
Negros Occidental, officially the Province of Negros Occidental, is a province in the Philippines located in the Negros Island Region. Its capital is the city of Bacolod, of which it is geographically situated and grouped under by the Philippine Statistics Authority, but remains politically independent from the provincial government and also one of the two regional centers in Negros Island Region. It occupies the northwestern half of the large island of Negros, and borders Negros Oriental, which comprises the southeastern half. Known as the "Sugarbowl of the Philippines", Negros Occidental produces more than half the nation's sugar output.

Bacolod, officially the City of Bacolod, is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Negros Island Region in the Philippines. With a total of 600,783 inhabitants as of the 2020 census, it is the most populous city in the Negros Island Region and the second most populous city in the entire Visayas after Cebu City.

Silay, officially the City of Silay, is a 3rd class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 130,478 people.

Talisay, officially the City of Talisay, is a fourth class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 108,909 people.

Aniceto Ledesma Lacson is a Filipino revolutionary general, sugar farmer, and businessman. He is known as the first and only president of the Negros Republic from 1898 to 1901, and for leading the Negros Revolution alongside Juan Araneta.

The Negros Revolution, commemorated and popularly known as the Fifth of November or Negros Day, was a political movement that in 1898 created a government on Negros Island in the Philippines, ending Spanish control of the island and paving the way for a republican government run by the Negrense natives. The newly established Negros Republic lasted for approximately three months. American forces landed on the island unopposed on February 2, 1899, ending the island's independence. Negros was then annexed to the Philippine Islands on 20 April 1901.

The MassKara Festival is an annual festival with highlights held every 4th Sunday of October in Bacolod, Philippines. The festival sites include the Bacolod Public Plaza, the Lacson Tourism Strip and the Bacolod City Government Center.

The Panaad sa Negros Festival, also called simply as the Panaad Festival, is a festival held annually during the month of April in Bacolod, the capital of Negros Occidental province in the Philippines. Panaad is the Hiligaynon word for "vow" or "promise" coming from the root-word saad; the festival is a form of thanksgiving to Divine Providence and commemoration of a vow in exchange for a good life. The celebration is held at the Panaad Park, which also houses the Panaad Stadium, and is participated in by the 13 cities and 19 towns of the province. For this reason, the province dubs it the "mother" of all its festivals.
The Bacolod Arts and Youth Sports Center is a multi-use gym located in Bacolod, fronting the Bacolod Public Plaza, in Negros Occidental, Philippines. It is used mostly for basketball, karatedo and boxing matches, and was used in events in the city like the MassKara Festival activities and other government related activities like seminars, business and political gatherings.

The Capitol Park and Lagoon is a provincial park located in Bacolod, Negros Occidental, in the Philippines. One of the features of the park are matching sculptures depicting a woman standing alongside a water buffalo and that of a man pulling another water buffalo. These sculptures are located at the northern and southern ends of the lagoon. These figures were executed by Italian sculpture Francesco Riccardo Monti who also did the sculptures of the Metropolitan Manila Theater and the University of the Philippines - Visayas Iloilo campus. Guillermo Tolentino also contributed as a sculptor of the figures.

The Fountain of Justice is a historic landmark in Bacolod, Negros Occidental, Philippines. It marks the location where the house of Jose Ruiz de Luzurriaga used to stand. It was in this house that the surrender of Bacolod by Spanish authorities to the Filipino forces of General Aniceto Lacson took place on November 6, 1898, during the Negros Revolution. Luzurriaga acted as mediator between the two belligerents. Colonel Isidro de Castro, Spanish governor of Negros, signed the surrender document on behalf of the Spanish forces. The landmark now lies in front of the old Bacolod City Hall.

Antonio Ledesma Jayme was a Filipino lawyer, revolutionary hero, Governor of Negros Occidental, and assemblyman, as well as a lawmaker and a revolutionary nation's founding father and a signatory to a nation-state's constitution.

Metro Bacolod is the 8th-most populous and the 6th-most densely populated metropolitan area out of the 12 metropolitan areas in the Philippines. This metropolitan area as defined by the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) has an estimated population of 840,170 inhabitants as of the 2020 official census by the Philippine Statistics Authority.

San Sebastian Cathedral is a late 19th-century Roman Catholic church in Bacolod, Negros Occidental in the Philippines. It is the seat of the Diocese of Bacolod.
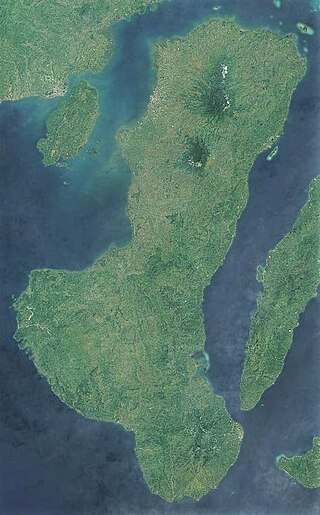
Negros is the fourth largest and third most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of 13,309 km2 (5,139 sq mi). The coastal zone of the southern part of Negros is identified as a site of highest marine biodiversity importance in the Coral Triangle.
MassKara Festival Queen is a local beauty pageant in Bacolod, Negros Occidental, Philippines. Begun in 1981, it is one of the highlights of a week-long celebration called the MassKara Festival.

The Negros Occidental Provincial Capitol is the seat of the provincial government of Negros Occidental located at Gatuslao St., Bacolod, Philippines. Within its complex is the Capitol Park and Lagoon.

The Paglaum Sports Complex is a sports venue in Bacolod, Philippines adjacent to the Negros Occidental High School. It was established during the administration of Governor Alfredo Montelibano Jr. in the 1970s. It hosted three editions of the Palarong Pambansa.

Mambukal Resort, officially the Township of Mambukal or simply known as Mambukal, is a resort township located within the boundaries of the municipality of Murcia, Negros Occidental. As a township, it is directly governed by the Provincial Government of Negros Occidental, which also manages Mambukal Mountain Resort in the 6-hectare townsite near Brgy. Minoyan. The resort is owned and managed by the Provincial Government of Negros Occidental under its Economic Enterprise Development Department.

Capitol Central, previously called the Negros Occidental Provincial Capitol Complex, is a government complex and mixed-use estate centered around the Negros Occidental Provincial Capitol, currently co-managed with Ayala Land. Certain portions are leased or sold to Ayala Land, as part of their industrial estate in Bacolod, Philippines.






















