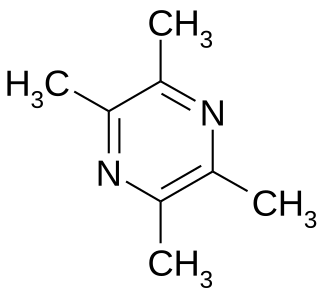
Bacillus cereus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, aerobic, facultatively anaerobic, motile, beta-hemolytic bacterium commonly found in soil and food. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals. It is the cause of "fried rice syndrome", as the bacteria are classically contracted from fried rice dishes that have been sitting at room temperature for hours. B. cereus bacteria are facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus Bacillus, can produce protective endospores. Its virulence factors include cereolysin and phospholipase C.

An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside of that cell. Exoenzymes are produced by both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and have been shown to be a crucial component of many biological processes. Most often these enzymes are involved in the breakdown of larger macromolecules. The breakdown of these larger macromolecules is critical for allowing their constituents to pass through the cell membrane and enter into the cell. For humans and other complex organisms, this process is best characterized by the digestive system which breaks down solid food via exoenzymes. The small molecules, generated by the exoenzyme activity, enter into cells and are utilized for various cellular functions. Bacteria and fungi also produce exoenzymes to digest nutrients in their environment, and these organisms can be used to conduct laboratory assays to identify the presence and function of such exoenzymes. Some pathogenic species also use exoenzymes as virulence factors to assist in the spread of these disease causing microorganisms. In addition to the integral roles in biological systems, different classes of microbial exoenzymes have been used by humans since pre-historic times for such diverse purposes as food production, biofuels, textile production and in the paper industry. Another important role that microbial exoenzymes serve is in the natural ecology and bioremediation of terrestrial and marine environments.

Bacillus subtilis, known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants and humans. A member of the genus Bacillus, B. subtilis is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. B. subtilis has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. B. subtilis is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies.
Metabolic engineering is the practice of optimizing genetic and regulatory processes within cells to increase the cells' production of a certain substance. These processes are chemical networks that use a series of biochemical reactions and enzymes that allow cells to convert raw materials into molecules necessary for the cell’s survival. Metabolic engineering specifically seeks to mathematically model these networks, calculate a yield of useful products, and pin point parts of the network that constrain the production of these products. Genetic engineering techniques can then be used to modify the network in order to relieve these constraints. Once again this modified network can be modeled to calculate the new product yield.

Brown rice (malt) syrup, also known as rice syrup or rice malt, is a sweetener which is rich in compounds categorized as sugars and is derived by culturing cooked rice starch with saccharifying enzymes to break down the starches, followed by straining off the liquid and reducing it by evaporative heating until the desired consistency is reached. The enzymes used in the saccharification step are supplied by an addition of sprouted barley grains to the rice starch or by adding bacterial- or fungal-derived purified enzyme isolates.

Clostridium acetobutylicum, ATCC 824, is a commercially valuable bacterium sometimes called the "Weizmann Organism", after Jewish-Russian-born Chaim Weizmann. A senior lecturer at the University of Manchester, England, he used them in 1916 as a bio-chemical tool to produce at the same time, jointly, acetone, ethanol, and butanol from starch. The method has been described since as the ABE process,, yielding 3 parts of acetone, 6 of butanol, and 1 of ethanol. Acetone was used in the important wartime task of casting cordite. The alcohols were used to produce vehicle fuels and synthetic rubber.
Fed-batch culture is, in the broadest sense, defined as an operational technique in biotechnological processes where one or more nutrients (substrates) are fed (supplied) to the bioreactor during cultivation and in which the product(s) remain in the bioreactor until the end of the run. An alternative description of the method is that of a culture in which "a base medium supports initial cell culture and a feed medium is added to prevent nutrient depletion". It is also a type of semi-batch culture. In some cases, all the nutrients are fed into the bioreactor. The advantage of the fed-batch culture is that one can control concentration of fed-substrate in the culture liquid at arbitrarily desired levels.
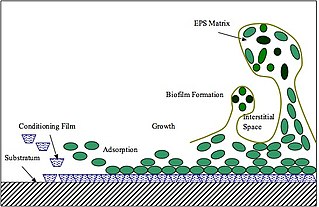
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physiochemical properties of a biofilm.

Glycerol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.6, also known as NAD+-linked glycerol dehydrogenase, glycerol: NAD+ 2-oxidoreductase, GDH, GlDH, GlyDH) is an enzyme in the oxidoreductase family that utilizes the NAD+ to catalyze the oxidation of glycerol to form glycerone (dihydroxyacetone).
Sakacins are bacteriocins produced by Lactobacillus sakei. They are often clustered with the other lactic acid bacteriocins. The best known sakacins are sakacin A, G, K, P, and Q. In particular, sakacin A and P have been well characterized.
Keratinases are proteolytic enzymes that digest keratin.
Pediococcus acidilactici is a species of Gram-positive cocci that is often found in pairs or tetrads. P. acidilactici is a homofermentative bacterium that can grow in a wide range of pH, temperature, and osmotic pressure, therefore being able to colonize the digestive tract. It has emerged as a potential probiotic that has shown promising results in animal and human experiments, though some of the results are limited. They are commonly found in fermented vegetables, fermented dairy products, and meat.

Biopreservation is the use of natural or controlled microbiota or antimicrobials as a way of preserving food and extending its shelf life. The biopreservation of food, especially utilizing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) that are inhibitory to food spoilage microbes, has been practiced since early ages, at first unconsciously but eventually with an increasingly robust scientific foundation. Beneficial bacteria or the fermentation products produced by these bacteria are used in biopreservation to control spoilage and render pathogens inactive in food. There are a various modes of action through which microorganisms can interfere with the growth of others such as organic acid production, resulting in a reduction of pH and the antimicrobial activity of the un-dissociated acid molecules, a wide variety of small inhibitory molecules including hydrogen peroxide, etc. It is a benign ecological approach which is gaining increasing attention.
Bacillus pumilus is a Gram-positive, aerobic, spore-forming bacillus commonly found in soil.
Lactobacillus sakei is a bacterium species in the genus Lactobacillus. It is a facultatively heterofermentative Lactobacillus species.

Neopullulanase is an enzyme of the alpha-amylase family with systematic name pullulan 4-D-glucanohydrolase (panose-forming). This enzyme principally catalyses the following chemical reaction by cleaving pullulan's alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds:
Streptomyces isolates have yielded the majority of human, animal, and agricultural antibiotics, as well as a number of fundamental chemotherapy medicines. Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus of actinobacteria, producing chemotherapy, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic drugs, and immunosuppressants. Streptomyces isolates are typically initiated with the aerial hyphal formation from the mycelium.
Lactobacillus fabifermentans is a member of the genus Lactobacillus, the most diverse genus among lactic acid bacteria (LAB), a group of Gram-positive bacteria that produce lactic acid as their major fermented end product and that are often involved in food fermentation. L. fabifermentans was proposed in 2009 as a new species, after the type strain LMG 24284T has been isolated from Ghanaian cocoa fermentation. Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence demonstrated that this species is a member of the Lactobacillus plantarum species group but further analysis demonstrated that it is possible to differentiate it from the nearest neighbors by means of DNA-DNA hybridization experiments, pheS sequence analysis, whole-cell protein electrophoresis, fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis and biochemical characterization.