
The Bromeliaceae is a family of monocot flowering plants of 75 genera and around 3590 known species native mainly to the tropical Americas, with several species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, Pitcairnia feliciana.

Ocotea is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Lauraceae. Many are evergreen trees with lauroid leaves.

Staphylea, called bladdernuts, is a small genus of 10 or 11 species of flowering plants in the family Staphyleaceae, native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The highest species diversity is in China, where four species occur.

Monoon longifolium, the false ashoka, also commonly known by its synonym Polyalthia longifolia, is an Asian small tree species in the family Annonaceae. It is native to southern India and Sri Lanka, but has been widely introduced elsewhere in tropical Asia. This evergreen tree is known to grow over 20 m. in height and is commonly planted due to its effectiveness in alleviating noise pollution. It exhibits symmetrical pyramidal growth with willowy weeping pendulous branches and long narrow lanceolate leaves with undulate margins.

Araeococcus is a genus of the botanical family Bromeliaceae, subfamily Bromelioideae. It is native to northern South America, Central America and Trinidad.

Ardisia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Primulaceae. It was in the former Myrsinaceae family now recognised as the myrsine sub-family Myrsinoideae. They are distributed in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and the Pacific Islands, mainly in the tropics. There are over 700 accepted species. One species, Ardisia japonica is one of the 50 fundamental herbs in traditional Chinese medicine.

Aiouea is a genus of shrubs and trees in the family Lauraceae. It is native to tropical forests and montane forests of North and South America. The name is a curiosity because it consists entirely of vowels.

Aniba is an American neotropical flowering plant genus in the family Lauraceae. They are present in low and mountain cloud forest in Caribbean islands, Central America, and northern to central South America.

Aniba rosaeodora, also known as pau-rosa, is a species of Magnoliid tree in the family Lauraceae. Although sometimes wrongly referred to as rosewood this name is totally misleading; it is no tree of the genus Dalbergia. It grows in parts of the tropical rainforest of South America. It is an endangered species that sees exploitation for its essential oil.

Euplassa is a genus of flowering plants in the protea family. It is native to tropical South America, including Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.

Licaria is a flowering plant genus in the family Lauraceae, native to Central America and South America. It is a Neotropical genus with around 80 species.

Nectandra is a genus of plant in the family Lauraceae. They are primarily Neotropical, with Nectandra coriacea being the only species reaching the southernmost United States. They have fruit with various medical effects. Sweetwood is a common name for some plants in this genus.

Turpinia is a genus of trees and shrubs in family Staphyleaceae, native to Asia and North, Central, and South America. Species include:
A megaphone is a portable funnel-shaped device used to amplify a person's voice or other sounds.
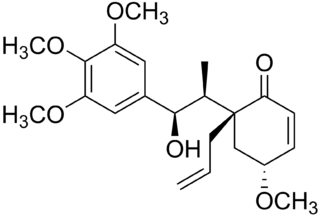
Megaphone is a cytotoxic neolignan obtained from Aniba megaphylla, a flowering plant of Laurel family which gave the compound its name. Megaphone has also been prepared synthetically.

Endlicheria is a neotropical plant genus consisting of approximately 60 species, occurring mostly in northern South America and the Amazon region. Most species are medium-sized trees, sometime up to 40 metres in height, but a few species are shrubs. DNA molecular data shows that it is closely related to Rhodostemonodaphne and Ocotea.
Cipuropsis is a genus of flowering plant in the family Bromeliaceae, native to the Caribbean, southern Central America and northwestern South America. The genus was first described by Ule in 1907.
Barfussia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Bromeliaceae.
Sadiria is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Primulaceae.













