Banks
The scheduled banks in Karnataka had total deposit of Rs. 1346.99 billion constituting 6.4% of the total deposits in scheduled banks in India as of March 2006. The credit given by these banks stood at Rs. 1034.55 billion, 6.8% of total credit given by scheduled banks. The per capita deposit stood at Rs. 23,976 and per capita credit at Rs. 18,415.
Canara Bank
Canara Bank was established in 1906 by Ammembai Subba Rao Pai established the Canara Bank Hindu Permanent Fund in Mangalore, India, on 1 July 1906.Who collected handful of rice from each household, pooled the rice and sold it and used the money earned for the bank's capital. [2] It has grown since then and now has 2542 branches in India and one overseas branch in London. [4] In the fiscal year 2005-06, Canara Bank became India's second-largest public sector bank in terms of advances and deposits. The bank changed its name to Canara Bank Limited in 1910 when it incorporated. [5] In 2002-03, the bank went in for its Initial Public Offer (IPO) and raised Rs.110 crores. [2] The India government holds a 73% stake in Canara Bank. [5]
Corporation Bank
Corporation Bank was founded by a group philanthropists headed by Khan Bahadur Haji Abdulla Haji Kasim Saheb Bahadur in the town of Udupi in 1906 under the name of "The Canara Banking Corporation (Udupi) Ltd". [6] In 1972, it got its present name of Corporation Bank and it was nationalised in 1980.
State Bank of Mysore
State Bank of Mysore (SBM) was established in 1913 under the name Bank of Mysore Ltd. [7] A banking committee headed by Sir M Visweswaraiah was formed under the patronage of the Mysore state which led to the formation of this bank. In 1960, this bank was made an associate bank of the State Bank of India which holds 92.33% of shares of SBM. As of Mar-2007, SBM has 644 branches and provides employment to 9604 employees. [7]
Karnataka Bank
The Karnataka Bank was founded on 18 February 1924 at Mangalore.The bank initially catered to people of Karnataka, has now spread its network of branches throughout the country.
Syndicate Bank
Syndicate Bank was established in the town of Udupi in 1925 under the name "Canara Industrial and Banking Syndicate Ltd" with a capital of Rs.8000/- by three people - Upendra Ananth Pai, Vaman Kudva, and Dr. T M A Pai. [8] The main objective for stating the bank was to extend financial assistance to the local weavers who were crippled by a crisis in the handloom industry. In 1963, it got its present name of Syndicate Bank. [8] Now the bank has 2125 branches.
Vysya Bank
Vysya Bank was established in 1930, in Bangalore (now Bengaluru) with the aim of offering banking services to those who were currently not privileged enough to do so. In 1948 Vysya Bank became a scheduled bank. On 7 October 2002 ING Group took over the Management of the Bank. But again ING Vysya Bank has merged with Kotak Mahindra Bank with effect from 1 April 2015 and the combined entity bears the name Kotak Mahindra Bank. [9] Before merger ING Vysya Bank had about 470 branches spread all over India.
Vijaya Bank
Vijaya Bank was established on 23 October 1931 at coastal city Mangalore by A. B. Shetty and others. The bank was established to help farming community. Later bank grew phenomenally under leadership of Mulki Sunder Ram Shetty during the 1960s. The Vijaya bank was nationalised in the 1980s by Government of India. The bank has presence in most of states of India. Later it was merged with Bank of Baroda along with Dena Bank on First April 2019.

Karnataka is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, and renamed Karnataka in 1973. The state is bordered by the Lakshadweep Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the southwest. With 61,130,704 inhabitants at the 2011 census, Karnataka is the eighth-largest state by population, comprising 31 districts. With 15,257,000 residents, the state capital Bangalore is the largest city of Karnataka.

Mangalore, officially known as Mangaluru, is a major industrial port city in the Indian state of Karnataka and on the west coast of India. It is located between the Laccadive Sea and the Western Ghats about 352 km (219 mi) west of Bangalore, the state capital, 14 km north of Karnataka–Kerala border and 297 km south of Goa. Mangalore is the state's only city to have all four modes of transport—air, road, rail and sea. The population of the urban agglomeration was 619,664 according to the 2011 national census of India. It is known for being one of the locations of the Indian strategic petroleum reserves.
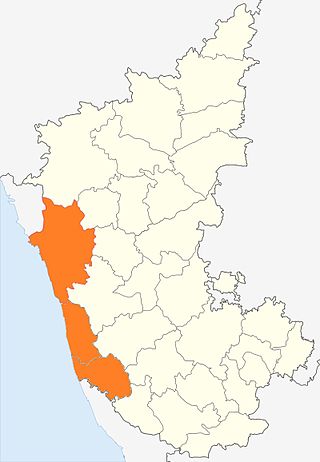
Kanara or Canara, also known as Karavali, is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern Konkan coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka. The subregion comprises three civil districts, namely: Uttara Kannada, Udupi, and Dakshina Kannada. Kasaragod was included prior to the States Reorganisation Act.

Dakshina Kannada district is located in the state of Karnataka in India, with its headquarters in the coastal city of Mangalore. The district covers an area nestled in between the Western Ghats to its east and the Arabian Sea to its west. Dakshina Kannada receives abundant rainfall during the Indian monsoon. It is bordered by Udupi district to the north, Chikmagalur district to the northeast, Hassan district to the east, Kodagu to the southeast and Kasaragod district of Kerala to the south. According to the 2011 census of India, Dakshina Kannada district had a population of 2,083,625. It is the only district in Karnataka state to have all modes of transport like road, rail, water and air due to the presence of a major hub, Mangalore. This financial district is also known as the Cradle of Indian banking.

Tulu Nadu or Tulunad, is a region and proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva', speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, are the preponderant ethnic group of this region. The proposed region, which once existed as the district South Canara, encompasses the undivided territory of the contemporary Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka and Kasargod of Kerala.

State Bank of Mysore was a Public Sector bank in India, with headquarters at Bangalore. It was one of the five associate banks of State Bank of India, all of which were consolidated with the State Bank of India with effect from 1 April 2017.

Modern banking in India originated in the mid of 18th century. Among the first banks were the Bank of Hindustan, which was established in 1770 and liquidated in 1829–32; and the General Bank of India, established in 1786 but failed in 1791.

Syndicate Bank was one of the oldest major commercial banks in India. It was founded by Upendra Ananth Pai, T. M. A. Pai and Vaman Srinivas Kudva. At the time of its establishment, the bank was known as Canara Industrial and Banking Syndicate Limited. The bank, along with 13 major commercial banks of India, was nationalised on 19 July 1969, by the government of India. It was headquartered in the university town of Manipal, India. On 1 April 2020, the bank was merged into Canara Bank.
Canara Bank is an Indian public sector bank based in Bangalore, India. Established in 1906 at Mangalore by Ammembal Subba Rao Pai. The bank was nationalized in 1969. Canara Bank also has offices in London, Dubai and New York.
Kotak Mahindra Bank Limited is an Indian banking and financial services company headquartered in Mumbai. It offers banking products and financial services for corporate and retail customers in the areas of personal finance, investment banking, life insurance, and wealth management. As of December 2023, the bank has 1,869 branches and 3,239 ATMs, including branches in GIFT City and DIFC (Dubai).
Karnataka Bank Limited is an Indian private sector bank based in Mangalore. It is an 'A' Class Scheduled Commercial Bank with a network of 915 branches, 1188 ATMs & Cash recyclers and 588 e-lobbies/mini e-lobbies across 22 states and 2 union territories. It has 8,652 employees and over 11 million customers throughout the country. Its shares are listed on the NSE and BSE. The tagline of the bank is "Your Family Bank Across India."
The economy of South India after independence in 1947 conformed to a socialist framework, with strict governmental control over private sector participation, foreign trade and foreign direct investment (FDI). Through 1960s–1990s, South Indian economies experienced mixed economic growth. In the 1960s, Kerala achieved above-average economic growth, while Andhra Pradesh's economy declined during this period. Similarly, Kerala experienced an economic decline in the 1970s while the economies of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka consistently exceeded national average growth rates after 1970. South India first started to overtake the rest of India economically in the 1980s. Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka were noted by some to be more reform-oriented in terms of economic policy when compared to other Indian states. Over the last decade South India has grown at 8% annually. Future savings may be negatively impacted by a growth in an aging population in South Indian states, as the aging population will require more money for healthcare expenses. However, this will not severely impact state domestic product as India's overall population is also expected to decline. Today, South India has about 20% of India's population, and contributes about 31% of India's GDP; it is projected to contribute 35% by 2030.

Karnataka is one of the highest economic growth states in India with an expected GSDP growth of 9.5% in the 2021–22 fiscal year. The total expected GSDP of Karnataka in 2022–2023 is about $240 billion. Karnataka recorded the highest growth rates in terms of GDP and per capita GDP in the last decade compared to other states. In 2008–09, the tertiary sector contributed the most to GSDP, followed by the secondary sector, and the primary sector.

ING Vysya Bank was a privately owned Indian multinational bank based in Bangalore, with retail, wholesale, and private banking platforms formed from the 2002 purchase of an equity stake in Vysya Bank by the Dutch ING Group. This merger marked the first between an Indian bank and a foreign bank. Prior to this transaction, Vysya Bank had a seven-year-old strategic alliance and shareholding arrangement with erstwhile Belgian bank Banque Bruxelles Lambert, which was also acquired by ING Group in 1998.
A prevailing trend from the medieval period, most Indians invest more than half of personal savings physical assets such as land, houses, gold, livestock, and other precious metals and ornaments. Since liberalisation in the 1990s, the Government of India has approved significant banking reforms. While some of these relate to nationalised banks, other reforms have opened up the banking and insurance sectors to private and foreign players.
Mulki Sunder Ram Shetty (1915–1981) was an Indian banker. He was associated with Vijaya Bank since 1946 and joined the board of directors of the bank as chairman from 1962, became the honorary chairman from 1962 to 1969 resulting in growth of Vijaya bank. and then remained as full-time chairman till 1978. Under the chairmanship of Shri Mulki Sunder Ram Shetty, Vijaya Bank steadily grew into a large All India Bank with nine smaller banks merging with it during 1963–1968. During the year 1965, the bank registered its own logo.

Vaman Srinivas Kudva, popularly called V. S. Kudva, was a founding director of Syndicate Bank, one of the oldest and major commercial banks of India.
Public Sector Undertakings (Banks) are a major type of government-owned banks in India, where a majority stake (i.e., more than 50%) is held by the Ministry of Finance (India) of the Government of India or State Ministry of Finance of various State Governments of India. The shares of these government-owned-banks are listed on stock exchanges. Their main objective is social welfare.

The Karnataka Vikas Grameena Bank (KVGB), an Indian Regional Rural Bank sponsored by Canara Bank. It is under the ownership of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. The bank provides retail banking services to rural users and has 629 branches in areas of Karnataka, around North and Western Karnataka.

Vysya Bank was an Indian private bank in Karnataka, India during 1930-2003.











