Asan-Maina is a village located on the western shore of the United States territory of Guam. The municipality combines the names of the coastal community of Asan with Maina, a community along the slopes of the Fonte River valley to the east. Asan was the northern landing site for United States Marines during Guam's liberation from the Japanese during World War II. Asan Beach Park is part of the War in the Pacific National Historic Park. The third community comprising Asan-Maina is Nimitz Hill Annex in the hills above Asan and Maina, which is the location of the Joint Region Marianas headquarters. Asan-Maina is located in the Luchan (Western) District.

The War in the Pacific National Historical Park is a multi-unit protected area in the United States territory of Guam, which was established in 1978 in honor of those who participated in the Pacific Theater of World War II. Uniquely among the National Park System, it honors the bravery and sacrifices of all those who participated in the Pacific Theater.

Tumon Bay is a bay in the United States territory of Guam, opening to the Philippine Sea. It is bounded to the north by Two Lovers Point and to the south by Ypao Point. The entirety of the bay falls within the Tumon Bay Marine Preserve, also known as the Tumon Bay Marine Preserve Area (MPA) and Tumon Preserve, one of five marine preserves on Guam. The Preserve measures 4.54 square kilometers and is roughly two miles long. The platform of the fringing reef that separates the open ocean from the lagoon is up to 1,450 feet (440 m) wide. and up to one mile from the shore. The bay is located off of the Tumon area, the tourist center of the island, in the village of Tamuning. The bay is extensively utilized for recreation and fishing.
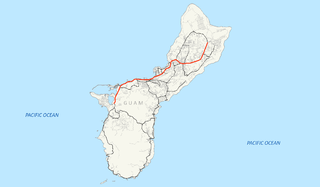
Guam Highway 1 (GH-1), also known as Marine Corps Drive, is one of the primary automobile routes in the United States territory of Guam. It runs in a southwest-to-northeast direction, from the main gate of Naval Base Guam in the southwestern village of Santa Rita in a northeasterly direction to the main gate of Andersen Air Force Base in the village of Yigo. It passes through Guam's capital, Hagåtña, as well as intersecting other territorial highways. The highway runs through tropical forest, urbanized commercial areas, and residential neighborhoods. The US military upgraded and extended the road starting in 1941. Construction ceased with the Japanese invasion in December 1941 and resumed after the Second Battle of Guam in 1944. The highway was formally dedicated to the U.S. Marine Corps by the governor in 2004.

Nimitz Hill Annex is a community and census-designated place (CDP) in Asan-Maina, Guam. It contains the geographic feature of Nimitz Hill, and is located immediately northeast of the Nimitz Hill CDP in Piti. In normal conversation, the Nimitz Hill CDP and Nimitz Hill Annex CDP are often collectively referred to as "Nimitz Hill."

Landing Beaches; Aslito/Isely Field & Marpi Point, Saipan Island is a National Historic Landmark District consisting of several discontiguous areas of the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. The sites were designated for their association with the Japanese defense of Saipan during World War II, the 1944 Battle of Saipan in which United States forces captured the island, and the subsequent campaigns which used Saipan as a base. The district includes the landing beaches where the U.S. forces landed, the remnants of Japanese airfields Aslito and Marpi Point and Isely Field, the airfield built over much of Aslito from which B-29 bombers were used to bomb the Japanese home islands. Included in the Marpi Point area are Suicide Cliff and Banzai Cliff, two locations where significant numbers of Japanese military and civilians jumped to their deaths rather than surrender to advancing U.S. forces. The loss of Saipan was a major blow to the Japanese war effort, leading to the resignation of Prime Minister Hideki Tojo, The landmark designation was made in 1985.

Agat Bay is a bay on the west coast of Guam. Its northern boundary is the Orote Peninsula, occupied entirely by Naval Base Guam, which itself lies within the village of Santa Rita. The bay stretches south along the coast of the village of Agat to Facpi Point. With a length of some seven kilometers, the bay stretches for nearly one fifth of the west coast of Guam. The Asan Invasion Beach of the 1944 Battle of Guam is commemorated by the Agat Unit of War in the Pacific National Historical Park, which spans surce and subsurface areas from Apaca Point to Bangi Point. The NRHP-listed Agat World War II Amtrac is submerged off Agat Cemetery.

The Piti Guns or Piti Coastal Defense Guns is the site of three Vickers-type Model 3 140-millimetre (5.5 in) coastal defense guns in the War in the Pacific National Historical Park in Piti, Guam. The Japanese manufactured these Model 3 coastal defense guns in 1914. During the Japanese Occupation of Guam from 1941 to 1944, they built up defensive positions on the island. The Chamorro population was forced to work in building up these defenses, and did so here at the Piti Guns.

The Asan River is a river in the United States territory of Guam that lies entirely within the village of Asan-Maina. It originates in the highlands of Nimitz Hill Annex and flows through the Asan Inland Unit of War in the Pacific National Historical Park (WAPA) and enters the community of Asan. It then briefly re-enters WAPA at its Asan Inland Unit, with the mouth at the eastern end of Asan Memorial Park into Asan Bay. The river was thus a significant geographical feature of the Asan Invasion Beach for U.S. forces during the initial landings on Guam in July 1944.
The Maritime Heritage Trail – Battle of Saipan is located within the protected waters of Saipan lagoon in the Northern Marianas archipelago. The majority of the dive sites including two Japanese shipwrecks, two Japanese aircraft, two US aircraft, a US landing vehicle and two Japanese landing craft can be found in the clear waters between Garapan, Tanapag Harbor, and Mañagaha Island while further south in Chalan Kanoa Lagoon there are three US tanks.

The As Sombreru Pillbox I, As Sombreru Pillbox II, and As Sombreru Pillbox III are three historic defensive fortifications on Guam, near Tumon, that were listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 1991. They are pillboxes, a type of defensive fortification, built by the 48th Independent Mixed Brigade; 29th Division of the Imperial Japanese Army during 1941-1944, between Japan capturing Guam on December 8, 1941 from the United States and the U.S. recapturing Guam in 1944.

The Agat Invasion Beach is a historic site in the village of Agat, Guam. The beaches of Agat were one of the landing sites of American forces in the 1944 Battle of Guam, in which the island was retaken from occupying Japanese forces. The designated historic site includes the beaches and inland areas extending between Bangi Point and Togcha Beach. Surviving remnants of the Japanese defenses on this stretch of coast include trenches and rifle pits located a short way inland, and a fortified bunker and 40mm gun emplacements at Ga'an Point. Remnants of pillboxes that had lined the beach also survive, with one at Gangi Point in relatively good condition.

The Agat World War II Amtrac is an underwater relic of World War II, located off Ga'an Point in Agat Bay on the west side of the island of Guam. It is the remains of an LVT 4, an amphibious tracked landing vehicle. It is located about 500 yards (460 m) off Agat Invasion Beach in 45 feet (14 m) of water, and was described as being in good condition when it was discovered and surveyed in 1985. These vehicles were used during the 1944 Battle of Guam, in which American forces recaptured the island from occupying Japanese forces. This particular vehicle does not appear to exhibit significant war damage. This is the most intact of the three Amtracks remaining on Guam from the 850 that participated in the battle. It was re-surveyed by maritime archaeological field schools conducted from 2009 to 2012.

Hill 40 is a militarily historic landform on the island of Guam. It is located about 325 metres (1,066 ft) east of Bangi Point, south of Agat on the island's west coast, rising to a height of 40 to 60 feet above the coastal plain, with a strategically significant view of the Agat Invasion Beach. This hill was the scene of some of the most intense fighting during the landing phase of the 1944 Battle of Guam as Allied forces sought to establish their beachhead against the defending Japanese forces. The American 4th Marine Regiment of the 1st Provisional Marine Brigade captured Hill 40 on June 21, 1944, the day of the landing. That night the Japanese launched a counteroffensive that successfully retook the hill on three occasions. The Marines regrouped and regained the hill each time. The final push came in the early morning hours of July 22. The Japanese 38th Regiment was wiped out during this military action, with 345 killed on the Bangi Point plain, immediately west of Hill 40 near the beach.

The Asan Ridge Battle Area was the scene of some of the heaviest fighting in the 1944 Battle of Guam, the World War II battle in which Allied forces recaptured Guam from occupying Japanese forces. The area is now part of the Asan Inland Unit of the War in the Pacific National Historical Park, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975. The area is just inland of the Asan Invasion Beach, one of the two major beachheads established by the Allies, and has a commanding view over that area. The landforms included in this area are Chorrito Cliff, Bundschuh Ridge, and Nimitz Hill, and they were heavily fortified by the Japanese prior to the battle. Surviving elements of these fortifications include two concrete pillboxes, and an unfinished battery of 4-inch guns.

The Matgue River Valley Battle Area was the site of a decisive Allied victory during the 1944 Battle of Guam. The area was the scene of a major counterattack by Japanese forces against the Allied beachhead, in which the Japanese suffered extremely heavy casualties and were beaten back. After this attack, the remaining Japanese forces on the island retreated to the north. The area is located in the hills southwest of Asan Point along the Matgue River. The only surviving structural remnants associated with the battle are caves dug by the Japanese as defensive positions prior to the invasion.

Adelup Point is limestone promontory in Hagåtña, Guam that extends into the Philippine Sea and separates Asan Bay from Hagåtña Bay. It has been the site of the Ricardo J. Bordallo Governor's Complex since 1990. Adelup is therefore a metonym for the Office of the Governor of Guam.

Piti Bomb Holes Marine Preserve is a marine protected area comprising all of Piti Bay on the western coast of Guam, located off of the village of Piti in the Philippine Sea. The defining "bomb hole" features, named because they look like bomb craters in the reef flat, are actually natural percolation pits where fresh water filters into the shallow lagoon at a depth of 25 to 30 feet. The largest pit houses the commercial Fish Eye Marine Park tourist attraction, which includes a wooden pier to a underwater observatory and a Seawalker tour of the lagoon bottom. It is visited by more than 200,000 people annually. The Piti preserve is the most ecologically diverse of Guam's five marine preserves. The pit around Fish Eye is a popular snorkeling and recreational diving site.

Asan is a community and census-designated place (CDP) along the western coast of the U.S. territory of Guam. Asan, along with Maina and Nimitz Hill Annex, are the three communities in the village of Asan-Maina. It is known for being the location of northern invasion beach used by the United States during the retaking of Guam in 1944.