
Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a Babesia or Theileria, in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via tick bite is most common in the Northeastern and Midwestern United States and parts of Europe, and sporadic throughout the rest of the world. It occurs in warm weather. People can get infected with Babesia parasites by the bite of an infected tick, by getting a blood transfusion from an infected donor of blood products, or by congenital transmission . Ticks transmit the human strain of babesiosis, so it often presents with other tick-borne illnesses such as Lyme disease. After trypanosomes, Babesia is thought to be the second-most common blood parasite of mammals. They can have major adverse effects on the health of domestic animals in areas without severe winters. In cattle, the disease is known as Texas cattle fever or redwater.

Stefan Żeromski was a Polish novelist and dramatist belonging to the Young Poland movement at the turn of the 20th century. He was called the "conscience of Polish literature".

Florian Witold Znaniecki was a Polish and American philosopher and sociologist who taught and wrote in Poland and in the United States. Over the course of his work, he shifted his focus from philosophy to sociology. He remains a major figure in the history of Polish and American sociology; the founder of Polish academic sociology, and of an entire school of thought in sociology. He won international renown as co-author, with William I. Thomas, of the study, The Polish Peasant in Europe and America (1918–1920), which is considered the foundation of modern empirical sociology. He also made major contributions to sociological theory, introducing terms such as humanistic coefficient and culturalism.

Władysław Tatarkiewicz was a Polish philosopher, historian of philosophy, historian of art, esthetician, and ethicist.

The Warsaw Corps of Cadets was the first state school in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Podaga is a Polabian deity who had his statue in a temple in Plön. Mentioned only in Helmold's Chronicle, which does not give a depiction or function of the deity.
Among the Slavs there are many modes of idolatry and not all of them coincide with the same kind of superstition. Some create in their temples statues of fantastic forms, such as the idol of Plön, who is called Podaga, others live in forests and groves, as is the case of the god Prone of Oldenburg, of whom no image exists.

Babesia, also called Nuttallia, is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by the Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888, over 100 species of Babesia have since been identified.

Jerzy Ryszard Szacki was a Polish sociologist and historian of ideas. From 1973 he was a professor at the University of Warsaw, and in 1991 became a member of the Polish Academy of Sciences. He is considered one of the most prominent representatives of the Warsaw School of the History of Ideas.
Antonina Kłoskowska, was a Polish sociologist. In her work, she focused on the sociology of culture. Kłoskowska taught at the universities Łódź (1966-1977) and Warsaw (1977-1990). She was a member of the Polish Academy of Sciences (PAN) since 1973 and worked in its Institute for Political Studies since 1990. Since 1983, she edited the journal Kultura i Społeczeństwo. From 1989 until 1993, she was the president of the Polish Sociological Association. With Władysław Markiewicz and others, Kłoskowska co-edited a multi-volume Polish complete edition of Bronisław Malinowski's works which appeared 1984-1990.

Maria Ossowska was a Polish sociologist and social philosopher.

Czesław Zakaszewski was a Polish hydro-technician and meliorator. Professor of the Warsaw University of Technology, member of the Warsaw Scientific Society.

Tomasz Marceli Szarota is a Polish historian and publicist. As a historian, his areas of expertise relate to history of World War II, and everyday life in occupied Poland, in particular, in occupied Warsaw and other occupied major European cities.

Adam Mahrburg was a Polish philosopher—the outstanding philosophical mind of Poland's Positivist period.
Bellona Publishing House is a private publishing house based in Warsaw, Poland. It was created in 1990 from restructuring of the state-run Wydawnictwo MON. It specialises in books on military history. Among the authors who published with Bellona are academic historians Henryk Samsonowicz, Lech Wyszczelski, Leszek Moczulski, and Tadeusz Panecki as well as journalists and writers like Krzysztof Daukszewicz, Grzegorz Miecugow, Magdalena Kozak. Bellona issues more than 300 books yearly. It is also the publisher of Mówią Wieki, a monthly historical magazine established in 1958.

Syngonium podophyllum is a species of aroid that is a popular houseplant. Common names include: arrowhead plant, arrowhead vine, arrowhead philodendron, goosefoot, nephthytis, African evergreen, and American evergreen. The species is native to a wide region of Latin America from Mexico through Bolivia, and naturalized in the West Indies, Florida, Texas, Hawaii, and other places.
Babesia bigemina is a species of alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa and the family Babesiidae, a type of protozoan parasite. In cattle, it causes babesiosis, also called "Texas fever". Its length is 4–5 μm and its width is 2–3 μm. Usually, it has an oval shape. In blood cells, it is located midsagittally and can reach up to two-thirds of the diameter of the blood cell in size. It is transmitted by Boophilus ticks which are prevalent in the tropics. The genome for B. bigemina is incomplete and unassembled.
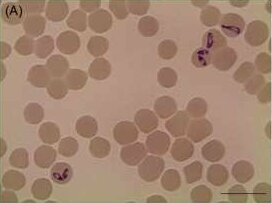
Babesia caballi is a species belonging to Alveolata and the family Babesiidae. In horses, it causes the babesiosis disease, called "equine babesiosis". Its length is 2.5-5 μm, while its width is 2 μm. It is usually oval-shaped. Its vector and second feeders are ticks. In North America B. caballi is being spread by Dermacentor nitens.

Janina Oyrzanowska-Poplewska was a Polish academic and veterinarian. A professor at the Warsaw University of Life Sciences, she specialized in epizootiology but her main area of research concerned viral diseases of canines, which led to the development of the first vaccine for canine distemper in Poland.

The Gdańsk Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) with capital in Gdańsk, that was located in the region of Pomerelia. It existed from 1945 to 1975. Until 28 June 1945, it remained under the administration of the Provisional Government of the Republic of Poland, which then was replaced by the Provisional Government of National Unity. On, 19 February 1947, the provisional government was replaced by the Polish People's Republic. It was established on 7 April 1945, from the parts of the territories of the Pomeranian Voivodeship, and the Masurian District, Poland. The voivodeship ceased to exist on 31 May 1975, when it was partitioned by then-established voivodeships of Elbląg, Gdańsk, and Słupsk.

Pleurotus calyptratus, is a species of fungus from the family Pleurotaceae. It has a distinctive delicate veil on young fruiting bodies. Phylogenetic research has shown that while it belongs to P. djamor-cornucopiae clade, it forms its own intersterility group.















