
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. On Earth, it includes sunlight, atmosphere, water, land, all minerals along with all vegetation, and wildlife.
Sustainable development is an approach to growth and human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The aim is to have a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining planetary integrity. Sustainable development aims to balance the needs of the economy, environment, and social well-being. The Brundtland Report in 1987 helped to make the concept of sustainable development better known.

Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital.
Agroecology is an academic discipline that studies ecological processes applied to agricultural production systems. Bringing ecological principles to bear can suggest new management approaches in agroecosystems. The term can refer to a science, a movement, or an agricultural practice. Agroecologists study a variety of agroecosystems. The field of agroecology is not associated with any one particular method of farming, whether it be organic, regenerative, integrated, or industrial, intensive or extensive, although some use the name specifically for alternative agriculture.
Integrated coastal zone management (ICZM), integrated coastal management (ICM), or integrated coastal planning is a coastal management process for the management of the coast using an integrated approach, regarding all aspects of the coastal zone, including geographical and political boundaries, in an attempt to achieve sustainability. This concept was born in 1992 during the Earth Summit of Rio de Janeiro. The specifics regarding ICZM is set out in the proceedings of the summit within Agenda 21, Chapter 17.
The term "sustainable communities" has various definitions, but in essence refers to communities planned, built, or modified to promote sustainable living. Sustainable communities tend to focus on environmental and economic sustainability, urban infrastructure, social equity, and municipal government. The term is sometimes used synonymously with "green cities," "eco-communities," "livable cities" and "sustainable cities."
The "Melbourne Principles" for Sustainable Cities are ten short statements on how cities can become more sustainable. They were developed in Melbourne (Australia) on 2 April 2002 during an international Charrette, sponsored by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the International Council for Local Environmental Initiatives. Experts at the Charrette were drawn from developing and developed countries.
Regenerative design is about designing systems and solutions that work with or mimic the ways that natural ecosystems return energy from less usable forms to more usable forms. Regenerative design uses systems thinking and other approaches to create resilient and equitable systems that integrate the needs of society and the well-being of nature. Regenerative design is an active topic of discussion in engineering, economics, medicine, landscape design, food systems, and urban design & community development generally.
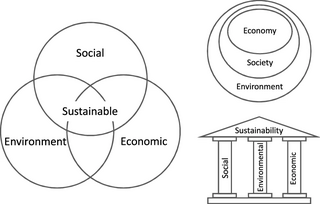
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions : environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "Sustainability is often thought of as a long-term goal, while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it."
Sustainopreneurship is an idea that emerged from the earlier concepts of social entrepreneurship and ecopreneurship, via sustainability entrepreneurship. The concept aims to use creative business organization in order to solve problems related to sustainability. With social and environmental sustainability as a strategic objective and purpose, sustainopreneurship aims to respect the boundaries set in order to maintain the life support systems in the process. In other words, it is a "business with a cause" – where ideally world problems are turned into business opportunities by deploying sustainability innovations.

Sustainable gardening includes the more specific sustainable landscapes, sustainable landscape design, sustainable landscaping, sustainable landscape architecture, resulting in sustainable sites. It comprises a disparate group of horticultural interests that can share the aims and objectives associated with the international post-1980s sustainable development and sustainability programs developed to address that humans are now using natural biophysical resources faster than they can be replenished by nature.

The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was established in July 1970 when the White House and the United States Congress came together due to the public's demand for cleaner natural resources. The purpose of the EPA is to repair the damage done to the environment and to set up new criteria to allow Americans to make a clean environment a reality. The ultimate goal of the EPA is to protect human health and the environment.
Richard Steven "Dick" Levine is an American environmental architect, solar energy and sustainability pioneer, and professor at the University of Kentucky. He is one of the early solar energy innovators in the U.S., a holder of U.S. patents on structural systems and solar energy applications, and the architect of a number of award winning solar buildings including his widely published Raven Run Solar House (1974). Levine is co-director of the Center for Sustainable Cities at the University of Kentucky. His contributions to sustainable urban planning are in both the theory and practice of the sustainable city-region. He has over 150 publications on solar energy and sustainability research, conducted in Italy, Austria, China and the Middle East.
Planetary management is intentional global-scale management of Earth's biological, chemical and physical processes and cycles. Planetary management also includes managing humanity’s influence on planetary-scale processes. Effective planetary management aims to prevent destabilisation of Earth's climate, protect biodiversity and maintain or improve human well-being. More specifically, it aims to benefit society and the global economy, and safeguard the ecosystem services upon which humanity depends – global climate, freshwater supply, food, energy, clean air, fertile soil, pollinators, and so on.

Future generations are cohorts of hypothetical people not yet born. Future generations are contrasted with current and past generations and evoked in order to encourage thinking about intergenerational equity. The moral patienthood of future generations has been argued for extensively among philosophers, and is thought of as an important, neglected cause by the effective altruism community. The term is often used in describing the conservation or preservation of cultural heritage or natural heritage.
A regenerative city is an urban development built on an environmentally enhancing, restorative relationship with the natural systems from which the city draws resources for its sustenance. A regenerative city maintains a symbiotic, mutually beneficial relationship with its surrounding hinterland not only by minimizing its environmental impact but by actively improving and regenerating the productive capacity of the ecosystems from which it depends.
Robert L. Stivers is an American theologian, environmentalist, and Professor Emeritus of Ethics at Pacific Lutheran University, Tacoma, Washington, known for his early works of environmental ethics and sustainable development. and as "long-time advocate of Presbyterian ecojustice concerns."
Julian K. Agyeman is a professor of Urban & Environmental Policy & Planning and Fletcher Professor of Rhetoric and Debate at Tufts University. He is a co-founder and the editor-in-chief of the journal Local Environment. During his career, Agyeman has developed the concept of just sustainabilities, defined as "the need to ensure a better quality of life for all, now, and into the future, in a just and equitable manner, whilst living within the limits of supporting ecosystems."
Sustainable construction aims to reduce the negative health and environmental impacts caused by the construction process and by the operation and use of buildings and the built environment. It can be seen as the construction industry's contribution to more sustainable development. Precise definitions vary from place to place, and are constantly evolving to encompass varying approaches and priorities. More comprehensively, sustainability can be considered from three dimension of planet, people and profit across the entire construction supply chain. Key concepts include the protection of the natural environment, choice of non-toxic materials, reduction and reuse of resources, waste minimization, and the use of life-cycle cost analysis.

The Doughnut, or Doughnut economics, is a visual framework for sustainable development – shaped like a doughnut or lifebelt – combining the concept of planetary boundaries with the complementary concept of social boundaries. The name derives from the shape of the diagram, i.e. a disc with a hole in the middle. The centre hole of the model depicts the proportion of people that lack access to life's essentials while the crust represents the ecological ceilings that life depends on and must not be overshot. The diagram was developed by University of Oxford economist Kate Raworth in her 2012 Oxfam paper A Safe and Just Space for Humanity and elaborated upon in her 2017 book Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century Economist and paper.








