The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to promote economic cooperation and integration among its member states.

The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a political and economic union of 10 states in Southeast Asia. Together, its member states represent a population of more than 600 million people and land area of over 4.5 million km2 (1.7 million sq mi). The bloc generated a purchasing power parity (PPP) gross domestic product (GDP) of around US$10.2 trillion in 2022, constituting approximately 6.5% of global GDP (PPP). ASEAN member states include some of the fastest growing economies in the world, and the institution plays an integral role in East Asian regionalism.

Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Following the success of ASEAN's series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, APEC started in 1989, in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; it aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe. Headquartered in Singapore, APEC is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts significant global influence.

The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. SAARC comprises 3% of the world's land area, 21% of the world's population and 5.21% of the global economy, as of 2021.

The Economic Cooperation Organization or ECO is a Eurasian political and economic intergovernmental organization that was founded in 1985 in Tehran by the leaders of Iran, Pakistan, and Turkey. It provides a platform to discuss ways to improve development and promote trade and investment opportunities. The ECO is an ad hoc organisation under the United Nations Charter. The objective is to establish a single market for goods and services, much like the European Union. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the ECO expanded to include Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan in 1992.

The Asia Cooperation Dialogue (ACD) is an intergovernmental organization created on 18 June 2002 to promote Asian cooperation at a continental level and to ensure coordination among different regional organizations such as the ASEAN, the Gulf Cooperation Council, the Eurasian Economic Union, the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, and the SAARC. It is the first international organization to cover the whole of Asia. Its secretariat is in Kuwait City.

The ASEAN Agreement on Transboundary Haze Pollution is a legally binding environmental agreement signed in 2002 by the member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations to reduce haze pollution in Southeast Asia. The Agreement recognises that transboundary haze pollution which results from land and/or forest fires should be mitigated through concerted national efforts and international co-operation.

The Korea Foundation is a non-profit public diplomacy organization established in 1991 to promote a better understanding of Korea and strengthen friendships in the international community. The foundation carries out various projects for exchange between the South Korea and foreign countries to cultivate mutual understanding.

The Korea Forest Service is a central administrative agency under the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFR), responsible for protecting and nurturing forests, increasing forest resources, developing forest products, conducting research on forest management and improvement, and is located in Daejeon Government Complex. In the past, during the national forestation campaign from 1973 to 1986, it was temporarily under the Ministry of Home Affairs, but returned to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries in 1987. However, as the agency's work was focused solely on maintaining and managing successful national forestation policies, questions were raised about its necessity for a period of time. Currently, the agency has transformed its identity into one that strives to generate continuous income through forest resources.

The Department of Foreign Affairs is the executive department of the Philippine government tasked to contribute to the enhancement of national security, protection of the territorial integrity and national sovereignty, to participate in the national endeavor of sustaining development and enhancing the Philippines' competitive edge, to protect the rights and promote the welfare of Filipinos overseas and to mobilize them as partners in national development, to project a positive image of the Philippines, and to increase international understanding of Philippine culture for mutually-beneficial relations with other countries.

The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) is a high-level intergovernmental policy forum. The forum includes all United Nations member states and permanent observers, the UNFF Secretariat, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests, Regional Organizations and Processes and Major Groups.

The Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia or ERIA is an international organization established in Jakarta, Indonesia in 2008 by a formal agreement among Leaders of 16 countries in the East Asian region to conduct research activities and make policy recommendations for further economic integration in the East Asia. ERIA works very closely with both the ASEAN Secretariat and 16 Research Institutes to undertake and disseminate policy research under the three pillars, namely “Deepening Economic Integration”, ”Narrowing Development Gaps”, and “Sustainable Development” and provide analytical policy recommendations to Leaders and Ministers at their regional meetings. ERIA provides intellectual contributions to East Asian Community building and serves as a Sherpa international organization. ERIA Ranks 9th among the world's "Top International Economics Think Tanks" according to the 2020 Global Go To Think Tanks Index Report conducted by the University of Pennsylvania.
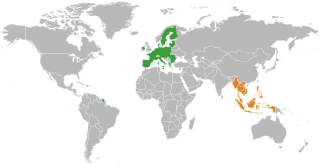
The ASEAN–European Union relations are the bilateral foreign relations between the two organisations; the European Union (EU), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). EU and ASEAN have been interacting with each other on the economic, trade, and political levels for more than four decades. The partnership between the EU and ASEAN dates back to 1972, when the EU established ties with ASEAN. The EU became an ASEAN Dialogue Partner in 1977.

The China–Japan–South Korea trilateral summit is an annual summit meeting attended by the People's Republic of China, Japan and South Korea, three major countries in East Asia and the world's second, fourth and 12th largest economies. The first summit was held during December 2008 in Fukuoka, Japan. The talks are focused on maintaining strong trilateral relations, the regional economy and disaster relief.
The ASEAN Summit is a biannual meeting held by the members of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in relation to economic, political, security, and socio-cultural development of Southeast Asian countries. The league of ASEAN is currently connected with other countries who aim to participate on the missions and visions of the league.
The Comprehensive Economic Partnership for East Asia (CEPEA) is a Japanese led proposal for trade co-operation and free trade agreement among the 16 present member countries of the East Asia Summit. All those movements and efforts were taken over by the following Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
The ASEAN Wildlife Enforcement Network (ASEAN-WEN) was officially launched on 1 December 2005, as a regional inter-agency and inter-governmental initiative to counter the illegal cross-border trade in endangered flora and fauna. It helps countries share information on and tackle cross-border wildlife crime and facilitates the exchange of regional best practices in combating those crimes. As the world's largest wildlife law enforcement network, it comprises the law enforcement agencies of the 10 ASEAN countries forming a regional intergovernmental law-enforcement network.

The Trilateral Cooperation Secretariat (TCS) is an international organization established with a vision to promote "Lasting Peace, Common Prosperity, and Shared Culture" among China, Japan, and South Korea. Upon the agreement signed and ratified by each of the three governments, the TCS was officially inaugurated in Seoul, on 1 September 2011. On the basis of equal participation, each government shares 1/3 of the total operational budget.

The ASEAN Inter-Parliamentary Assembly (AIPA) is a regional parliamentary body which acts as a primary point for communication and information sharing between member countries. Its primary objectives are to provide information to Southeast Asian citizens about policies aimed at establishing an ASEAN community by 2025 and to foster mutual understanding and collaboration among these parliaments.

The Non-Timber Forest Products – Exchange Programme(NTFP-EP) is a network of non-governmental organizations and community-based organizations in Southeast Asia and South Asia that promotes the use of non-timber forest products (NTFPs) for forest conservation and as a source of livelihood for forest-based communities. The network has a regional secretariat office in the Philippines with country-level offices in Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam.