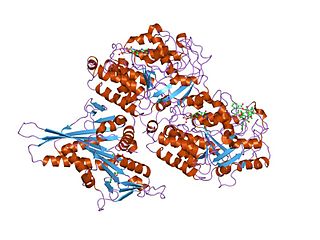
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division.

Hexafluoroisopropanol, commonly abbreviated HFIP, is the organic compound with the formula (CF3)2CHOH. This fluoroalcohol finds use as solvent in organic chemistry. Hexafluoro-2-propanol is transparent to UV light with high density, low viscosity and low refractive index. It is a colorless, volatile liquid with a pungent odor.

In organic chemistry, the Michael reaction or Michael 1,4 addition is a reaction between a Michael donor and a Michael acceptor to produce a Michael adduct by creating a carbon-carbon bond at the acceptor's β-carbon. It belongs to the larger class of conjugate additions and is widely used for the mild formation of carbon-carbon bonds.
The Ugi reaction is a multi-component reaction in organic chemistry involving a ketone or aldehyde, an amine, an isocyanide and a carboxylic acid to form a bis-amide. The reaction is named after Ivar Karl Ugi, who first reported this reaction in 1959.
The Pictet–Spengler reaction is a chemical reaction in which a β-arylethylamine undergoes condensation with an aldehyde or ketone followed by ring closure. The reaction was first discovered in 1911 by Amé Pictet and Theodor Spengler. Traditionally an acidic catalyst in protic solvent was employed with heating, however the reaction has been shown to work in aprotic media in superior yields and sometimes without acid catalysis. The Pictet–Spengler reaction can be considered a special case of the Mannich reaction, which follows a similar reaction pathway. The driving force for this reaction is the electrophilicity of the iminium ion generated from the condensation of the aldehyde and amine under acid conditions. This explains the need for an acid catalyst in most cases, as the imine is not electrophilic enough for ring closure but the iminium ion is capable of undergoing the reaction.
The Reformatsky reaction is an organic reaction which condenses aldehydes or ketones with α-halo esters using metallic zinc to form β-hydroxy-esters:

The Robinson–Gabriel synthesis is an organic reaction in which a 2-acylamino-ketone reacts intramolecularly followed by a dehydration to give an oxazole. A cyclodehydrating agent is needed to catalyze the reaction It is named after Sir Robert Robinson and Siegmund Gabriel who described the reaction in 1909 and 1910, respectively.
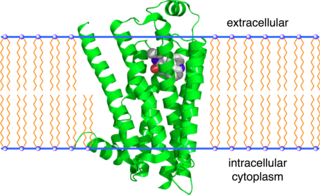
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increased cAMP, and downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation.

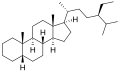
Cholestane is a saturated tetracyclic triterpene. This 27-carbon biomarker is produced by diagenesis of cholesterol and is one of the most abundant biomarkers in the rock record. Presence of cholestane, its derivatives and related chemical compounds in environmental samples is commonly interpreted as an indicator of animal life and/or traces of O2, as animals are known for exclusively producing cholesterol, and thus has been used to draw evolutionary relationships between ancient organisms of unknown phylogenetic origin and modern metazoan taxa. Cholesterol is made in low abundance by other organisms (e.g., rhodophytes, land plants), but because these other organisms produce a variety of sterols it cannot be used as a conclusive indicator of any one taxon. It is often found in analysis of organic compounds in petroleum.
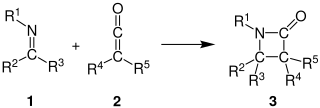
The Staudinger synthesis, also called the Staudinger ketene-imine cycloaddition, is a chemical synthesis in which an imine 1 reacts with a ketene 2 through a non-photochemical 2+2 cycloaddition to produce a β-lactam3. The reaction carries particular importance in the synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. The Staudinger synthesis should not be confused with the Staudinger reaction, a phosphine or phosphite reaction used to reduce azides to amines.
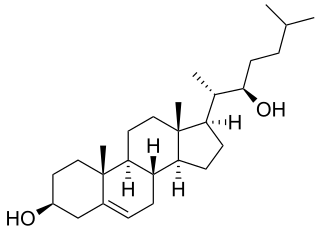
22R-Hydroxycholesterol, or (3β)-cholest-5-ene-3,22-diol is an endogenous, metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones from cholesterol. Cholesterol ( -cholest-5-en-3-ol) is hydroxylated by cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (P450scc) to form 22R-hydroxycholesterol, which is subsequently hydroxylated again by P450scc to form 20α,22R-dihydroxycholesterol, and finally the bond between carbons 20 and 22 is cleaved by P450scc to form pregnenolone ( -3-hydroxypregn-5-en-20-one), the precursor to the steroid hormones.
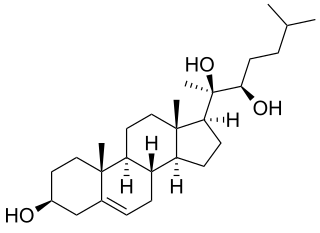
20α,22R-Dihydroxycholesterol, or (3β)-cholest-5-ene-3,20,22-triol is an endogenous, metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones from cholesterol. Cholesterol ( -cholest-5-en-3-ol) is hydroxylated by cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (P450scc) to form 22R-hydroxycholesterol, which is subsequently hydroxylated again by P450scc to form 20α,22R-dihydroxycholesterol, and finally the bond between carbons 20 and 22 is cleaved by P450scc to form pregnenolone ( -3-hydroxypregn-5-en-20-one), the precursor to the steroid hormones.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators, also known as GABAkines or GABAA receptor potentiators, are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.

Ergostane is a tetracyclic triterpene, also known as 24S-methylcholestane. The compound itself has no known uses; however various functionalized analogues are produced by plants and animals. The most important of these are the heavily derivatised withanolides. However simpler forms do exist, such as the sterane campestane (24R-methylcholestane). Along with cholestane and stigmastane, this sterane is used as a biomarker for early eukaryotes.
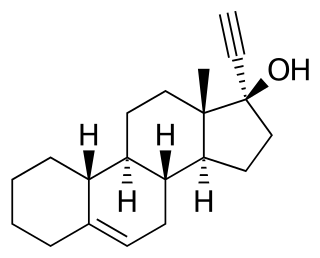
Cingestol, also known as 17α-ethynylestr-5-en-17β-ol, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group that was never marketed. It was synthesized in 1969 and was developed in the 1970s by Organon as a low-dose, progestogen-only contraceptive, but in 1984, was still described as "under investigation". The drug is an isomer of lynestrenol with the double bond between C5 and C6.
Christopher Joseph Schofield is the Head of Organic Chemistry at the University of Oxford and a Fellow of the Royal Society. Chris Schofield is a professor of organic chemistry at the University of Oxford, Department of Chemistry and a Fellow of Hertford College. Prof Schofield studied functional, structural and mechanistic understanding of enzymes that employ oxygen and 2-oxoglutarate as a co-substrate. His work has opened up new possibilities in antibiotic research, oxygen sensing, and gene regulation.
Nicholas Frederick Chilton is an Australian chemist and a Professor in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Manchester. His research is in the areas of magnetochemistry and computational chemistry, and includes the design of high-temperature single molecule magnets, molecular spin qubits for quantum information science, methods and tools for modelling magnetic calculations.
The Cadogan–Sundberg indole synthesis, or simply Cadogan indole synthesis, is a name reaction in organic chemistry that allows for the generation of indoles from o-nitrostyrenes with the use of trialkyl phosphites, such as triethyl phosphite.
Jin-Quan Yu is a Chinese-born American chemist. He is the Frank and Bertha Hupp Professor of Chemistry at Scripps Research, where he also holds the Bristol Myers Squibb Endowed Chair in Chemistry. He is a 2016 recipient of the MacArthur Fellowship, and is a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, American Association for the Advancement of Science, and the Royal Society of Chemistry. Yu is a leader in the development of C–H bond activation reactions in organic chemistry, and has reported many C–H activation reactions that could be applicable towards the synthesis of drug molecules and other biologically active compounds. He also co-founded Vividion Therapeutics in 2016 with fellow Scripps chemists Benjamin Cravatt and Phil Baran, and is a member of the scientific advisory board of Chemveda Life Sciences.