
Processual archaeology is a form of archaeological theory. It had its beginnings in 1958 with the work of Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips, Method and Theory in American Archaeology, in which the pair stated that "American archaeology is anthropology, or it is nothing", a rephrasing of Frederic William Maitland's comment: "My own belief is that by and by, anthropology will have the choice between being history, and being nothing." The idea implied that the goals of archaeology were the goals of anthropology, which were to answer questions about humans and human culture. This was meant to be a critique of the former period in archaeology, the cultural-history phase in which archaeologists thought that information artifacts contained about past culture would be lost once the items became included in the archaeological record. Willey and Phillips believed all that could be done was to catalogue, describe, and create timelines based on the artifacts.
Post-processual archaeology, which is sometimes alternatively referred to as the interpretative archaeologies by its adherents, is a movement in archaeological theory that emphasizes the subjectivity of archaeological interpretations. Despite having a vague series of similarities, post-processualism consists of "very diverse strands of thought coalesced into a loose cluster of traditions". Within the post-processualist movement, a wide variety of theoretical viewpoints have been embraced, including structuralism and Neo-Marxism, as have a variety of different archaeological techniques, such as phenomenology.

Environmental archaeology is a sub-field of archaeology which emerged in 1970s and is the science of reconstructing the relationships between past societies and the environments they lived in. The field represents an archaeological-palaeoecological approach to studying the palaeoenvironment through the methods of human palaeoecology and other geosciences. Reconstructing past environments and past peoples' relationships and interactions with the landscapes they inhabited provide archaeologists with insights into the origins and evolution of anthropogenic environments and human systems. This includes subjects such as including prehistoric lifestyle adaptations to change and economic practices.

The practice of human sacrifice in pre-Colombian cultures, in particular Mesoamerican and South American cultures, is well documented both in the archaeological records and in written sources. The exact ideologies behind child sacrifice in different pre-Colombian cultures are unknown but it is often thought to have been performed to placate certain gods.
Bloodletting was the ritualized practice of self-cutting or piercing of an individual's body that served a number of ideological and cultural functions within ancient Mesoamerican societies, in particular the Maya. When performed by ruling elites, the act of bloodletting was crucial to the maintenance of sociocultural and political structure. Bound within the Mesoamerican belief systems, bloodletting was used as a tool to legitimize the ruling lineage's socio-political position and, when enacted, was important to the perceived well-being of a given society or settlement.

The Pyramid of the Sun is the largest building in Teotihuacan, and one of the largest in Mesoamerica. It is believed to have been constructed about 200 CE. Found along the Avenue of the Dead, in between the Pyramid of the Moon and the Ciudadela, and in the shadow of the mountain Cerro Gordo, the pyramid is part of a large complex in the heart of the city.

Spiro Mounds is an Indigenous archaeological site located in present-day eastern Oklahoma. The site was built by people from the Arkansas Valley Caddoan culture. that remains from an American Indian culture that was part of the major northern Caddoan Mississippian culture. The 80-acre site is located within a floodplain on the southern side of the Arkansas River. The modern town of Spiro developed approximately seven miles to the south.
Entheogenic drugs have been used by various groups for thousands of years. There are numerous historical reports as well as modern, contemporary reports of indigenous groups using entheogens, chemical substances used in a religious, shamanic, or spiritual context.
Timothy R. Pauketat is an American archaeologist, director of the Illinois State Archaeological Survey, the Illinois State Archaeologist, and professor of anthropology and medieval studies at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. He is known for his historical theories and his investigations at Cahokia, the major center of precolonial Mississippian culture in the American Bottom region of Illinois near St. Louis, Missouri.

Paleolithic religions are a set of spiritual beliefs and practices that are theorized to have appeared during the Paleolithic time period. Paleoanthropologists Andre Leroi-Gourhan and Annette Michelson believe unmistakably religious behavior emerged by the Upper Paleolithic, before 30,000 years ago at the latest, but behavioral patterns such as burial rites that one might characterize as religious — or as ancestral to religious behavior — reach back into the Middle Paleolithic, as early as 300,000 years ago, coinciding with the first appearance of Homo neanderthalensis and possibly Homo naledi.

Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology, history or geography.
Mayan cave sites are associated with the Mayan civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Beliefs and observances connected with these cave sites persist among some contemporary Mayan communities. Many of the Mayan caves served religious purposes. For this reason, the artifacts found there, alongside the epigraphic, iconographic, and ethnographic studies, help build the modern-day understanding of the Mayan religion and society.
Household archaeology has a long history of anthropological inquiry. Archaeological investigations of the household serve as a microcosm for the greater social universe. The household serves as a space for socialization processes. Household archaeology focuses on the household as a social unit, and involves research on the household's dwelling and other related architecture, material culture, features, and larger sociopolitical organizations that are associated with a specific culture. Household social relationships have been associated as serving as an "atom" for society. Therefore, household studied effectively convey information pertaining to flexible economic and ecological conditions Household activity encompasses spheres of activity related to function and how people act. Household archaeology redefines the notion of the household and the domestic by challenging notions of what households are, how they operate and the social implications of such analysis. The material culture provides information about such activities. Households are families, domestic groups, and co-habitations. Households function in a variety of fashions.

Incidents of Travel in Chichén Itzá is an ethnographic film . Jeff Himpele and Quetzil E. Castañeda, filmmakers and producers. Production 1995 and 1997. Postproduction release: 1997.

Signals of Belief in Early England: Anglo-Saxon Paganism Revisited is an academic anthology edited by the British archaeologists Martin Carver, Alex Sanmark and Sarah Semple which was first published by Oxbow Books in 2010. Containing nine separate papers produced by various scholars working in the fields of Anglo-Saxon archaeology and Anglo-Saxon history, the book presents a number of new perspectives on Anglo-Saxon paganism and, to a lesser extent, early Anglo-Saxon Christianity. The collection – published in honour of the archaeologist Audrey Meaney – was put together on the basis of a conference on "Paganism and Popular Practice" held at the University of Oxford in 2005.

Timothy Insoll is a British archaeologist and Africanist and Islamic Studies scholar. Since 2016 he has been Al-Qasimi Professor of African and Islamic Archaeology at the University of Exeter. He is also founder and director of the Centre for Islamic Archaeology. Previously he was at the Department of Archaeology at the University of Manchester (1999–2016).
The archaeology of trade and exchange is a sub-discipline of archaeology that identifies how material goods and ideas moved across human populations. The terms “trade” and “exchange” have slightly different connotations: trade focuses on the long-distance circulation of material goods; exchange considers the transfer of persons and ideas.
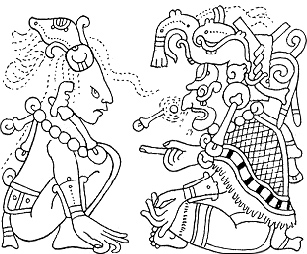
The Classic Maya used dedication rituals to sanctify their living spaces and family members by associating their physical world with supernatural concepts through religious practice. The existence of such rituals is inferred from the frequent occurrence of so-called 'dedication' or 'votive' cache deposits in an archaeological context.

Prehistoric religion is the religious practice of prehistoric cultures. Prehistory, the period before written records, makes up the bulk of human experience; over 99% of human experience occurred during the Paleolithic period alone. Prehistoric cultures spanned the globe and existed for over two and a half million years; their religious practices were many and varied, and the study of them is difficult due to the lack of written records describing the details of their faiths.
Funerary archaeology is a branch of archaeology that studies the treatment and commemoration of the dead. It includes the study of human remains, their burial contexts, and from single grave goods through to monumental landscapes. Funerary archaeology might be considered a sub-set of the study of religion and belief. A wide range of expert areas contribute to funerary archaeology, including epigraphy, material culture studies, thanatology, human osteology, zooarchaeology and stable isotope analysis.










