Nazran is the largest city in Ingushetia, Russia. It served as the republic's capital from 1991 to 2000, until it was replaced by Magas, which was built for this purpose. It is the most populous city in the republic: 122,350 (2021 Census); 93,335 (2010 Census); 125,066 (2002 Census); 18,246 (1989 Soviet census).
Yalkharoy is a rural locality in Urus-Martanovsky District of the Republic of Chechnya, Russia.

Karabulak is a town in the Republic of Ingushetia, Russia, located on the Sunzha River, 20 kilometers (12 mi) north of the republic's capital of Magas. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 30,961.

Nadterechny District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the fifteen in the Chechen Republic, Russia. It is located in the northwest of the republic. The area of the district is 938 square kilometers (362 sq mi). Its administrative center is the rural locality of Znamenskoye. Population: 55,782 (2010 Census); 51,755 ; 35,742 (1989 Soviet census). The population of Znamenskoye accounts for 18.4% of the district's total population.

Kildinstroy is an urban locality in Kolsky District of Murmansk Oblast, Russia, located on the Kola Peninsula on the lower Kola River, 9 kilometers (5.6 mi) south of Murmansk. Population: 2,063 (2010 Census); 2,861 ; 3,731.

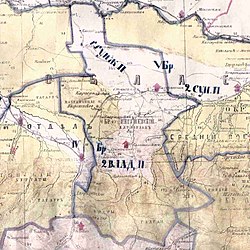
The Orstkhoy, historically commonly known under their exonyms: Karabulaks, Balsu, Baloy, are a historical ethnoterritorial society among the Chechen and Ingush peoples. Their homeland is in the upper reaches of the Assa and Fortanga rivers in the historical region of Orstkhoy-Mokhk. In the tradition of the Chechen ethno-hierarchy, it is considered one of the nine historical Chechen tukkhums, in the Ingush tradition as one of the seven historical Ingush shahars.
Galashki is a rural locality in Sunzhensky District of the Republic of Ingushetia, Russia, located on the left bank of the Sunzha River near the border with the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania. Its population was about 9,000 people in 2009. Galashki forms the municipality of the rural settlement of Galashki as the only settlement in its composition.

Sernovodskoye is a rural locality in Sernovodsky District, Chechnya. Population: 10,805 (2010 Census); 9,860 (2002 Census); The republican balneological resort "Sernovodsk-Kavkazsky" is located in the village.
Galanchozh, formerly Akhbosoy, is a non-residential rural locality in Urus-Martanovsky District of the Republic of Chechnya, Russia.
Bamut is a non-residential rural locality in Sernovodsky District of the Republic of Chechnya, Russia. From 1922 to 1934, Bamut was a part of the Ingush Autonomous Oblast.

Shalazhi is a rural locality in the Urus-Martanovsky District, the Chechen Republic, Russia.

The Feappii were an Ingush subgroup (society) that mostly inhabited the mountainous Fappi region of Ingushetia in the Caucasus. Historically, they bordered on the west with Dzherakh, on the east with Khamkhins, on the north with Nazranians, and in the south with Gudomakarians. The center of the society was the fortified village (aul) of Erzi or Metskhal.

The Dzherakh, also spelled Jerakh, historically also known as Erokhan people, were a historical Ingush ethnoterritorial society, today a tribal organization/clan (teip), that was formed in the Dzheyrakhin gorge, as well as in the area of the lower reaches of the Armkhi River and the upper reaches of the Terek River.

Plievo is a rural locality in Nazranovsky District of the Republic of Ingushetia, Russia. It forms the municipality of the rural settlement of Plievo as the only settlement in its composition.

Ingush okrug was a district (okrug) of the Terek Oblast of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. The area of the Ingushskiy okrug made up part of the North Caucasian Federal District of Russia.
Khay is a non-residential rural locality in Achkhoy-Martanovsky District of the Republic of Chechnya, Russia.

Meredzhi is a non-residential rural locality in Galanchozhsky District of the Republic of Chechnya, Russia.

Metskhal is an abandoned aul in the Dzheyrakhsky District of Ingushetia. It is part of the rural settlement of Lyazhgi.

Guli or Khuli is a rural locality in Dzheyrakhsky District of the Republic of Ingushetia, Russia. It forms the municipality of the rural settlement of Guli as its administrative center. Guli is the ancestral village of Ingush clan (teip) Hulakhoy.

Erzi is a medieval village (aul) in the Dzheyrakhsky District of Ingushetia. It is part of the rural settlement of Olgeti. The entire territory of the settlement is included in the Dzheyrakh-Assa State Historical-Architectural and Natural Museum-Reserve and is under state protection.