Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information (intelligence). A person who commits espionage is called an espionage agent or spy. Any individual or spy ring, in the service of a government, company, criminal organization, or independent operation, can commit espionage. The practice is clandestine, as it is by definition unwelcome. In some circumstances, it may be a legal tool of law enforcement and in others, it may be illegal and punishable by law.

The Security Service, also known as MI5, is the United Kingdom's domestic counter-intelligence and security agency and is part of its intelligence machinery alongside the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), and Defence Intelligence (DI). MI5 is directed by the Joint Intelligence Committee (JIC), and the service is bound by the Security Service Act 1989. The service is directed to protect British parliamentary democracy and economic interests and to counter terrorism and espionage within the United Kingdom (UK).

Counterintelligence (counter-intelligence) or counterespionage (counter-espionage) is any activity aimed at protecting an agency's intelligence program from an opposition's intelligence service. It includes gathering information and conducting activities to prevent espionage, sabotage, assassinations or other intelligence activities conducted by, for, or on behalf of foreign powers, organizations or persons.
In espionage jargon, a mole is a long-term spy who is recruited before having access to secret intelligence, subsequently managing to get into the target organization. However, it is popularly used to mean any long-term clandestine spy or informant within an organization. In police work, a mole is an undercover law-enforcement agent who joins an organization in order to collect incriminating evidence about its operations and to eventually charge its members.
An intelligence officer is a person employed by an organization to collect, compile or analyze information which is of use to that organization. The word of officer is a working title, not a rank, used in the same way a "police officer" can also be a sergeant, or in the military, in which non-commissioned personnel may serve as intelligence officers.
A sleeper agent, also called sleeper cell, is a spy who is placed in a target country or organization not to undertake an immediate mission, but instead to act as a potential asset if activated. Even if not activated, the "sleeper agent" is still an asset and can still play an active role in sedition, espionage, or possibly treason by virtue of agreeing to act if activated. Sleeper agents may also work in groups of a clandestine cell system with other agents.

The Foreign Intelligence Service of the Russian Federation or SVR RF is Russia's external intelligence agency, focusing mainly on civilian affairs. The SVR RF succeeded the First Chief Directorate (PGU) of the KGB in December 1991. The SVR has its headquarters in the Yasenevo District of Moscow.
A cover in foreign, military or police human intelligence or counterintelligence is the ostensible identity and/or role or position in an infiltrated organization assumed by a covert agent during a covert operation.
In intelligence organizations, agent handling is the management of so-called agents, principal agents, and agent networks by intelligence officers typically known as case officers.

An informant is a person who provides privileged information, or information intended to be intimate, concealed, or secret, about a person or organization to an agency, often a government or law enforcement agency. The term is usually used within the law-enforcement world, where informants are officially known as confidential human sources (CHS), or criminal informants (CI). It can also refer pejoratively to someone who supplies information without the consent of the involved parties. The term is commonly used in politics, industry, entertainment, and academia.
As early as the 1920s, the Soviet Union, through its GRU, OGPU, NKVD, and KGB intelligence agencies, used Russian and foreign-born nationals, as well as Communists of American origin, to perform espionage activities in the United States, forming various spy rings. Particularly during the 1940s, some of these espionage networks had contact with various U.S. government agencies. These Soviet espionage networks illegally transmitted confidential information to Moscow, such as information on the development of the atomic bomb. Soviet spies also participated in propaganda and disinformation operations, known as active measures, and attempted to sabotage diplomatic relationships between the U.S. and its allies.
Subversion refers to a process by which the values and principles of a system in place are contradicted or reversed in an attempt to sabotage the established social order and its structures of power, authority, tradition, hierarchy, and social norms. Subversion can be described as an attack on the public morale and, "the will to resist intervention are the products of combined political and social or class loyalties which are usually attached to national symbols. Following penetration, and parallel with the forced disintegration of political and social institutions of the state, these tendencies may be detached and transferred to the political or ideological cause of the aggressor".
An agent of influence is an agent of some stature who uses their position to influence public opinion or decision making to produce results beneficial to the country whose intelligence service operates the agent. Agents of influence are often the most difficult agents to detect, as there is seldom material evidence that connects them with a foreign power, but they can be among the most effective means of influencing foreign opinion and actions as they hold considerable credibility among the target audience. Most commonly they serve the interests of a foreign power in one of three ways: either as a controlled agent directly recruited and controlled by a foreign power; as a "trusted contact" that consciously collaborates to advance foreign interests but is not directly recruited or controlled by a foreign power; or as a "useful idiot" that is completely unaware of how their actions further the interests of a foreign power.
A resident spy in the world of espionage is an agent operating within a foreign country for extended periods of time. A base of operations within a foreign country with which a resident spy may liaise is known as a "station" in English and a rezidentura in Russian. What the U.S. would call a "station chief", the head spy, is known as a rezident in Russian.
Intelligence analysis is the application of individual and collective cognitive methods to weigh data and test hypotheses within a secret socio-cultural context. The descriptions are drawn from what may only be available in the form of deliberately deceptive information; the analyst must correlate the similarities among deceptions and extract a common truth. Although its practice is found in its purest form inside national intelligence agencies, its methods are also applicable in fields such as business intelligence or competitive intelligence.
Clandestine human intelligence is intelligence collected from human sources using clandestine espionage methods. These sources consist of people working in a variety of roles within the intelligence community. Examples include the quintessential spy, who collects intelligence; couriers and related personnel, who handle an intelligence organization's (ideally) secure communications; and support personnel, such as access agents, who may arrange the contact between the potential spy and the case officer who recruits them. The recruiter and supervising agent may not necessarily be the same individual. Large espionage networks may be composed of multiple levels of spies, support personnel, and supervisors. Espionage networks are typically organized as a cell system, in which each clandestine operator knows only the people in his own cell, perhaps the external case officer, and an emergency method to contact higher levels if the case officer or cell leader is captured, but has no knowledge of people in other cells. This cellular organization is a form of compartmentalisation, which is an important tactic for controlling access to information, used in order to diminish the risk of discovery of the network or the release of sensitive information.
The Clandestine HUMINT page adheres to the functions within the discipline, including espionage and active counterintelligence.
Clandestine HUMINT asset recruiting refers to the recruitment of human agents, commonly known as spies, who work for a foreign government, or within a host country's government or other target of intelligence interest for the gathering of human intelligence. The work of detecting and "doubling" spies who betray their oaths to work on behalf of a foreign intelligence agency is an important part of counterintelligence.
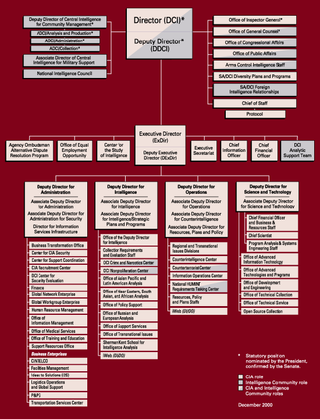
The CIA publishes organizational charts of its agency. Here are a few examples.
Technical Intelligence (TECHINT) is intelligence about weapons and equipment used by the armed forces of foreign nations. The related term, scientific and technical intelligence, addresses information collected or analyzed about the broad range of foreign science, technology, and weapon systems.




