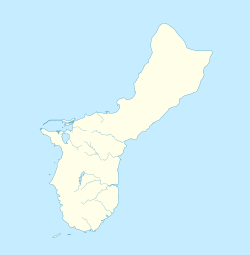
Tumon Bay is a bay in the United States territory of Guam, opening to the Philippine Sea. It is bounded to the north by Two Lovers Point and to the south by Ypao Point. The entirety of the bay falls within the Tumon Bay Marine Preserve, also known as the Tumon Bay Marine Preserve Area (MPA) and Tumon Preserve, one of five marine preserves on Guam. The Preserve measures 4.54 square kilometers and is roughly two miles long. The platform of the fringing reef that separates the open ocean from the lagoon is up to 1,450 feet (440 m) wide. and up to one mile from the shore. The bay is located off of the Tumon area, the tourist center of the island, in the village of Tamuning. The bay is extensively utilized for recreation and fishing.
10th Independent Mixed Regiment was a regiment of the Imperial Japanese Army that has association with a number of U.S. National Register of Historic Places-listed places in Guam.

The Ilik River Fortification II near Yona, Guam was built by Japanese forces during World War II. It was listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 1991.

The Mataguac Hill Command Post, near Yigo, Guam, has significance from 1944 during the Battle of Guam. It was the location of "the last organized resistance by the Japanese to the American liberation of Guam during World War II and therefore is considered a highlight of the invasion of Guam."

The Agana Historic District in Hagåtña, Guam is a 2-acre (0.81 ha) historic district that was listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 1985. It includes five contributing buildings: the Calvo-Torres, Rosario, Martinez-Notley, Lujan and Leon Guerrero houses. The area is roughly bounded by 2nd S., 3rd S., and 9th W., Santa Cruz and Legaspi Sts. in Agana.

The Japanese 20mm Cannon Blockhouse is one of many relics of World War II on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is a concrete blockhouse, semi-circular in shape with a diameter of about 6 metres (20 ft). Its walls are 1.22 metres (4.0 ft) thick with four firing ports large enough to accommodate 20mm cannons, originally equipped with steel sliding shutters. A steel door 25 millimetres (0.98 in) thick provides access to the structure at the rear, sheltered by a concrete wall and covered defensively by a machine gun port. The blockhouse is located near the center of what is locally called Big Agingan Beach, on the south coast of the island, about 20 metres (66 ft) from the shore. It was built in some haste by the Japanese forces defending Saipan in 1944, and was captured by Allied forces early in the Battle of Saipan.

The Agat Invasion Beach is a historic site in the village of Agat, Guam. The beaches of Agat were one of the landing sites of American forces in the 1944 Battle of Guam, in which the island was retaken from occupying Japanese forces. The designated historic site includes the beaches and inland areas extending between Bangi Point and Togcha Beach. Surviving remnants of the Japanese defenses on this stretch of coast include trenches and rifle pits located a short way inland, and a fortified bunker and 40mm gun emplacements at Ga'an Point. Remnants of pillboxes that had lined the beach also survive, with one at Gangi Point in relatively good condition.

The Asan Invasion Beach is a historic site in the village of Asan, Guam. The beaches of Asan were one of the landing sites of American forces in the 1944 Battle of Guam, in which the island was retaken from occupying Japanese forces. The designated historic site includes the beaches extending between Asan Point and Adelup Point, and extends inland roughly to Guam Highway 1. It also includes the water area extending from the beach to the reef, about 100 metres (330 ft) out, an area that includes at least one abandoned Allied landing vehicle.

The Agana-Hagåtña Pillbox is a former Japanese defensive fortification in Hagåtña, Guam. It is a six-sided reinforced concrete structure, located a short way above the high-tide line on the west side of the Paseo de Susana, a small peninsula jutting north from the village center. There is another wall providing cover for the entrance on the land side. The interior is divided into two chambers, each of which has a gun port. The structure was built by Guam's Japanese defenders during their occupation of the island (1941–44) in World War II.

The Asan Ridge Battle Area was the scene of some of the heaviest fighting in the 1944 Battle of Guam, the World War II battle in which Allied forces recaptured Guam from occupying Japanese forces. The area is now part of the Asan Inland Unit of the War in the Pacific National Historical Park, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975. The area is just inland of the Asan Invasion Beach, one of the two major beachheads established by the Allies, and has a commanding view over that area. The landforms included in this area are Chorrito Cliff, Bundschuh Ridge, and Nimitz Hill, and they were heavily fortified by the Japanese prior to the battle. Surviving elements of these fortifications include two concrete pillboxes, and an unfinished battery of 4-inch guns.

The Gongna Beach defenses are a collection of World War II structures built on or near Gongna Beach in Tamuning on the island of Guam, now a United States territory. These defenses were erected by the Imperial Japanese Army during its occupation of the island 1941–44. The three surviving elements were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991. They are located well north of the main Allied landing areas of the 1944 Battle of Guam.

The Inarajan Pillbox is a World War II-era defensive fortification near the mouth of Inarajan Bay in the United States territory of Guam. Set on a limestone outcrop on the south side of the bay, the fortification occupies a natural niche in the formation, with a wall of piled coral rocks and cement covering part of the opening. This wall is about 1.8 metres (5.9 ft) long, 2.0 metres (6.6 ft) high, and 1.0 metre (3.3 ft) thick. A cement gunport is set in the wall, about 0.75 metres (2.5 ft) above ground level. This fortification was built by Japanese soldiers occupying Guam between 1941 and 1944. The structure was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991, as "Inalahan Pillbox".

The Ipao Pillbox I is one of three surviving World War II-era fortifications on Ypao Point, located west of Tumon Bay on the west side of the island of Guam. It is built into the limestone cliff overlooking the beach on the property of the Hilton Hotel, about 17 metres (56 ft) in from the high tide line. Its walls are fashioned out of coral rock and cement, varying in thickness from 1 metre (3.3 ft) to 1.6 metres (5.2 ft). Its entrance is on the east wall, and its gun port faces north, overlooking Ypao Channel. Parts of the structure have been restored.

The Malessu' Pillbox is a World War II-era Japanese-built defensive fortification on the shore of Merizo, Guam. Located about 15 metres (49 ft) from the high-tide line at Merizo Beach, it is a rectangular structure built of steel-reinforced concrete and basalt rock. It is 3.9 metres (13 ft) deep, 2.4 metres (7.9 ft) wide, and about 2.42 metres (7.9 ft) high, although only about 0.75 metres (2.5 ft) of the structure is visible above ground. Its gun port has a view of the Merizo pier, and is approximately at ground level. It was built by Japanese defenders during their occupation of the island 1941–44.

The Mana Pillbox is an old World War II-era Japanese-built defensive fortification on the east coast of the island of Guam. It is located south of the village of Talofofo, about 50 metres (160 ft) inland from the point marking the south end of As Anite Cove. It is a structure built out of coral limestone and concrete, with an interior chamber about 3 by 1.8 metres in size. The entrance is on the south side, measuring 0.85 by 1.45 metres. There is one gun port, facing north, measuring 0.32 by .9 metres. The structure was designed to be well hidden in view from the sea and air. It was built, probably by conscripted Chamorro labor, during the Japanese occupation period 1941–44.

The Pago Bay Japanese pillboxes are a pair of World War II-era coastal defense pillboxes located on the shore of Pago Bay, located on the central east coast of Guam. Built out of steel-reinforced concrete mixed with coral stone, these two structures were built by Japanese defenders during their occupation of the island between 1941 and 1944. They were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991 as Pagu' Pillbox I and Pagu' Pillbox II. Neither of these would have seen substantial action during the 1944 liberation of Guam, whose military activities were focused on the western, central, and northern parts of the island.

The San Vitores Beach Japanese Fortification are the remains of World War II-era defensive positions facing the beach of Tumon Bay on the west side of the island of Guam. Located near the stairs to the beach of the Guam Reef Hotel are the remains of two concrete pillboxes built by Japanese defenders during the occupation period 1941–44. One structure, of which little more than a gun embrasure is discernible, is located in the limestone cliff about 10 metres (33 ft) inland from the high tide line, and a second is located about 10 meters south and 8 meters further inland, with only a section of roof slab and supporting columns recognizable.

The Talofofo Pillbox is a historic World War II-era defensive fortification in Talofofo, Guam. It is located near the coast, about 127 metres (417 ft) south of the mouth of the Togcha River and 27 metres (89 ft) inland from the high-tide line. It is roughly 2.75 by 3.0 metres, built out of concrete and coral limestone. Its walls are about 0.5 metres (1.6 ft) thick, with an embrasure providing a view of the Togcha River, and a window looking over the coast to the east. Its entrance is on the landward (south) side. This structure was built under the direction of the Imperial Japanese Army during its occupation of Guam in 1941–44.

The Tokcha' Pillbox is a Japanese-built World War II-era defensive fortification on the island of Guam. It is built on a limestone terrace on Togcha Point, about 1 mile (1.6 km) north of the Togcha River and 0.7 miles (1.1 km) south of the Ylig River. It is set in a depression excavated from the limestone about 15 metres (49 ft) inland from the high tide land and 1 metre (3.3 ft) above sea level. It is a roughly rectangular structure built out of steel-reinforced concrete filled with coral and beach aggregate. The entrance is on the north wall, sheltered by a wall of coral blocks, and the gun port is on the south wall. This structure was built under the direction of the Japanese military during their occupation of the island 1941–44.

The Tumon Bay Japanese fortifications are a collection of World War II-era military structures along the coast of Guam in and near the village of Tumon. Many of these structures were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991, using the alternate spelling "Tomhum". They include pillboxes on or close to the beach, and concrete structures and caves located a short way inland on the limestone cliffs that overlook the beach.