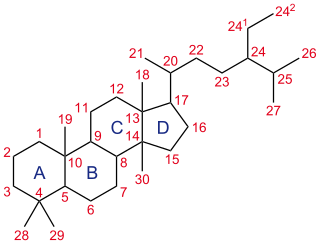
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four fused rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene.
Saponins, also selectively referred to as triterpene glycosides, are bitter-tasting usually toxic plant-derived organic chemicals that have a foamy quality when agitated in water. They are widely distributed but found particularly in soapwort, a flowering plant, the soapbark tree and soybeans. They are used in soaps, medicines, fire extinguishers, speciously as dietary supplements, for synthesis of steroids, and in carbonated beverages. Saponins are both water and fat soluble, which gives them their useful soap properties. Some examples of these chemicals are glycyrrhizin and quillaia, a bark extract used in beverages.

Nicandra physalodes is a species of flowering plant in subfamily Solanoideae of the nightshade family. It is known by the common names apple-of-Peru and shoo-fly plant. It is thought originally to have been native to western South America, including Peru, and is known elsewhere as an introduced and ruderal species – sometimes as a weed – in tropical, subtropical and, to a lesser extent, temperate areas all over the world. It has also long been cultivated as an ornamental plant for its attractive flowers and curious fruits and has been adopted into the traditional medicine of countries far-removed from its original home.
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term neurosteroid was coined by the French physiologist Étienne-Émile Baulieu and refers to steroids synthesized in the brain. The term, neuroactive steroid refers to steroids that can be synthesized in the brain, or are synthesized by an endocrine gland, that then reach the brain through the bloodstream and have effects on brain function. The term neuroactive steroids was first coined in 1992 by Steven Paul and Robert Purdy. In addition to their actions on neuronal membrane receptors, some of these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression via nuclear steroid hormone receptors. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation to treatment of epilepsy and traumatic brain injury. Ganaxolone, a synthetic analog of the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone, is under investigation for the treatment of epilepsy.

Steranes constitute a class of tetracyclic triterpanes derived from steroids or sterols via diagenetic and catagenetic degradation, such as hydrogenation. They are found in sediments and sedimentary rocks in nature. Steranes are derivatives of gonane, the steroid nucleus which is also called "cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene". They have an androstane skeleton with a side chain at carbon C-17. The sterane structure constitutes the core of all sterols. Steranes are widely used as biomarkers for the presence of eukaryotes in past ecosystems because steroids are nearly exclusively produced by eukaryotes. In particular, cholestanes are diagenetic products of cholesterol in animals, while stigmastanes are diagenetic products of stigmasterols in algae and land plants. However, some bacteria are now known to produce sterols and it is inferred that the ultimate origin of sterol biosynthesis is in bacteria. Sterols are produced via protosterols that are direct cyclization compounds of squalene by the catalysis of oxidosqualene cyclase. All known sterols in eukaryotes are enzymatically extensively modified from protosterols, while organisms that only produce protosterols are not known. The oldest record of modified steranes are in sedimentary rocks deposited ca. 720–820 million years ago. In contrast, diagenetic products of protosterols are widely distributed in older Proterozoic rocks and imply the presence of extinct proto-eukaryotes and/or sterol-producing bacteria before the evolution of crown-group eukaryotes.

Cholestane is a saturated tetracyclic triterpene. This 27-carbon biomarker is produced by diagenesis of cholesterol and is one of the most abundant biomarkers in the rock record. Presence of cholestane, its derivatives and related chemical compounds in environmental samples is commonly interpreted as an indicator of animal life and/or traces of O2, as animals are known for exclusively producing cholesterol, and thus has been used to draw evolutionary relationships between ancient organisms of unknown phylogenetic origin and modern metazoan taxa. Cholesterol is made in low abundance by other organisms (e.g., rhodophytes, land plants), but because these other organisms produce a variety of sterols it cannot be used as a conclusive indicator of any one taxon. It is often found in analysis of organic compounds in petroleum.
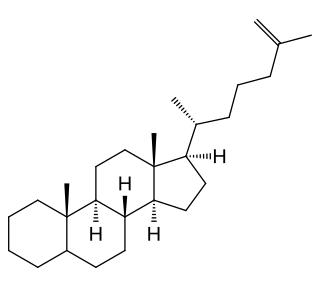
Cholestenes are chiral molecules that are derivatives of cholestanes that have a double bond. If there are two double bonds, the molecule is known as a "cholestadiene". Examples include fusidic acid, lanosterol, and stigmasterol. Cholestene is a widely available chemical, used and sold commercially with red yeast rice. There are also derivatives of the molecule, such as 5-cholestene and 2-cholestene. These molecules differ by the placement of a double bond in one of its cyclohexane rings.
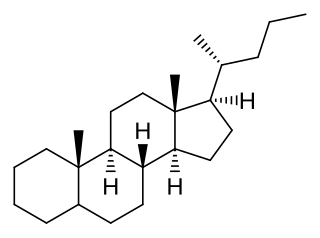
Cholane is a triterpene which can exist as either of two stereoisomers, 5α-cholane and 5β-cholane. Its name is derived from Greek: χολή (chole) meaning 'bile' in reference to its original discovery from the bile of the American bullfrog. The compound itself has no known uses. However, various functionalized analogues are produced by plants and animals, typically in the form of sterols, steroids and bile acids.

Trenbolone acetate, sold under brand names such as Finajet and Finaplix among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in veterinary medicine, specifically to increase the profitability of livestock by promoting muscle growth in cattle. It is given by injection into muscle.

Ergosterol peroxide (5α,8α-epidioxy-22E-ergosta-6,22-dien-3β-ol) is a steroid derivative. It has been isolated from a variety of fungi, yeast, lichens and sponges, and has been reported to exhibit immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, trypanocidal and antitumor activities in vitro.

Withanolides are a group of at least 300 naturally occurring steroids built on an ergostane skeleton. They occur as secondary metabolites primarily in genera of the Nightshade family, for example in the tomatillo.
Xenohormones or environmental hormones produced outside of the human body which exhibit endocrine hormone-like properties. They may be either of natural origin, such as phytoestrogens, which are derived from plants, or of synthetic origin. These compounds are able to activate the same endocrine receptors as their natural counterparts and are thus frequently implicated in endocrine disruption. The most commonly occurring xenohormones are xenoestrogens, which mimic the effects of estrogen. Other xenohormones include xenoandrogens and xenoprogesterones. Xenohormones are used for a variety of purposes including contraceptive & hormonal therapies, and agriculture. However, exposure to certain xenohormones early in childhood development can lead to a host of developmental issues including infertility, thyroid complications, and early onset of puberty. Exposure to others later in life has been linked to increased risks of testicular, prostate, ovarian, and uterine cancers.

Withaferin A is a steroidal lactone, derived from Acnistus arborescens, Withania somnifera and other members of family Solanaceae. It has been traditionally used in ayurvedic medicine. It is the first member of the withanolide class of ergostane type product to be discovered. This natural product has wide range of pharmacological activities including cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, immuno-modulatory, anti-angiogenesis, anti-metastasis and anti-carcinogenic properties.

Jaborosa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Solanaceae, the nightshades. There are about 23 species, all native to South America, where they are distributed from Peru to Patagonia. Most occur in the Andes. Most can be found in Argentina and ten are endemic to the country.
24-isopropyl cholestane is an organic molecule produced by specific sponges, protists and marine algae. The identification of this molecule at high abundances in Neoproterozoic rocks has been interpreted to reflect the presence of multicellular life prior to the rapid diversification and radiation of life during the Cambrian explosion. In this transitional period at the start of the Phanerozoic, single-celled organisms evolved to produce many of the evolutionary lineages present on Earth today. Interpreting 24-isopropyl cholestane in ancient rocks as indicating the presence of sponges before this rapid diversification event alters the traditional understanding of the evolution of multicellular life and the coupling of biology to changes in end-Neoproterozoic climate. However, there are several arguments against causally linking 24-isopropyl cholestane to sponges based on considerations of marine algae and the potential alteration of organic molecules over geologic time. In particular the discovery of 24-isopropyl cholestane in rhizarian protists implies that this biomarker cannot be used on its own to trace sponges. Interpreting the presence of 24-isopropyl cholestane in the context of changingglobal biogeochemical cycles at the Proterozoic-Phanerozoic transition remains an area of active research.

24-n-Propylcholestane is a sterane biomarker molecule often found in marine source rocks. It is a C30 molecule, meaning that it is composed of thirty carbon atoms, and is one of the leading ways to distinguish a marine source rock from a terrigenous sample. It is composed of three six-carbon rings and one five-carbon ring, with two methyl groups and one eleven carbon side chain. 24-n-Propylcholestane has a molar mass of 414.76 g/mol.

24-Norcholestane, a steroid derivative, is used as a biomarker to constrain the source age of sediments and petroleum through the ratio between 24-norcholestane and 27-norcholestane, especially when used with other age diagnostic biomarkers, like oleanane. While the origins of this compound are still unknown, it is thought that they are derived from diatoms due to their identification in diatom rich sediments and environments. In addition, it was found that 24-norcholestane levels increased in correlation with diatom evolution. Another possible source of 24-norcholestane is from dinoflagellates, albeit to a much lower extent.

Stigmastane or 24R-ethylcholestane is a tetracyclic triterpene, along with cholestane and ergostane, this sterane is used as a biomarker for early eukaryotes.

Campestane or 24R-methylcholestane is a tetracyclic triterpene. Its derivative campesterol (campest-5-en-3β-ol) was first isolated from the rapeseed, hence the name.

19-Norcholestane is a 26-carbon (C26) sterane.















