Related Research Articles

Laemanctus is a genus of lizards in the family Corytophanidae. Species in the genus Laemanctus are commonly referred to as conehead lizards or casquehead iguanas. The genus is endemic to Central America.

Compsognathus is a genus of small, bipedal, carnivorous theropod dinosaur. Members of its single species Compsognathus longipes could grow to around the size of a turkey. They lived about 150 million years ago, during the Tithonian age of the late Jurassic period, in what is now Europe. Paleontologists have found two well-preserved fossils, one in Germany in the 1850s and the second in France more than a century later. Today, C. longipes is the only recognized species, although the larger specimen discovered in France in the 1970s was once thought to belong to a separate species and named C. corallestris.

The bushwren, bush wren, or mātuhituhi in Māori, was a very small and almost flightless bird that was endemic to New Zealand. It had three subspecies on each of the major islands of New Zealand, the North Island, South Island, and Stewart Island and nearby smaller islands. The species disappeared gradually after the introduction of invasive mammalian predators, last being seen on the North Island in 1955 and the South Island in 1968. Attempts were made to save the remaining population on small islands off Stewart Island, but they ultimately failed with the death of the last remaining known birds in 1972.

The white-bellied antbird, is a passerine bird which breeds in the tropical New World from Panama to northern Brazil and in Trinidad. It is also called Swainson's antcatcher after William John Swainson, who first described it scientifically. The genus is monotypic.

Bryan Lee Cranston is an American actor, director, producer, and screenwriter. He is best known for his roles as Walter White in the AMC crime drama series Breaking Bad (2008–2013), Hal in the Fox sitcom Malcolm in the Middle (2000–2006), Tim Whatley in the NBC sitcom Seinfeld (1994–1997), and Vince Lonigan in the Prime Video crime drama series Sneaky Pete (2015–2019).
Herbstosaurus is the name given to a genus of pterosaurs that lived during the Late Jurassic period, in what is now Argentina. In 1969 Argentine paleobotanist Rafael Herbst in the province Neuquén at Picun Leufú dug up a piece of sandstone holding a number of disarticulated bones of a small reptile. At the time it was assumed the rock dated to the Middle Jurassic (Callovian), about 163 million years ago.
Cavillator is a monotypic genus of Zimbabwean jumping spiders containing the single species, Cavillator longipes. It was first described by Wanda Wesołowska in 2000, and is only found in Zimbabwe.

Potoroo is a common name for species of Potorous, a genus of smaller marsupials. They are allied to the Macropodiformes, the suborder of kangaroo, wallaby, and other rat-kangaroo genera. All three extant species are threatened by ecological changes since the colonisation of Australia, especially the long-footed Potorous longipes (Endangered) and P. gilbertii. The broad-faced P. platyops disappeared after its first description in the nineteenth century. The main threats are predation by introduced species and habitat loss.
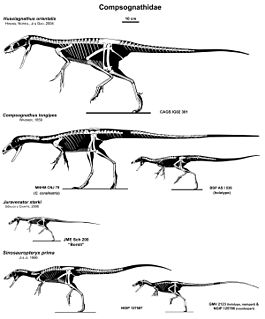
Compsognathidae is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Compsognathids were small carnivores, generally conservative in form, hailing from the Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. The bird-like features of these species, along with other dinosaurs such as Archaeopteryx inspired the idea for the connection between dinosaur reptiles and modern-day avian species. Compsognathid fossils preserve diverse integument — skin impressions are known from four genera commonly placed in the group, Compsognathus, Sinosauropteryx, Sinocalliopteryx, and Juravenator. While the latter three show evidence of a covering of some of the earliest primitive feathers over much of the body, Juravenator and Compsognathus also show evidence of scales on the tail or hind legs. Ubirajara, described in 2020, had elaborate integumentary structures on its back and shoulders superficially similar to the display feathers of a standardwing bird-of-paradise, and unlike any other non-avian dinosaur currently described.

Long-footed potoroo – Potorous longipes – is a small marsupial found in southeastern Australia, restricted to an area around the coastal border between New South Wales and Victoria. It was discovered in 1967 when an adult male was caught in a dog trap in the forest southwest of Bonang, Victoria. It is classified as vulnerable.

The Savanna swamp shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to Nigeria. Its natural habitat is swamps. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Lineodes is a genus of snout moths of the subfamily Spilomelinae in the family Crambidae. The genus was described by Achille Guenée in 1854, with Lineodes hieroglyphalis as the type species.
Erythrochampsa is an extinct genus of protosuchian crocodylomorph. Fossils have been found from the Red Beds of the Stormberg Group, the youngest group of strata from the Karoo Supergroup outcropping in South Africa.
Notochampsa is an extinct genus of protosuchian crocodylomorph. Fossils have been found from the lower Clarens Formation of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa, dating back to the Early Jurassic.

Stegomosuchus is an extinct genus of small protosuchian crocodylomorph. It is known from a single incomplete specimen discovered in the late 19th century in Lower Jurassic rocks of south-central Massachusetts, United States. It was originally thought to be a species of Stegomus, an aetosaur, but was eventually shown to be related to Protosuchus and thus closer to the ancestry of crocodilians. Stegomosuchus is also regarded as a candidate for the maker of at least some of the tracks named Batrachopus in the Connecticut River Valley.

Psathyrella longipes is a species of agaric fungus in the family Psathyrellaceae. It was originally described as Hypholoma longipes by Charles Horton Peck in 1895; Alexander H. Smith transferred it to Psathyrella in 1941.

Attopsis is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Formicinae. While formerly containing a number of species, the genus is currently monotypic; the type species, Attopsis longipennis, is known from a single Early Miocene fossil found in what is now Croatia.

Panulirus longipes, the longlegged spiny lobster, is a species of spiny lobster that lives on shallow rocky and coral reefs in the tropical Indo-Pacific region. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Xylaria longipes, commonly known as dead moll's fingers, is a species of fungus in the family Xylariaceae.
Hologymnosus longipes, the sidespot longface wrasse or the plain slender wrasse, is a species of marine ray-finned fish from the family Labridae, the wrasses. It occurs in the western Pacific Ocean.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Cranston, Peter S. (2000). "Austrobrillia Freeman: immature stages, and new species from the Neotropics" (PDF). Spixiana. 23 (2): 1–8. Retrieved 7 February 2013.[ permanent dead link ]