphitidae were found all around the world although the abundance of found fossils is rather limited. Known fossils from collections were found largely in Europe, South America and Africa. It is known for some species of which complete specimens were found that these animals developed a hetermorphic shell, i.e. the coiling of the shell was not regular, such that the first whirls formed a planispirally coiled evolute section as seen in homomorphic ammonites, but had an additional straight middle part and a presumably upwards facing aperture. Due to their odd morphology the taxonomic classification of Macroscaphitidae changed often over time since their discovery and may not be finally settled even now.














