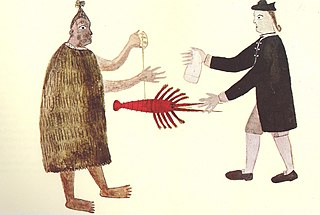
The Treaty of Waitangi, sometimes referred to as Te Tiriti, is a document of central importance to the history of New Zealand, its constitution, and its national mythos. It has played a major role in the treatment of the Māori people in New Zealand by successive governments and the wider population, something that has been especially prominent from the late 20th century. The treaty document is an agreement, not a treaty as recognised in international law. It was first signed on 6 February 1840 by Captain William Hobson as consul for the British Crown and by Māori chiefs from the North Island of New Zealand. The treaty's quasi-legal status satisfies the demands of biculturalism in contemporary New Zealand society. In general terms, it is interpreted today as having established a partnership between equals in a way the Crown likely did not intend it to in 1840. Specifically, the treaty is seen, first, as entitling Māori to enjoyment of land and of natural resources and, if that right were ever breached, to restitution. Second, the treaty's quasi-legal status has clouded the question of whether Māori had ceded sovereignty to the Crown in 1840, and if so, whether such sovereignty remains intact.

Captain William Hobson was an Anglo-Irish officer in the British Royal Navy, who served as the first Governor of New Zealand. He was a co-author of the Treaty of Waitangi.

George Eden, 1st Earl of Auckland, was an English Whig politician and colonial administrator. He was thrice First Lord of the Admiralty and also served as Governor-General of India between 1836 and 1842. The province of Auckland, which includes the present regions of Northland, Auckland, Waikato, Bay of Plenty and Gisborne along with the city of Auckland, in New Zealand, was named after him.

Waitangi Day, the national day of New Zealand, marks the anniversary of the initial signing—on 6 February 1840—of the Treaty of Waitangi. The Treaty of Waitangi was an agreement towards British sovereignty by representatives of the Crown and indigenous Māori chiefs, and so is regarded by many as the founding document of the nation.

The provinces of the Colony of New Zealand existed as a form of sub-national government. Initially established in 1846 when New Zealand was a Crown colony without responsible government, two provinces were first created. Each province had its own legislative council and governor. With the passing of the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852 the provinces were recreated around the six planned settlements or "colonies". By 1873 the number of provinces had increased to nine, but they had become less isolated from each other and demands for centralised government arose. In 1875 the New Zealand Parliament decided to abolish the provincial governments, and they came to an end in November 1876. They were superseded by counties, which were later replaced by territorial authorities.
James Busby was the British Resident in New Zealand from 1833 to 1840. He was involved in drafting the 1835 Declaration of the Independence of New Zealand and the 1840 Treaty of Waitangi. As British Resident, he acted as New Zealand's first jurist and the "originator of law in Aotearoa", to whom New Zealand "owes almost all of its underlying jurisprudence". Busby is regarded as the father of the Australian wine industry, as he brought the first collection of vine stock from Spain and France to Australia.

The Treaty House at Waitangi in Northland, New Zealand, is the former house of the British Resident in New Zealand, James Busby. The Treaty of Waitangi, the document that established the British Colony of New Zealand, was signed in the grounds of the Treaty House on 6 February 1840.

Waitangi is a locality on the north side of the Waitangi River in the Bay of Islands, 60 kilometres north of Whangārei, on the North Island of New Zealand. It is close to the town of Paihia, to which it is connected by a bridge near the mouth of the Waitangi River estuary. While Statistics New Zealand and NZ Post consider the southern boundary of Waitangi to be the river and estuary, with the area further south being part of Paihia, the area by Te Tī Bay, immediately south of the river, is sometimes referred to as part of Waitangi.

Public holidays in New Zealand consist of a variety of cultural, national, and religious holidays that are legislated in New Zealand. Workers can get a maximum of 12 public holidays and a minimum of 20 annual leave days a year.

Daniel Pollen was an Irish-New Zealand politician who became the ninth premier of New Zealand, serving from 6 July 1875 to 15 February 1876.
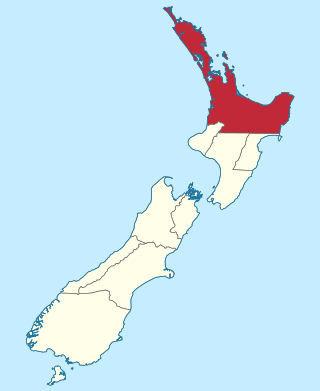
The Auckland Province was a province of New Zealand from 1853 until the abolition of provincial government in 1876.

The United Tribes of New Zealand was a confederation of Māori tribes based in the north of the North Island, existing legally from 1835 to 1840. It received diplomatic recognition from the United Kingdom, which shortly thereafter proclaimed the foundation of the Colony of New Zealand upon the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi.
The human history of the Auckland metropolitan area stretches from early Māori settlers in the 14th century to the first European explorers in the late 18th century, over a short stretch as the official capital of (European-settled) New Zealand in the middle of the 19th century to its current position as the fastest-growing and commercially dominating metropolis of the country.

There have been two Waitangi Day acts passed by the New Zealand Parliament: the Waitangi Day Act 1960 and the Waitangi Day Act 1976. Neither made 6 February a public holiday; this was done by the New Zealand Day Act 1973. The first Waitangi Day act acknowledged the Treaty of Waitangi. The second changed the name of the day from New Zealand Day back to Waitangi Day.
1840 is considered a watershed year in the history of New Zealand: The Treaty of Waitangi is signed, British sovereignty over New Zealand is proclaimed, organised European settlement begins, and Auckland and Wellington are both founded.

Wellington has been the capital of New Zealand since 1865. New Zealand's first capital city was Old Russell (Okiato) in 1840–41. Auckland was the second capital from 1841 until 1865, when Parliament was permanently moved to Wellington after an argument that persisted for a decade. As the members of parliament could not agree on the location of a more central capital, Wellington was decided on by three Australian commissioners.

The Colony of New Zealand was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1841 to 1907. British authority was vested in a governor. The colony had three successive capitals: Okiato in 1841; Auckland from 1841 to 1865; and Wellington from 1865. Following the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852, the colony became a Crown colony with its first elected parliament in 1853. Responsible self-government was established in 1856 with the governor being required to act on the advice of his ministers. In 1907, the colony became the Dominion of New Zealand within the British Empire.

Edward Marsh Williams was a missionary, interpreter, and judge who played a significant role in the British colonisation of New Zealand. He was born in Hampstead, Middlesex, the eldest son of Archdeacon Henry Williams and Marianne Williams.
James Coates was a prominent pioneer settler of Auckland, New Zealand. He was also a senior official within the administration of the newly-established colony of New Zealand, following the proclamation of sovereignty by William Hobson and the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in 1840.

George Cooper was a customs official and government administrator in Ireland, England, Australia and New Zealand. He was the first Colonial Treasurer and head of Customs of New Zealand.