This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
Antun Domic is a Chilean-American engineer and mathematician.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
Antun Domic is a Chilean-American engineer and mathematician.
Domic obtained his Ph.D. in Mathematics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1978, with a dissertation in partial differential equations. [1]
In 1982, Domic became a member of the technical staff of MIT Lincoln Laboratory in Lexington, MA. While there, Domic and his colleagues developed the Lincoln Boolean Synthesizer. [2]
In 1985, Domic joined Digital Equipment Corporation where one of the EDA tools developed by Domic and his colleagues was CLEO, [3] an automatic layout generator (from schematic) which was used to design blocks of several RISC processors at DEC. [4]
Domic joined Synopsys in 1997 as vice-president of engineering for the Design Tools Group. [5] At the end of 2016, Domic was appointed Synopsys CTO. [6]
In 1987, Domic and Domingo Toledo wrote the paper "The Gromov norm of the Kähler class of symmetric domains" (Mathematische Annalen. 276 no. 3, 425–43).
Domic is an IEEE Fellow, [7] and the recipient of the 2019 IEEE Robert N. Noyce Medal. [8]
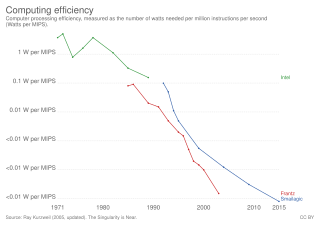
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's processor speed. For complex instruction set computers (CISCs), different instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depends on the instruction mix; even for comparing processors in the same family the IPS measurement can be problematic. Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few branches and no cache contention, whereas realistic workloads typically lead to significantly lower IPS values. Memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, synthetic benchmarks such as Dhrystone are now generally used to estimate computer performance in commonly used applications, and raw IPS has fallen into disuse.
The Intel i860 is a RISC microprocessor design introduced by Intel in 1989. It is one of Intel's first attempts at an entirely new, high-end instruction set architecture since the failed Intel iAPX 432 from the beginning of the 1980s. It was the world's first million-transistor chip. It was released with considerable fanfare, slightly obscuring the earlier Intel i960, which was successful in some niches of embedded systems. The i860 never achieved commercial success and the project was terminated in the mid-1990s.
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal is an electronic logic signal which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions.
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs).
Asynchronous circuit is a sequential digital logic circuit that does not use a global clock circuit or signal generator to synchronize its components. Instead, the components are driven by a handshaking circuit which indicates a completion of a set of instructions. Handshaking works by simple data transfer protocols. Many synchronous circuits were developed in early 1950s as part of bigger asynchronous systems. Asynchronous circuits and theory surrounding is a part of several steps in integrated circuit design, a field of digital electronics engineering.
In digital logic design, an asynchronous circuit is quasi delay-insensitive (QDI) when it operates correctly, independent of gate and wire delay with the weakest exception necessary to be turing-complete.
V850 is a 32-bit RISC CPU architecture produced by Renesas Electronics for embedded microcontrollers. It was designed by NEC as a replacement for their earlier NEC V60 family, and was introduced shortly before NEC sold their designs to Renesas in the early 1990s. It has continued to be developed by Renesas as of 2018.

The R3000 is a 32-bit RISC microprocessor chipset developed by MIPS Computer Systems that implemented the MIPS I instruction set architecture (ISA). Introduced in June 1988, it was the second MIPS implementation, succeeding the R2000 as the flagship MIPS microprocessor. It operated at 20, 25 and 33.33 MHz.

The NEC V60 is a CISC microprocessor manufactured by NEC starting in 1986. Several improved versions were introduced with the same instruction set architecture (ISA), the V70 in 1987, and the V80 and AFPP in 1989. They were succeeded by the V800 product families, which is currently produced by Renesas Electronics.

Mark A. Horowitz is an American electrical engineer, computer scientist, inventor, and entrepreneur who is the Yahoo! Founders Professor in the School of Engineering and the Fortinet Founders Chair of the Department of Electrical Engineering at Stanford University. He holds a joint appointment in the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science departments and previously served as the Chair of the Electrical Engineering department from 2008 to 2012. He is a co-founder of Rambus Inc., now a technology licensing company. Horowitz has authored over 700 published conference and research papers and is among the most highly-cited computer architects of all time. He is a prolific inventor and holds 374 patents as of 2023.
Intrinsity was a privately held Austin, Texas based fabless semiconductor company; it was founded in 1997 as EVSX on the remnants of Exponential Technology and changed its name to Intrinsity in 2000. It had around 100 employees and supplied tools and services for highly efficient semiconductor logic design, enabling high performance microprocessors with fewer transistors and low power consumption. The acquisition of the firm by Apple Inc. was confirmed on April 27, 2010.
Krishna V. Palem is a computer scientist and engineer of Indian origin and is the Kenneth and Audrey Kennedy Professor of Computing at Rice University and the director of Institute for Sustainable Nanoelectronics (ISNE) at Nanyang Technological University (NTU). He is recognized for his "pioneering contributions to the algorithmic, compilation, and architectural foundations of embedded computing", as stated in the citation of his 2009 Wallace McDowell Award, the "highest technical award made solely by the IEEE Computer Society".
The IEEE Robert N. Noyce Medal is a science award presented by the IEEE for outstanding contributions to the microelectronics industry. It is given to individuals who have demonstrated contributions in multiple areas including technology development, business development, industry leadership, development of technology policy, and standards development. The medal is named in honour of Robert N. Noyce, the co-founder of Intel Corporation. He was also renowned for his 1959 invention of the integrated circuit. The medal is funded by Intel Corporation and was first awarded in 2000.
The RH-32 was a radiation-hardened 32-bit MIPS R3000 based microprocessor chipset developed by the USAF Rome Laboratories for the Ballistic Missile Defense Agency, and produced by Honeywell for Aerospace applications. It achieves a throughput of 20 MIPS. It was a three-chip set, consisting of Central Processing Unit, Floating Point Unit, and Cache Memory.
OVPsim is a multiprocessor platform emulator used to run unchanged production binaries of the target hardware. It has public APIs allowing users to create their own processor, peripheral and platform models. Various models are available as open source. OVPsim is a key component of the Open Virtual Platforms initiative (OVP), an organization created to promote the use of open virtual platforms for embedded software development. OVPsim requires OVP registration to download.
Yehia Massoud is the Dean of the School of Systems and Enterprises at Stevens Institute of Technology. As the dean of school, SSE has seen a record increase in research awards and peer-reviewed publications, as well as a significant increase in student enrollment. He was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2015 for contributions to the modeling and design of nanoscale interconnects. Massoud has had significant progressive academic leadership and has been involved in forging and building effective partnerships with numerous academic and industrial institutions, and international organizations, and governmental funding agencies.
Chris Rowen is an American entrepreneur and technologist. Rowen is one of the founders of MIPS Computer Systems, Inc in 1984, of Tensilica Inc. in 1997 and of Babblelabs, Inc in 2017. Rowen was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2016 for leadership in the development of microprocessors and reduced instruction set computers.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link){{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link){{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)