
In number theory, the Mertens function is defined for all positive integers n as

Oscillatoria is a genus of filamentous cyanobacterium which is often found in freshwater environments, such as hot springs, and appears blue-green. Its name refers to the oscillating motion of its filaments as they slide against each other to position the colony facing a light source. Oscillatoria reproduces by fragmentation, facilitated by dead cells which separate a filament into separate sections, or hormogonia, which then grow. Oscillatoria uses photosynthesis to survive and reproduce. Each filament of oscillatoria consists of trichome which is made up of rows of cells. The tip of the trichome oscillates like a pendulum. In reproduction, it takes place by vegetative means only. Usually the filament breaks into a number of fragments called hormogonia. Each hormogonium consist of one or more cells and grow into a filament by cell division in one direction.
Dinocysts or dinoflagellate cysts are typically 15 to 100 µm in diameter and produced by around 15–20% of living dinoflagellates as a dormant, zygotic stage of their lifecycle, which can accumulate in the sediments as microfossils. Organic-walled dinocysts are often resistant and made out of dinosporin. There are also calcareous dinoflagellate cysts and siliceous dinoflagellate cysts. Many books provide overviews on dinocysts.

Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAPB gene. The VAPB gene is found on the 20th human chromosome. Together with VAPA, it forms the VAP protein family.

Activating transcription factor 5, also known as ATF5, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ATF5 gene.

DNA replication complex GINS protein PSF2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GINS2 gene.

Peridinium is a genus of motile, marine and freshwater dinoflagellates. Their morphology is considered typical of the armoured dinoflagellates, and their form is commonly used in diagrams of a dinoflagellate's structure. Peridinium can range from 30 to 70 μm in diameter, and has very thick thecal plates.
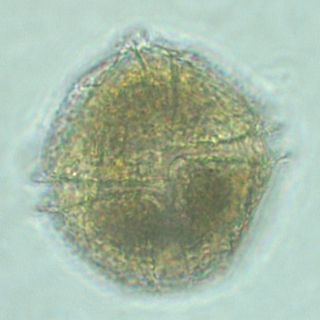
Lingulodinium polyedra is a species of motile photosynthetic dinoflagellates. L. polyedra are often the cause of red tides in southern California, leading to bioluminescent displays on beaches at night.

Banna virus (BAV) is a virus belonging to Reoviridae, a family of segmented, non-enveloped, double-stranded RNA viruses. It is an arbovirus, being primarily transmitted to humans from the bite of infected mosquitoes of the genus Culex. Pigs and cattle have also been shown to become infected. The most common symptom of infection is fever, but in some cases encephalitis may occur. There is no specific treatment for infection, so treatment is aimed at alleviating the severity of symptoms until the immune system has cleared the infection.

Austrodyptornithes is a clade of birds that include the orders Sphenisciformes (penguins) and Procellariiformes. A 2014 analysis of whole genomes of 48 representative bird species concluded that penguins are the sister group of Procellariiformes, from which they diverged about 60 million years ago.
WASP-36 is a yellow main sequence star in the Hydra constellation.
WASP-67 is a K-type main-sequence star about 620 light-years away. The stars age is poorly constrained, but is likely older than the Sun`s at approximately 8.7+5.5
−8.6 billion years. WASP-67 is slightly depleted in heavy elements, having 85% of the solar abundance of iron.
WASP-55 is a G-type main-sequence star about 980 light-years away. The star is much younger than the Sun at approximately 1.1+0.8
−0.6 billion years. WASP-55 is similar to the Sun in concentration of heavy elements.
WASP-42 is a K-type main-sequence star. Its surface temperature is 5315±79 K. WASP-42 is similar to the Sun in concentration of heavy elements, with metallicity ([Fe/H]) of 0.05±0.13, and is much older than the Sun at 11.3+1.5
−4.8 billion years. The star does exhibit starspot activity as is typical for its spectral class.
WASP-41 is a G-type main-sequence star. Its surface temperature is 5450±150 K. WASP-41 is similar to the Sun in its concentration of heavy elements, with a metallicity Fe/H index of −0.080±0.090, but is much younger at an age of 2.289±0.077 billion years. The star does exhibit strong starspot activity, with spots covering 3% of the stellar surface.
HATS-3 is a F-type main-sequence star. Its surface temperature is 6351±76 K. HATS-3 is relatively depleted in its concentration of heavy elements, with a metallicity Fe/H index of −0.157±0.07, but is slightly younger than the Sun at an age of 3.2+0.6
−0.4 billion years.
Lingulodiniaceae is a family of dinoflagellates belonging to the order Gonyaulacales.
Protoperidiniaceae is a family of dinoflagellates belonging to the order Peridiniales.








