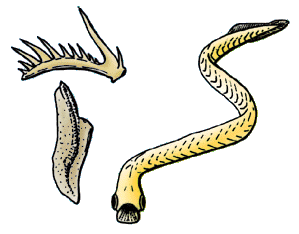
Conodonts are extinct agnathan chordates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from tooth-like microfossils found in isolation and now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. The animals are also called Conodontophora to avoid ambiguity.
The Moscovian is in the ICS geologic timescale a stage or age in the Pennsylvanian, the youngest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Moscovian age lasted from 315.2 to 307 Ma, is preceded by the Bashkirian and is followed by the Kasimovian. The Moscovian overlaps with the European regional Westphalian stage and the North American Atokan and Desmoinesian stages.
Archaeognathus is a fossilized jaw apparatus from the Ordovician that has been compared to the conodonts and vertebrates, yet remains unclassified.
Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts", is a large clade of conodonts that includes two major evolutionary grades; the Prioniodinina and the Ozarkodinina. It includes many of the more famous conodonts, such as the giant ordovician Promissum (Prioniodinina) from the Soom Shale and the Carboniferous specimens from the Granton Shrimp bed (Ozarkodinina). They are euconodonts, in that their elements are composed of two layers; the crown and the basal body, and are assumed to be a clade.
Paleontology in Missouri refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Missouri. The geologic column of Missouri spans all of geologic history from the Precambrian to present with the exception of the Permian, Triassic, and Jurassic. Brachiopods are probably the most common fossils in Missouri.
Maurice Goldsmith Mehl was an American paleontologist. A longtime professor in the Department of Geology at the University of Missouri, Mehl was a founding member and officer of the American Association of Petroleum Geologists. Mehl was a fellow of the Geological Society of America (1922), the Paleontological Society, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Edward B. Branson was an American geologist and paleontologist. He worked at the University of Missouri.
Ozarkodinida is an extinct conodont order. It is part of the clade Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts". There are two suborders of Ozarkodinida : Prioniodinina and Ozarkodinina.
Ozarkodina is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Spathognathodontidae.
Palmatolepis is an extinct conodont genus in the family Palmatolepidae. It was the most abundant genus of conodonts of the Late Devonian, disappearing during the Devonian/Carboniferous crisis.
Curtognathus is an extinct genus of conodonts from the Ordovician in the family Distacodontidae.
Acodus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Chirognathus is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Chirognathidae.
Idiognathodus is an extinct conodont genus in the family Idiognathodontidae.
Raymond (Ray) Lindsay Ethington is an American paleontologist. He works in the Geology department at the University of Missouri.
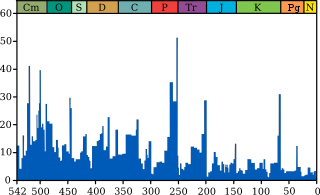
Conodonts are an extinct class of animals whose feeding apparatuses called teeth or elements are common microfossils found in strata dating from the Stage 10 of the Furongian, the fourth and final series of the Cambrian, to the Rhaetian stage of the Late Triassic. These elements can be used alternatively to or in correlation with other types of fossils in the subfield of the stratigraphy named biostratigraphy.
Cryptotaxis is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Cryptotaxidae from the Famennian.
Oulodus is a genus of conodonts in the family Prioniodinidae.