Apscaviroid is a genus of ssRNA viroids that belongs to the family Pospiviroidae . [1]
Apscaviroid is a genus of ssRNA viroids that belongs to the family Pospiviroidae . [1]
| Name | Abbr | GenBank | REFSEQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple dimple fruit viroid | ADFVd | X99487 | NC_003463 |
| Apple scar skin viroid | ASSVd | X17696 | NC_001340 |
| Apscaviroid aclsvd | ACFSVd | MF521431 | N/A |
| Apscaviroid cvd-VII | CVd-VII | KX013549 | N/A |
| Apscaviroid dvd | DVd | MT013216 | N/A |
| Apscaviroid glvd | GLVd | KR605505 | NC_028131 |
| Apscaviroid lvd | LVd | MF156698 | NC_035620 |
| Apscaviroid plvd-I | PlVd-I | MN734702 | N/A |
| Apscaviroid pvd | PVd | AB366022 | NC_010308 |
| Apscaviroid pvd-2 | PVd-2 | AB817729 | NC_021720 |
| Australian grapevine viroid | AGVd | X17101 | NC_003553 |
| Citrus bent leaf viroid | CBLVd | U21125 | NC_001651 |
| Citrus dwarfing viroid | CDVd | AF447788 | NC_003264 |
| Citrus viroid V | CVdV | EF617306 | NC_010165 |
| Citrus viroid VI | CVdVI | AB019508 | NC_004359 |
| Grapevine yellow speckle viroid 1 | GYSVd1 | AF059712 | NC_001920 |
| Grapevine yellow speckle viroid 2 | GYSVd2 | J04348 | NC_003612 |
| Pear blister canker viroid | PBCVd | D12823 | NC_001830 |
Viroids are small single-stranded, circular RNAs that are infectious pathogens. Unlike viruses, they have no protein coating. All known viroids are inhabitants of angiosperms, and most cause diseases, whose respective economic importance to humans varies widely. A recent metatranscriptomics study suggests that the host diversity of viroids and other viroid-like elements is broader than previously thought and that it would not be limited to plants, encompassing even the prokaryotes.
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.
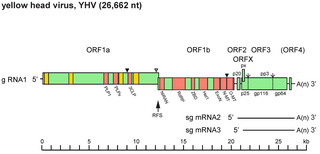
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.

Barnaviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses. Cultivated mushrooms serve as natural hosts. The family has one genus, Barnavirus, which contains one species: Mushroom bacilliform virus. Diseases associated with this family includes La France disease.
Pospiviroid is a genus of ssRNA viroids that infects plants, most commonly tubers. It belongs to the family Pospiviroidae. The first viroid discovered was a pospiviroid, the PSTVd species.
The Pospiviroidae are a incertae sedis family of ssRNA viroids with 5 genera and 39 species, including the first viroid to be discovered, PSTVd, which is part of genus Pospiviroid. Their secondary structure is key to their biological activity. The classification of this family is based on differences in the conserved central region sequence. Pospiviroidae replication occurs in an asymmetric fashion via host cell RNA polymerase, RNase, and RNA ligase. Its hosts are plants, specifically dicotyledons and some monocotyledons. The severity of the infection can vary from no effect to devastating and widespread damage to a population. This can also depend on the virus-host combination.

Chrysoviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Members of the family are called chrysoviruses.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.
Simplexvirus bovinealpha2, also known as Bovine alphaherpesvirus 2 (BoHV2) is a virus of the family Herpesviridae. It causes two diseases in cattle, bovine mammillitis and pseudo-lumpy skin disease.

The Avsunviroidae are a family of viroids. There are five species in three genera. They consist of RNA genomes between 246 and 375 nucleotides in length. They are single-stranded covalent circles and have intramolecular base pairing. All members lack a central conserved region.
Guttaviridae is a family of viruses. Archaea serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in this family, containing one species each. The name is derived from the Latin gutta, meaning 'droplet'.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Hostuviroid is a genus of ssRNA viroids that includes Hop stunt viroid, a species of viroids that infects many different types of plants, including the common hop plant. It belongs to the family Pospiviroidae.

Bottigliavirus is the only genus in the family Ampullaviridae and contains 3 species. Ampullaviridae infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.
Hukuchivirus is a genus of double-stranded DNA viruses that infect thermophilic bacteria. The genus was previously named Gammasphaerolipovirus.

Alvernaviridae is a family of non-enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Dinoflagellates serve as natural hosts. There is one genus in this family, Dinornavirus, which contains one species: Heterocapsa circularisquama RNA virus 01. Diseases associated with this family include host population control, possibly through lysis of the host cell.

Peribunyaviridae is a family of viruses in the order Bunyavirales. Its name partially derives from Bunyamwera, Uganda, where the founding species was first isolated.
Pleolipoviridae is a family of DNA viruses that infect archaea.

Thaspiviridae is a family of incertae sedis spindle-shaped viruses. The family contains a single genus, Nitmarvirus, which contains a single species, Nitmarvirus NSV1.