Related Research Articles

Pitch is a perceptual property that allows sounds to be ordered on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre.
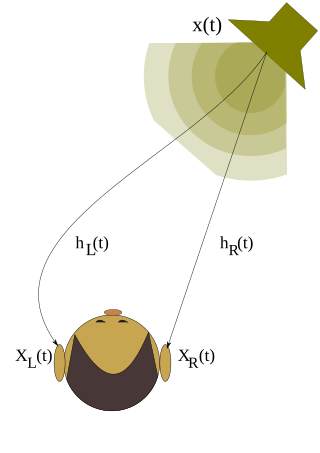
A head-related transfer function (HRTF) is a response that characterizes how an ear receives a sound from a point in space. As sound strikes the listener, the size and shape of the head, ears, ear canal, density of the head, size and shape of nasal and oral cavities, all transform the sound and affect how it is perceived, boosting some frequencies and attenuating others. Generally speaking, the HRTF boosts frequencies from 2–5 kHz with a primary resonance of +17 dB at 2,700 Hz. But the response curve is more complex than a single bump, affects a broad frequency spectrum, and varies significantly from person to person.
The absolute threshold of hearing (ATH), also known as the absolute hearing threshold or auditory threshold, is the minimum sound level of a pure tone that an average human ear with normal hearing can hear with no other sound present. The absolute threshold relates to the sound that can just be heard by the organism. The absolute threshold is not a discrete point and is therefore classed as the point at which a sound elicits a response a specified percentage of the time.
Psychophysics quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimuli and the sensations and perceptions they produce. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual processes by studying the effect on a subject's experience or behaviour of systematically varying the properties of a stimulus along one or more physical dimensions".

In acoustics, loudness is the subjective perception of sound pressure. More formally, it is defined as the "attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud". The relation of physical attributes of sound to perceived loudness consists of physical, physiological and psychological components. The study of apparent loudness is included in the topic of psychoacoustics and employs methods of psychophysics.
The precedence effect or law of the first wavefront is a binaural psychoacoustical effect concerning sound reflection and the perception of echoes. When two versions of the same sound presented are separated by a sufficiently short time delay, listeners perceive a single auditory event; its perceived spatial location is dominated by the location of the first-arriving sound. The lagging sound does also affect the perceived location; however, its effect is mostly suppressed by the first-arriving sound.
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance.

Audiometry is a branch of audiology and the science of measuring hearing acuity for variations in sound intensity and pitch and for tonal purity, involving thresholds and differing frequencies. Typically, audiometric tests determine a subject's hearing levels with the help of an audiometer, but may also measure ability to discriminate between different sound intensities, recognize pitch, or distinguish speech from background noise. Acoustic reflex and otoacoustic emissions may also be measured. Results of audiometric tests are used to diagnose hearing loss or diseases of the ear, and often make use of an audiogram.
Auditory imagery is a form of mental imagery that is used to organize and analyze sounds when there is no external auditory stimulus present. This form of imagery is broken up into a couple of auditory modalities such as verbal imagery or musical imagery. This modality of mental imagery differs from other sensory images such as motor imagery or visual imagery. The vividness and detail of auditory imagery can vary from person to person depending on their background and condition of their brain. Through all of the research developed to understand auditory imagery behavioral neuroscientists have found that the auditory images developed in subjects' minds are generated in real time and consist of fairly precise information about quantifiable auditory properties as well as melodic and harmonic relationships. These studies have been able to recently gain confirmation and recognition due to the arrival of Positron emission tomography and fMRI scans that can confirm a physiological and psychological correlation.
In audiology and psychoacoustics the concept of critical bands, introduced by Harvey Fletcher in 1933 and refined in 1940, describes the frequency bandwidth of the "auditory filter" created by the cochlea, the sense organ of hearing within the inner ear. Roughly, the critical band is the band of audio frequencies within which a second tone will interfere with the perception of the first tone by auditory masking.

Hearing range describes the frequency range that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels. The human range is commonly given as 20 to 20,000 Hz, although there is considerable variation between individuals, especially at high frequencies, and a gradual loss of sensitivity to higher frequencies with age is considered normal. Sensitivity also varies with frequency, as shown by equal-loudness contours. Routine investigation for hearing loss usually involves an audiogram which shows threshold levels relative to a normal.
Perceptual Evaluation of Audio Quality (PEAQ) is a standardized algorithm for objectively measuring perceived audio quality, developed in 1994–1998 by a joint venture of experts within Task Group 6Q of the International Telecommunication Union's Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R). It was originally released as ITU-R Recommendation BS.1387 in 1998 and last updated in 2023. It utilizes software to simulate perceptual properties of the human ear and then integrates multiple model output variables into a single metric.
In audio signal processing, auditory masking occurs when the perception of one sound is affected by the presence of another sound.

In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of 17 meters (56 ft) to 1.7 centimeters (0.67 in). Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound. Different animal species have varying hearing ranges, allowing some to even hear ultrasounds.

William M. Hartmann is a noted physicist, psychoacoustician, author, and former president of the Acoustical Society of America. His major contributions in psychoacoustics are in pitch perception, binaural hearing, and sound localization. Working with junior colleagues, he discovered several major pitch effects: the binaural edge pitch, the binaural coherence edge pitch, the pitch shifts of mistuned harmonics, and the harmonic unmasking effect. His textbook, Signals, Sound and Sensation, is widely used in courses on psychoacoustics. He is currently a professor of physics at Michigan State University.

Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science.
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of the perception of sound by the human auditory system. It is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound including noise, speech, and music. Psychoacoustics is an interdisciplinary field including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science.
Ernst Terhardt was a German engineer and psychoacoustician who made significant contributions in diverse areas of audio communication including pitch perception, music cognition, and Fourier transformation. He was professor in the area of acoustic communication at the Institute of Electroacoustics, Technical University of Munich, Germany. Terhardt died on 26 December 2024, at the age of 90.
Temporal envelope (ENV) and temporal fine structure (TFS) are changes in the amplitude and frequency of sound perceived by humans over time. These temporal changes are responsible for several aspects of auditory perception, including loudness, pitch and timbre perception and spatial hearing.
Auditory science or hearing science is a field of research and education concerning the perception of sounds by humans, animals, or machines. It is a heavily interdisciplinary field at the crossroad between acoustics, neuroscience, and psychology. It is often related to one or many of these other fields: psychophysics, psychoacoustics, audiology, physiology, otorhinolaryngology, speech science, automatic speech recognition, music psychology, linguistics, and psycholinguistics.
References
- ↑ Blauert, J.: Spatial hearing - the psychophysics of human sound localization; MIT Press; Cambridge, Massachusetts (1983), chapter 1