Related Research Articles

Adelaide is the capital city of the state of South Australia, and the fifth-most populous city of Australia. The demonym Adelaidean is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide.
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) is Australia's national broadcaster, founded in 1929. It is principally funded by the direct grants from the Australian government but is expressly independent of government and partisan politics. The ABC plays a leading role in journalistic independence and is fundamental in the history of broadcasting in Australia.

New South Wales is a state on the east coast of Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria to the south, and South Australia to the west. Its coast borders the Coral and Tasman Seas to the east. The Australian Capital Territory is an enclave within the state. New South Wales' state capital is Sydney, which is also Australia's most populous city. In March 2019, the population of New South Wales was over 8 million, making it Australia's most populous state. Just under two-thirds of the state's population, 5.1 million, live in the Greater Sydney area. Inhabitants of New South Wales are referred to as New South Welshmen.

Oceania is a geographic region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia. Spanning the eastern and western hemispheres, Oceania has a land area of 8,525,989 square kilometres (3,291,903 sq mi) and a population of over 47 million. Situated in the southeast of the Asia-Pacific region, Oceania, when compared to continental regions, is the smallest in land area and the second smallest in population after Antarctica.

Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia (WA). It is named after the city of Perth, Scotland and is Australia's fourth-most populous city, with a population of 2.06 million living in Greater Perth. Perth is part of the South West Land Division of Western Australia, with most of the metropolitan area on the Swan Coastal Plain, a narrow strip between the Indian Ocean and the Darling Scarp. The first areas settled were on the Swan River at Guildford, with the city's central business district and port (Fremantle) both later founded downriver.
Sydney is the state capital of New South Wales and the most populous city in Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Port Jackson and extends about 70 km (43.5 mi) on its periphery towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, the Royal National Park to the south and Macarthur to the south-west. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, 40 local government areas and 15 contiguous regions. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". As of June 2017, Sydney's estimated metropolitan population was 5,230,330 and is home to approximately 65% of the state's population.

Tasmania is an island state of Australia. It is located 240 km (150 mi) to the south of the Australian mainland, separated by Bass Strait. The state encompasses the main island of Tasmania, the 26th-largest island in the world, and the surrounding 334 islands. The state has a population of around 535,500 as of September 2019. Just over forty percent of the population resides in the Greater Hobart precinct, which forms the metropolitan area of the state capital and largest city, Hobart.

Western Australia is a state occupying the entire western third of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, and the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a total land area of 2,529,875 square kilometres, and the second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia's Sakha Republic. The state has about 2.6 million inhabitants – around 11 percent of the national total – of whom the vast majority live in the south-west corner, 79 per cent of the population living in the Perth area, leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated.

Queensland is the second-largest and third-most populous state in the Commonwealth of Australia. Situated in the north-east of the country, it is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Australia and New South Wales to the west, south-west and south respectively. To the east, Queensland is bordered by the Coral Sea and Pacific Ocean. To its north is the Torres Strait, with Papua New Guinea located less than 200 km across it from the mainland. The state is the world's sixth-largest sub-national entity, with an area of 1,852,642 square kilometres (715,309 sq mi).

The Order of Australia is an order of chivalry established on 14 February 1975 by Elizabeth II, Queen of Australia, to recognise Australian citizens and other persons for achievement or meritorious service. Before the establishment of the order, Australian citizens received British honours.

The High Court of Australia is the highest court in the Australian court hierarchy and the final court of appeal. It has both original and appellate jurisdiction, the power of judicial review over laws passed by the Parliament of Australia and the parliaments of the states and territories, and the ability to interpret the Constitution of Australia and thereby shape the development of federalism in Australia.

George Pell is an Australian cardinal of the Catholic Church. He served as the inaugural prefect of the Secretariat for the Economy between 2014 and 2019, and was a member of the Council of Cardinal Advisers between 2013 and 2018. Ordained in 1966 and made a cardinal in 2003, Pell served as the eighth Archbishop of Sydney (2001–2014), the seventh Archbishop of Melbourne (1996–2001) and an auxiliary bishop of Melbourne (1987–1996). He has also been an author, columnist and public speaker. Since 1996, Pell has maintained a high public profile on a wide range of issues, while retaining an adherence to Catholic orthodoxy.

Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands.

The ARIA Charts, stylised as the AR1A Charts since November 2018, are the main Australian music sales charts, issued weekly by the Australian Recording Industry Association. The charts are a record of the highest selling songs and albums in various genres in Australia. ARIA became the official Australian music chart in June 1988, succeeding the Kent Music Report which had been Australia's national charts since 1974.

Government in the Commonwealth of Australia is exercised on three levels: federal, states and territories, and local government.

Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country by total area. The population of 26 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australia's capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country's other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide.

Victoria is a state in south-eastern Australia. Victoria is Australia's smallest mainland state and its second-most populous state, making it the most densely populated state. Most of its population lives concentrated in the area surrounding Port Phillip Bay, which includes the metropolitan area of its state capital and largest city, Melbourne, Australia's second-largest city. Victoria is bordered by Bass Strait and Tasmania to the south, New South Wales to the north, the Tasman Sea to the east, and South Australia to the west.

Stephen Robert Irwin, nicknamed "The Crocodile Hunter", was an Australian zookeeper, television personality, wildlife expert, environmentalist and conservationist.

Melbourne is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia and Oceania. Its name refers to an urban agglomeration of 9,993 km2 (3,858 sq mi), comprising a metropolitan area with 31 municipalities, and is also the common name for its city centre. The city occupies much of the coastline of Port Phillip bay and spreads into the hinterlands towards the Dandenong and Macedon ranges, Mornington Peninsula and Yarra Valley. It has a population of 5 million, and its inhabitants are referred to as "Melburnians".
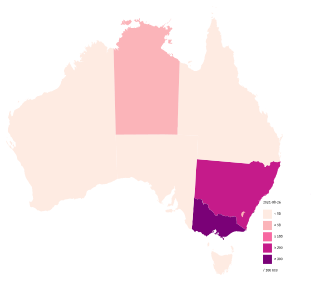
The 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic was confirmed to have reached Australia on 25 January 2020 in Victoria, when a man returning from Wuhan, China, was tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The total number of new cases initially grew exponentially, levelled out at about 350 per day around 22 March, and started falling at the beginning of April. As of 18 April 2020, 6,565 cases had been reported in Australia, with the highest number of cases being in New South Wales, with 2,936.
References
| This article on a moth of the family Anthelidae is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |