
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by possessing an army aviation component. Within a national military force, the word army may also mean a field army.

Hannibal was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
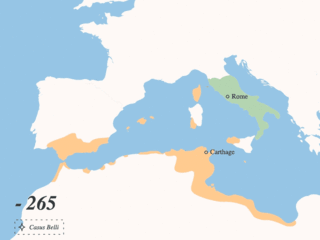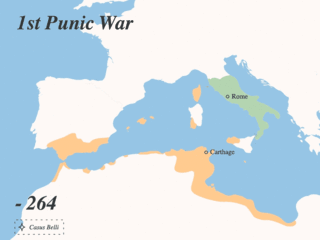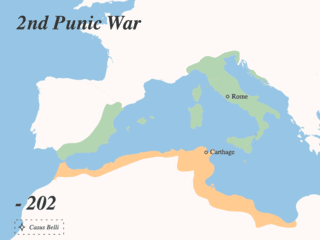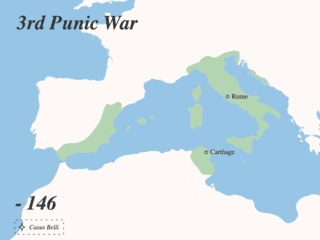
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage. Three wars took place, on both land and sea, across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.

The Roman legion, the largest military unit of the Roman army, comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic and 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire.

The Second Punic War was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war.

Trajan was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier-emperor who led the Roman Empire to its greatest territorial extent by the time of his death. He was given the title of Optimus by the Roman Senate.

The Visigoths were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied barbarian military group united under the command of Alaric I. Their exact origins are believed to have been diverse but they probably included many descendants of the Thervingi who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and Alaric's Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under Alaric, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sacked Rome in August 410.

Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics behind military tactics. Modern military engineering differs from civil engineering. In the 20th and 21st centuries, military engineering also includes CBRN defense and other engineering disciplines such as mechanical and electrical engineering techniques.

Gordian III was Roman emperor from 238 to 244. At the age of 13, he became the youngest sole emperor of the united Roman Empire. Gordian was the son of Antonia Gordiana and Junius Balbus, who died before 238. Antonia Gordiana was the daughter of Emperor Gordian I and younger sister of Emperor Gordian II. Very little is known of his early life before his acclamation. Gordian had assumed the name of his maternal grandfather in 238.

Constantine III was a common Roman soldier who was declared emperor in Roman Britain in 407 and established himself in Gaul. He was recognised as co-emperor of the Roman Empire from 409 until 411.

The Battle of Cannae was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by Hannibal, surrounded and practically annihilated a larger Roman and Italian army under the consuls Lucius Aemilius Paullus and Gaius Terentius Varro. It is regarded as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history and one of the worst defeats in Roman history, and it cemented Hannibal's reputation as one of antiquity's greatest tacticians.

The Praetorian Guard was an elite unit of the Imperial Roman army that served as personal bodyguards and intelligence agents for the Roman emperors.

The Roman legionary was a professional heavy infantryman of the Roman army. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the late Republic and Principate eras, alongside auxiliary and cavalry detachments. At its height, Roman legionaries were viewed as the foremost fighting force in the Roman world, with commentators such as Vegetius praising their fighting effectiveness centuries after the classical Roman legionary disappeared.

In modern historiography, ancient Rome encompasses the founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC, the Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic, Roman Empire, and the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD.

In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word castrum was a military-related term.

The Roman army was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom to the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, and its medieval continuation, the Eastern Roman Empire. It is thus a term that may span approximately 2,205 years, during which the Roman armed forces underwent numerous permutations in size, composition, organisation, equipment and tactics, while conserving a core of lasting traditions.

The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided between several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading barbarians outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the historiography of the ancient world and they inform much modern discourse on state failure.

Dux is Latin for "leader" and later for duke and its variant forms. During the Roman Republic and for the first centuries of the Roman Empire, dux could refer to anyone who commanded troops, both Roman generals and foreign leaders, but was not a formal military rank.

The Gauls were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period. Their homeland was known as Gaul (Gallia). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language.

Hannibal's crossing of the Alps in 218 BC was one of the major events of the Second Punic War, and one of the most celebrated achievements of any military force in ancient warfare.



















