
Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

Crappies are a genus, Pomoxis, of North American fresh water fish in the sunfish family Centrarchidae. Both species in this genus are popular pan fish.

Fish are gill-bearing aquatic craniate animals that lack limbs with digits. They form a sister group to the tunicates, together forming the olfactores. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Tetrapods emerged within lobe-finned fishes, so cladistically they are fish as well. However, traditionally fish are rendered paraphyletic by excluding the tetrapods. Because in this manner the term "fish" is defined negatively as a paraphyletic group, it is not considered a formal taxonomic grouping in systematic biology, unless it is used in the cladistic sense, including tetrapods. The traditional term pisces is considered a typological, but not a phylogenetic classification.

Raghunathpur subdivision is a subdivision of the Purulia district in the state of West Bengal, India.

Psilorhynchus balitora or Balitora minnow is a species of torrent minnow found in South Asia. It is found in the drainage basins of the Ganges and the Brahmaputra in eastern Nepal, northeast Bangladesh and adjacent West Bengal and northwest Assam. It can be found in hill streams and in rapids with substrates consisting of pebbles or sand, preferring hard substrates. It is exported as an aquarium fish.

Psilorhynchus is a genus of fish in the family Psilorhynchidae native to South Asia. This genus is the only member of its family. The members of Psilorhynchus are small benthic fishes which occur in rivers and streams with fast to swift currents, hence they are often referred to a torrent minnows. They are distributed in southern Asia, in the Indo-Burma region and the Western Ghats. The genus is the sister group to the family Cyprinidae, and with that family the Psilorhynchidae makes up the superfamily Cyprinoidea, with all the other cypriniform families in the superfamily Cobitoidea.
Hemimyzon nujiangensis is a species of hillstream loach endemic to Yunnan, China.
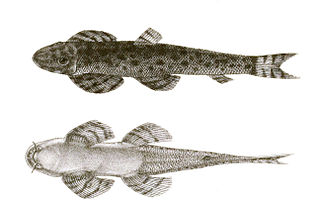
Balitora is a genus of fish in the family Balitoridae endemic to Asia.
Balitora annamitica is a species of hill-stream loach from the Mekong River Basin in Cambodia, Thailand, and Laos, and possibly Vietnam. It might be more than one species.
Hemimyzon elongata is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Hemimyzon. It has been found in the Mekong basin in Yunnan, China. It is a benthopelagic, freshwater fish.
Balitora lancangjiangensis is a species of hill-stream loach from the Mekong and Red River basins. Sources differ in distribution, but all list Yunnan (China) and Laos, and at least the International Union for Conservation of Nature also lists Vietnam, Burma, and Thailand.
Balitora meridionalis is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Balitora.
Hemimyzon tchangi is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Hemimyzon.

Gray's stone loach is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Balitora. It is endemic to India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Myanmar. It grows to a maximum length of 10.5 cm.
The Burmese stone loach is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Balitora. It occurs in the Irrawaddy, Salween, and Tenasserim basins in Burma, China, and Thailand. Its maximum length is 10 cm (3.9 in) TL.
Slender stone loach is a species of hill-stream loach. It is endemic to the Western Ghats, India, and known from Kerala and Karnataka, and possibly from Maharashtra. It inhabits torrential streams and can be found attached to bedrock, cobbles, and boulders.

Loaches are fishes of the superfamily Cobitoidea. They are freshwater, benthic (bottom-dwelling) fishes found in rivers and creeks throughout Eurasia and northern Africa. Loaches are among the most diverse groups of fishes; the 1249 known species of Cobitoidea comprise about 107 genera divided among nine families.
Balitora kwangsiensis is a species of hillstream loach found in Southeast Asia. It inhabits rapid-flowing rivers and grows to a total length of 12 cm (4.7 in).
Chooriyode is a village in the Palakkad district of Kerala State, South India. The headquarters is Mannarkkad Taluk. It is situated 35 km north-east of the district headquarters Palakkad, on the way to Kozhikode National Highway 213 (NH-213) and in the foothills of the Western Ghats. Silent Valley is only 45 km from Chooriyode.

Asansol Municipal Corporation (AMC) is the civic body that governs Asansol in Asansol Sadar subdivision of Paschim Bardhaman district, West Bengal, India.









