
A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and, in many instances, additional gear ranges.

A limited-slip differential (LSD) is a type of differential gear train that allows its two output shafts to rotate at different speeds but limits the maximum difference between the two shafts. Limited-slip differentials are often known by the generic trademark Positraction, a brand name owned by General Motors and originally used for its Chevrolet branded vehicles.

Quattro is the trademark used by the automotive brand Audi to indicate that all-wheel drive (AWD) technologies or systems are used on specific models of its automobiles.

In automotive design, a front-engine, front-wheel-drive (FWD) layout, or FF layout, places both the internal combustion engine and driven roadwheels at the front of the vehicle.

A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a component for transmitting mechanical power, torque, and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them.

BMW M GmbH, formerly known as BMW Motorsport GmbH, is a subsidiary of BMW AG that manufactures performance cars.
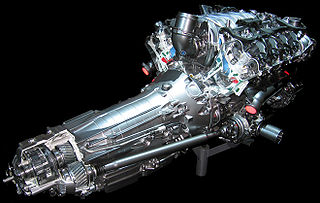
4Matic is the marketing name of an all-wheel drive system developed by Mercedes-Benz. It is designed to increase traction in slippery conditions. With the introduction of the 2017 E 63 S sedan, Mercedes-AMG announced a performance-oriented variant of the system called AMG Performance 4MATIC+.

A viscous coupling is a mechanical device which transfers torque and rotation by the medium of a viscous fluid.
ATTESA is a four-wheel drive system used in some automobiles produced by the Japanese automaker Nissan, including some models under its luxury marque Infiniti.
Jeep uses a variety of four-wheel drive systems on their vehicles. These range from basic part-time systems that require the driver to move a control lever to send power to four wheels, to permanent four-wheel systems that monitor and sense traction needs at all four wheels automatically under all conditions.

All-Trac was a proprietary full-time four-wheel drive system used on a variety of Toyota badged models and the nameplate was used from 1988 to 2000. It was considered a revolutionary advance for four wheel drive automobiles into the mainstream consumer market and its electronic/vacuum controlled locking center differential was rare in a passenger car. The system originated in Japan under the GT-Four name in 1986, but was not released in the U.S. until 1988 under the All-Trac name.

The BMW X6 is a mid-size luxury crossover SUV by German automaker BMW. The BMW X6 is the originator of the sports activity coupé (SAC), referencing its sloping rear roof design. It combines the attributes of an SUV with the stance of a coupé. It is built in BMW's North American plant in Greer, South Carolina alongside the BMW X5, whose platform it shares. Prior to the release of the X7, the X6 was considered a flagship SUV for BMW.
ControlTrac four-wheel drive is the brand name of a selectable automatic full-time four-wheel drive system offered by Ford Motor Company. The four-wheel drive system was designed and developed at BorgWarner under its TorqTransfer Systems division in the mid 1980s. BorgWarner calls the system Torque-On-Demand (TOD). ControlTrac was the first automatic system to use software control and no planetary or bevel geared center differential. Instead of a planetary or bevel geared center differential, the system uses a variable intelligent locking center multi-disc differential.
All Wheel Control (AWC) is the brand name of a four-wheel drive (4WD) system developed by Mitsubishi Motors. The system was first incorporated in the 2001 Lancer Evolution VII. Subsequent developments have led to S-AWC (Super All Wheel Control), developed specifically for the new 2007 Lancer Evolution. The system is referred by the company as its unique 4-wheel drive technology umbrella, cultivated through its motor sports activities and long history in rallying spanning almost half a century.

The BMW X5 (F15) is the third generation of the X5 series of mid-size luxury crossover SUVs manufactured and marketed worldwide by BMW since 2013. The car was unveiled at the 2013 Frankfurt International Motor Show. Early X5 models include xDrive50i, xDrive30d, M50d. BMW xDrive40d, xDrive35i, xDrive25d, sDrive25d were to be added in December 2013.

A drivetrain or transmission system, is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components of a motor vehicle that deliver power to the drive wheels. This excludes the engine or motor that generates the power. In marine applications, the drive shaft will drive a propeller, thruster, or waterjet rather than a drive axle, while the actual engine might be similar to an automotive engine. Other machinery, equipment and vehicles may also use a drivetrain to deliver power from the engine(s) to the driven components.

The Symmetrical All-Wheel Drive is a full-time four-wheel drive system developed by the Japanese automobile manufacturer Subaru. The system consists of a longitudinally mounted boxer engine coupled to a symmetrical drivetrain with equal length half-axles. The combination of the symmetrical layout with a flat engine and a transmission balanced over the front axle provides optimum weight distribution with low center of gravity, improving the steering characteristics of the vehicle. Ever since 1986, most of the Subaru models sold in the international market are equipped with the SAWD system by default, with the rear wheel drive BRZ and kei cars as the exceptions.

An all-wheel drive vehicle is one with a powertrain capable of providing power to all its wheels, whether full-time or on-demand.

The G05 BMW X5 is a mid-size luxury SUV produced by German automaker BMW. It is the fourth and current generation of the BMW X5. It was launched in 2018 as the successor to the F15 X5. Sales of the X5 started in November 2018. The X5 M and X5 M Competition (F95) performance models were revealed on 1 October 2019.

The BMW X5 M (F85) is a mid-size luxury SUV that is based on the BMW X5 (F15) which has been built by BMW since 2014. Unlike the BMW X5 M50d the X5 M is a full BMW M series car that has the M Powered engine. In comparison, the M50d is classified as an "M Performance Car" which means it isn't a full M car unlike the BMW M3 or the BMW M5.















