
Neurotrophins are a family of proteins that induce the survival, development, and function of neurons.
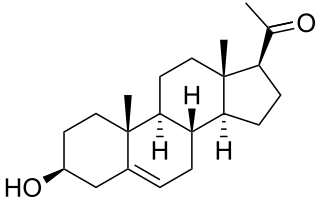
Pregnenolone (P5), or pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one, is an endogenous steroid and precursor/metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of most of the steroid hormones, including the progestogens, androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids. In addition, pregnenolone is biologically active in its own right, acting as a neurosteroid.

Pleiotrophin (PTN) also known as heparin-binding brain mitogen (HBBM) or heparin-binding growth factor 8 (HBGF-8) or neurite growth-promoting factor 1 (NEGF1) or heparin affinity regulatory peptide (HARP) or heparin binding growth associated molecule (HB-GAM) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTN gene. Pleiotrophin is an 18-kDa growth factor that has a high affinity for heparin. It is structurally related to midkine and retinoic acid induced heparin-binding protein.

Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA), also known as high affinity nerve growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1, or TRK1-transforming tyrosine kinase protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTRK1 gene.

Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), also known as tyrosine receptor kinase B, or BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor or neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTRK2 gene. TrkB is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The standard pronunciation for this protein is "track bee".

Neurotrophin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTF3 gene.

Artemin, also known as enovin or neublastin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARTN gene.

Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FRS2 gene.
Serum response factor, also known as SRF, is a transcription factor protein.

Fibroblast growth factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGF5 gene.

Fibroblast growth factor 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGF19 gene. It functions as a hormone, regulating bile acid synthesis, with effects on glucose and lipid metabolism. Reduced synthesis, and blood levels, may be a factor in chronic bile acid diarrhea and in certain metabolic disorders.

Cerevisterol (5α-ergosta-7,22-diene-3β,5,6β-triol) is a sterol. Originally described in the 1930s from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, it has since been found in several other fungi and, recently, in deep water coral. Cerevisterol has some in vitro bioactive properties, including cytotoxicity to some mammalian cell lines.

RU-58841, also known as PSK-3841 or HMR-3841, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which was initially developed in the 1980s by Roussel Uclaf, the French pharmaceutical company from which it received its name. It was formerly under investigation by ProStrakan for potential use as a topical treatment for androgen-dependent conditions including acne, pattern hair loss, and excessive hair growth. The compound is similar in structure to the NSAA RU-58642 but contains a different side-chain. These compounds are similar in chemical structure to nilutamide, which is related to flutamide, bicalutamide, and enzalutamide, all of which are NSAAs similarly. RU-58841 can be synthesized either by building the hydantoin moiety or by aryl coupling to 5,5-dimethylhydantoin.
Cerebrolysin is an experimental mixture of enzymatically-treated peptides derived from pig brain whose constituents can include brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF). Although it is under preliminary study for its potential to treat various brain diseases, it is used as a therapy in dozens of countries in Eurasia.

Dihexa is an oligopeptide drug derived from angiotensin IV that binds with high affinity to hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and potentiates its activity at its receptor, c-Met. The compound has been found to potently improve cognitive function in animal models of Alzheimer's disease-like mental impairment. In an assay of neurotrophic activity, dihexa was found to be seven orders of magnitude more potent than brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
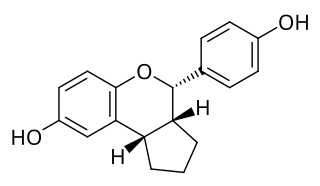
SERBA-2, short for selective estrogen receptor beta agonist-2, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen which acts as a selective ERβ agonist. For the ERα and ERβ, SERBA-2 has affinities (Ki) of 14.5 nM and 1.54 nM, efficacies of 85% and 100%, and EC50 values of 85 nM and 3.61 nM, respectively, demonstrating 9-fold binding selectivity and 11-fold functional selectivity for the ERβ over the ERα. An enantiomer of SERBA-2, erteberel (SERBA-1), is more potent and selective in comparison and is under development for the treatment of schizophrenia.

BNN-20, also known as 17β-spiro-(androst-5-en-17,2'-oxiran)-3β-ol, is a synthetic neurosteroid, "microneurotrophin", and analogue of the endogenous neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It acts as a selective, high-affinity, centrally active agonist of the TrkA, TrkB, and p75NTR, receptors for the neurotrophins nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), as well as for DHEA and DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S). The drug has been suggested as a potential novel treatment for Parkinson's disease and other conditions.

BNN-27, also known as 17α,20R-epoxypregn-5-ene-3β,21-diol, is a synthetic neurosteroid and "microneurotrophin" and analogue of the endogenous neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It acts as a selective, high-affinity, centrally active agonist of the TrkA and p75NTR, receptors for nerve growth factor (NGF) and other neurotrophins, as well as for DHEA and DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S). BNN-27 has neuroprotective and neurogenic effects and has been suggested as a potential novel treatment for neurodegenerative diseases and brain trauma.

Fluoromedroxyprogesterone acetate is a synthetic steroid medication which was under development by Meiji Dairies Corporation in the 1990s and 2000s for the potential treatment of cancers but was never marketed. It is described as an antiangiogenic agent, with about two orders of magnitude greater potency for inhibition of angiogenesis than its parent compound medroxyprogesterone acetate. FMPA showed about the same affinities for the progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors as MPA. It reached the preclinical phase of research prior to the discontinuation of its development.


















