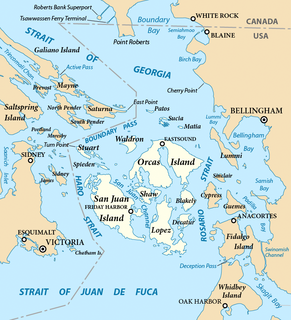
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of San Juan County.

Kitsap County is located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2010 census, its population was 251,133. Its county seat is Port Orchard, and its largest city is Bremerton. The county was formed out of King County and Jefferson County on January 16, 1857, and is named for Chief Kitsap of the Suquamish Tribe. Originally named Slaughter County, it was soon renamed.

Kingston is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. The population was 2,099 at the 2010 census. Kingston is along the shores of Appletree Cove and Puget Sound, and is home to a major Washington State Ferry terminal linking it to Edmonds.

Poulsbo is a city on Liberty Bay in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. It is the smallest of the four cities in Kitsap County. The population was 9,200 at the 2010 census and an estimated 10,927 in 2018.

Charles Wilkes was an American naval officer, ship's captain, and explorer. He led the United States Exploring Expedition, 1838-1842. His behavior led to two convictions by court-martial, one stemming from the massacre of almost 80 Fijians on Malolo in 1840. During the American Civil War (1861–1865) he commanded USS San Jacinto during the Trent Affair, where he stopped a Royal Mail Ship and removed two Confederate diplomats, which almost led to war between the US and the UK.
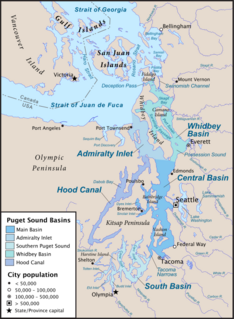
The Tacoma Narrows, a strait, is part of Puget Sound in the U.S. state of Washington. A navigable maritime waterway between glacial landforms, the Narrows separates the Kitsap Peninsula from the city of Tacoma.

The Kitsap Peninsula lies west of Seattle across Puget Sound, in Washington state in the Pacific Northwest. Hood Canal separates the peninsula from the Olympic Peninsula on its west side. The peninsula, a.k.a. "the Kitsap", encompasses all of Kitsap County except Bainbridge and Blake Islands, as well as the northeastern part of Mason County and the northwestern part of Pierce County. The highest point on the Kitsap Peninsula is Gold Mountain. The U.S. Navy's Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, and Naval Base Kitsap are on the Peninsula. Its main city is Bremerton.

Seabeck is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. The population was 1,105 at the 2010 census. Seabeck is a former mill town on Hood Canal.

Grays River is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately 30 miles (48 km) long, in southwestern Washington in the United States. One of the last tributaries of the Columbia on the Washington side, it drains an area of low hills north of the mouth of the river.
State Route 104 (SR 104) is a 31.75-mile-long (51.10 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Washington, serving four counties: Jefferson on the Olympic Peninsula, Kitsap on the Kitsap Peninsula, and Snohomish and King in the Puget Sound region. It begins south of Discovery Bay at U.S. Route 101 (US 101) south of Discovery Bay and crosses the Hood Canal Bridge over Hood Canal to the terminus of SR 3 near Port Gamble. SR 104 continues southeast onto the Edmonds–Kingston Ferry to cross the Puget Sound and intersects SR 99 and Interstate 5 (I-5) before ending at SR 522 in Lake Forest Park. SR 104 also has a short spur route that connects the highway to SR 99 at an at-grade signal on the Snohomish–King county line.

Southworth is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) on Puget Sound in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. It is best known for being the west end of the Fauntleroy-Vashon Island-Southworth Washington State Ferries run. Landmarks include Southworth Grocery, a US Post Office, ferry terminal, clay cliffs and a private beach on the point. Next to the ferry is a popular place to launch kayaks for trips to nearby Blake Island. The population of the Southworth CDP was 2,185 at the 2010 census.

The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby Jones. Funding for the original expedition was requested by President John Quincy Adams in 1828, however, Congress would not implement funding until eight years later. In May 1836, the oceanic exploration voyage was finally authorized by Congress and created by President Andrew Jackson.

Blake Island is a Puget Sound island in Kitsap County, Washington, United States, that is preserved as Blake Island Marine State Park. The island lies north of Vashon Island, south of Bainbridge Island, and east of Manchester. On the northeast end of the island is Tillicum Village, a showcase for Northwest Coast Indian arts, culture, and food. The park is managed by the Washington State Parks and Recreation Commission.

Hansville is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. Its population was 3,091 as of the 2010 U.S. Census. The coastal community is located at the northern end of the Kitsap Peninsula and is about 16 miles (26 km) northeast of Poulsbo, the nearest city.

The Colvos Passage is a tidal strait within Puget Sound in the American state of Washington running west of Vashon Island between the island and the Kitsap Peninsula. It lies just north of the Dalco Passage. Colvos Passage has a permanent predominantly northbound current, in contrast to the rest of Puget Sound which varies with the tide. The communities of Fragaria, Olalla, Sunrise Beach, Spring Beach, Maplewood, Lisabeula, Paradise Cove and Sylvan Beach are located on Colvos Passage.

Port Gamble is an unincorporated community on the northwestern shore of the Kitsap Peninsula in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. It is also a small, eponymous bay, along which the community lies, near the entrance to Hood Canal. The unincorporated communities of Port Gamble and Little Boston, part of Kitsap County, lie on the west and the east side, respectively, of the mouth of this bay. The Port Gamble Historic District, a U.S. National Historic Landmark, covers one of the nation's best-preserved western lumber towns.

Point No Point is an outcropping of land on the northeast point of the Kitsap Peninsula in Washington, the United States. It was the location of the signing of the Point No Point Treaty and is the site of the Point No Point Light. It was named by Charles Wilkes during the United States Exploring Expedition of Puget Sound in 1841.

Herron Island is an island in central Case Inlet in the southern part of Puget Sound in the U.S. state of Washington. The Pierce County island has a land area of 1.2326 km² and a population of 152 persons as of the 2000 census.

Harstine Island is an island in Mason County, Washington, United States. The US Census recognizes it as an unincorporated community. The island is located west of Case Inlet in southern Puget Sound, 16 km (9.9 mi) north of Olympia. It has a land area of 48.305 km2 (18.651 sq mi), and had a population of 1,002 as of the 2000 census.

Hat Island is a census-designated place (CDP) in Snohomish County, Washington, United States. The population was 41 at the 2010 census. The CDP occupies an island in Possession Sound called Hat Island, also known as Gedney Island. The island lies in Possession Sound between the mainland city of Everett, Washington, and the southern part of Whidbey Island. Gedney Island has a land area of 1.768 km2 and a population of 13 people was reported as of the 2000 census.

















