Attribution
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Antander". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 183.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Antander". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 183.
Antander (Greek : Ἄντανδρος - or Andro as he is called by the historian Orosius) [1] was a man of Syracuse, Magna Graecia, of the 3rd and 4th centuries BCE. He was the older brother of Agathocles, king of Syracuse, [2] and was a commander -- or strategos -- of the troops sent by the Syracusans to the relief of Crotona when it was besieged by the Bruttii tribe in 317. [3]
In the late 4th century, Sicily was invaded by Carthage and Syracuse itself was besieged by the Carthaginians. In 310, Agathocles hatched a daring plan to sneak out of Sicily with a sizable force to invade Libya, to draw the Carthaginians out of Sicily, leaving Antander together with Erymnon in command of Syracuse. [4] [5] During the absence of Agathocles in Africa, the Carthaginians under Hamilcar pressed their siege. [6]
Some ancient sources report that Antander wished to surrender to Hamilcar after receiving news that Agathocles's fleet had been burned and that Erymnon persuaded him not to. More recent scholarship indicates that Hamilcar tried a ruse to convince Antander his brother's army had been destroyed by showing Antander the charred remains of his brother's boats, while in reality, Agathocles had burned his own ships as a tactic to move to a land assault. A debate erupted in the Syracusan assembly in which a man named Diognetus (or Phalaeneus), proposed surrendering to the Carthaginians, and Antander had the man arrested to prevent the spread of the idea to the besieged Syracusans. [6] In any case, Syracuse survived the siege.
Antander is mentioned afterwards as the instrument of his brother's cruelty: in 307, Agathocles commanded Antander to execute the families of all the rebellious Syracusan soldiers who remained in Africa (whom Agathocles blamed for the death of his sons), and Antander is said to have ruthlessly carried out this order, slaughtering men, women, children, and the elderly. [7] Even more horrifying to the ancient mind, Antander's forces piled these bodies on the beach for the waves to take, denying them burial rites. [2] [8]
During Agathocles's absence from Syracuse, silver tetradrachms (previously issued under Agathocles's name only) were issued with Antander's monogram. [9] Antander was also the author of a historical work - an apologetic biography of his brother Agathocles - which is quoted by the ancient historian Diodorus Siculus. [10]
It is not known how long Antander lived, only that he outlived his brother Agathocles, who died in 289. [2]
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Antander". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 183.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Antander". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 183.
Agathocles was a Greek tyrant of Syracuse (317–289 BC) and self-styled king of Sicily (304–289 BC).

This article concerns the period 309 BC – 300 BC.

The Battle of Himera, supposedly fought on the same day as the Battle of Salamis, or at the same time as the Battle of Thermopylae, saw the Greek forces of Gelon, King of Syracuse, and Theron, tyrant of Agrigentum, defeat the Carthaginian force of Hamilcar the Magonid, ending a Carthaginian bid to restore the deposed tyrant of Himera. The alleged coincidence of this battle with the naval battle of Salamis and the resultant derailing of a Punic-Persian conspiracy aimed at destroying the Greek civilization is rejected by modern scholars. Scholars also agree that the battle led to the crippling of Carthage's power in Sicily for many decades. It was one of the most important battles of the Sicilian Wars.

The Battle of the Crimissus was fought in 339 BC between a large Carthaginian army commanded by Asdrubal and Hamilcar and an army from Syracuse led by Timoleon. Timoleon attacked the Carthaginian army by surprise near the Crimissus river in western Sicily and won a great victory. When he defeated another much smaller force of Carthaginians shortly afterwards, Carthage sued for peace. The peace allowed the Greek cities on Sicily to recover and began a period of stability. However, another war between Syracuse and Carthage erupted after Timoleon's death, not long after Agathocles seized power in 317 BC.

The Battle of the Himera River was fought in 311 BC between Carthage and Syracuse near the mouth of the Himera river. Hamilcar, grandson of Hanno the Great, led the Carthaginians, while the Syracusans were led by Agathocles. Agathocles initially surprised the Carthaginians with an attack on their camp, but the Greeks lost the battle when they were attacked by unexpected Carthaginian reinforcements. The Greek army took many casualties as it retreated. Agathocles managed to gather the remains of his army and retreat to Syracuse, but lost control of Sicily.
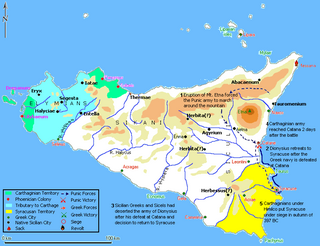
The siege of Syracuse in 397 BC was the first of four unsuccessful sieges Carthaginian forces would undertake against Syracuse from 397 to 278 BC. In retaliation for the siege of Motya by Dionysius of Syracuse, Himilco of the Magonid family of Carthage led a substantial force to Sicily. After retaking Motya and founding Lilybaeum, Himilco sacked Messana, then laid siege to Syracuse in the autumn of 397 BC after the Greek navy was crushed at Catana.

Kamarina or Camarina was an ancient city on the southern coast of Sicily in Magna Graecia. The ruins of the site and an archaeological museum are located south of the modern town of Scoglitti, a frazione (borough) of the comune (municipality) of Vittoria in the province of Ragusa.

The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580 and 265 BC.

Near the site of the first battle and great Carthaginian defeat of 480 BC, the Second Battle of Himera was fought near the city of Himera in Sicily in 409 between the Carthaginian forces under Hannibal Mago and the Ionian Greeks of Himera aided by an army and a fleet from Syracuse. Hannibal, acting under the instructions of the Carthaginian senate, had previously sacked and destroyed the city of Selinus after the Battle of Selinus in 409. Hannibal then destroyed Himera which was never rebuilt. Mass graves associated with this battle were discovered in 2008-2011, corroborating the stories told by ancient historians.
The Magonids were a political dynasty of Ancient Carthage from 550 BCE to 340 BCE. The dynasty was first established under Mago I, under whom Carthage became pre-eminent among the Phoenician colonies in the western Mediterranean. Under the Magonids, the Carthaginian Empire expanded to include Sardinia, Libya, and for almost a decade much of Sicily.
The Battle of Chrysas was fought in 392 BC in the course of the Sicilian Wars, between the Carthaginian army under Mago and a Greek army under Dionysius I, tyrant of Syracuse, who was aided by Agyris, tyrant of the Sicel city of Agyrium. Mago had been defeated by Dionysius at Abacaenum in 393, which had not damaged the Carthaginian position in Sicily. Reinforced by Carthage in 392, Mago moved to attack the Sicles allied with Syracuse in central Sicily. After the Carthaginians reached and encamped near the river Chrysas, the Sicels harassed the Carthaginian supply lines causing a supply shortage, while the Greek soldiers rebelled and deserted Dionysius when he refused to fight a pitched battle. Both Mago and Dionysius agreed to a peace treaty, which allowed the Carthaginians to formally occupy the area west of the River Halycus, while Dionysius was given lordship over the Sicel lands. The peace would last until 383, when Dionysius attacked the Carthaginians again.
The siege of Tauromenium was laid down by Dionysius, tyrant of Syracuse, in the winter of 394 BC, in the course of the Sicilian Wars against Carthage. After defeating the Carthaginians at the Battle of Syracuse in 397 BC, Dionysius had been expanding his territory and political influence by conquering Sicel lands and planting Greek colonies in northeastern Sicily. Tauromenium was a Sicel city allied to Carthage and in a position to threaten both Syracuse and Messina. Dionysius laid siege to the city in the winter of 394 BC, but had to lift the siege after his night assault was defeated. Carthage responded to this attack on their allies by renewing the war, which was ended by a peace treaty in 392 BC that granted Dionysius overlordship of the Sicels, while Carthage retained all territory west of the Halykos and Himera rivers in Sicily.
Himilco was a member of the Magonids, a Carthaginian family of hereditary generals, and had command over the Carthaginian forces between 406 BC and 397 BC. He is chiefly known for his war in Sicily against Dionysius I of Syracuse.
The siege of Segesta took place either in the summer of 398 BC or the spring of 397 BC. Dionysius the Elder, tyrant of Syracuse, after securing peace with Carthage in 405 BC, had steadily increased his military power and tightened his grip on Syracuse. He had fortified Syracuse against sieges and had created a large army of mercenaries and a large fleet, in addition to employing catapults and quinqueremes for the first time in history. In 398 BC he attacked and sacked the Phoenician city of Motya despite a Carthaginian relief effort led by Himilco II of Carthage. While Motya was under siege, Dionysius besieged and assaulted Segesta unsuccessfully. Following the sack of Motya, Segesta again came under siege by Greek forces, but the Elymian forces based in Segesta managed to inflict damage on the Greek camp in a daring night assault. When Himilco of Carthage arrived in Sicily with the Carthaginian army in the spring of 397 BC, Dionysius withdrew to Syracuse. The failure of Dionysius to secure a base in western Sicily meant the main events of the Second Sicilian war would be acted out mostly in eastern Sicily, sparing the Elymian and Phoenician cities the ravages of war until 368 BC.
The siege and subsequent sacking of Camarina took place in 405 BC during the Sicilian Wars.
The siege of Syracuse by the Carthaginians from 311 to 309 BC followed shortly after the Battle of the Himera River in the same year. In that battle the Carthaginians, under the leadership of Hamilcar the son of Gisco, had defeated the tyrant of Syracuse, Agathocles. Agathocles had to retreat to Syracuse and lost control over the other Greek cities on Sicily, who went over to the Carthaginian side.

The Battle of White Tunis was fought between Carthage and the tyrant Agathocles of Syracuse in 310 BC. It was the first large battle of the Agathocles' military expedition to Libya. Even though heavily outnumbered by the Carthaginian army, the soldiers of Agathocles were far more experienced in warfare than the Carthaginian citizen soldiers. Another important factor was the terrain, which prevented the Carthaginians from using their numbers to outflank Agathocles. The Carthaginian suffered a serious defeat, which caused some of the Carthaginian allies to change their allegiance to Agathocles.

The siege of Syracuse from 344 to 343/342 BC was part of a war between the Syracusan general Hicetas and the tyrant of Syracuse, Dionysius II. The conflict became more complex when Carthage and Corinth became involved. The Carthaginians had made an alliance with Hicetas to expand their power in Sicily. Somewhat later, the Corinthian general Timoleon arrived in Sicily to restore democracy to Syracuse. With the assistance of several other Sicilian Greek cities, Timoleon emerged victorious and reinstated a democratic regime in Syracuse. The siege is described by the ancient historians Diodorus Siculus and Plutarch, but there are important differences in their accounts.
The siege of Syracuse in 278 BC was the last attempt of Carthage to conquer the city of Syracuse. Syracuse was weakened by a civil war between Thoenon and Sostratus. The Carthaginians used this opportunity to attack and besiege Syracuse both by land and sea. Thoenon and Sostratus then appealed to king Pyrrhus of Epirus to come to the aid of Syracuse. When Pyrrhus arrived, the Carthaginian army and navy retreated without a fight.
The history of Greek Sicily began with the foundation of the first Greek colonies around the mid 8th century BC. The Greeks of Sicily were known as Siceliotes.