The 840s decade ran from January 1, 840, to December 31, 849.
Year 876 (DCCCLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.

Louis the German, also known as Louis II of Germany, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the Pious, emperor of Francia, and his first wife, Ermengarde of Hesbaye, he received the appellation Germanicus shortly after his death, when East Francia became known as the kingdom of Germany.

Charles the Bald, also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), King of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during the reign of his father, Louis the Pious, Charles succeeded, by the Treaty of Verdun (843), in acquiring the western third of the empire. He was a grandson of Charlemagne and the youngest son of Louis the Pious by his second wife, Judith.
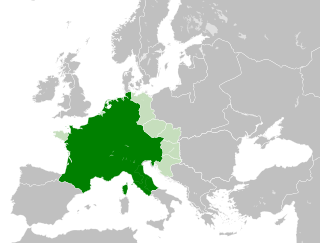
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from the Byzantine Empire to Western Europe. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire.

Lotharingia was a medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. It comprised present-day Lorraine (France), Luxembourg, Saarland (Germany), Netherlands, and the eastern half of Belgium, along with parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany) and Nord (France). It was named after King Lothair II, who received this territory after the Kingdom of Middle Francia of his father, Lothair I, had been divided among his three sons in 855.

Charles III, also known as Charles the Fat, was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 887. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandson of Charlemagne. He was the last Carolingian emperor of legitimate birth and the last to rule a united kingdom of the Franks.

The Treaty of Mersen or Meerssen, concluded on 8 August 870, was a treaty to partition the realm of Lothair II, known as Lotharingia, by his uncles Louis the German of East Francia and Charles the Bald of West Francia, the two surviving sons of Emperor Louis I the Pious. The treaty followed an earlier treaty of Prüm which had split Middle Francia between Lothair I's sons after his death in 855.

Alamannia, or Alemannia, was the kingdom established and inhabited by the Alemanni, a Germanic tribal confederation that had broken through the Roman limes in 213.

Ermengardeof Hesbaye, probably a member of the Robertian dynasty, was Carolingian empress from 813 and Queen of the Franks from 814 until her death as the wife of the Carolingian emperor Louis the Pious.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

East Francia or the Kingdom of the East Franks was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire into three kingdoms.

The Kingdom of Upper Burgundy was a Frankish dominion established in 888 by the Welf king Rudolph I of Burgundy within the territory of former Middle Francia. It grew out of the Carolingian margraviate of Transjurane Burgundy southeast of the Jura Mountains together with the adjacent County of Burgundy (Franche-Comté) in the northwest. The adjective 'upper' refers to its location upstream in the Rhône river valley, as distinct from Lower Burgundy and also from the Duchy of Burgundy west of the Saône river. Upper Burgundy reunited with the Kingdom of Lower Burgundy in 933 to form the Kingdom of Burgundy, later known as Kingdom of Arles or Arelat.
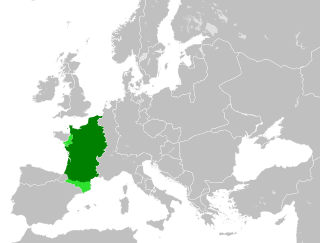
In medieval historiography, West Francia or the Kingdom of the West Franks constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capetian dynasty. It was created from the division of the Carolingian Empire following the death of Louis the Pious, with its neighbor East Francia eventually evolving into the Kingdom of Germany.

Middle Francia was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Francia was allocated to emperor Lothair I, the eldest son and successor of emperor Louis the Pious. His realm contained the imperial cities of Aachen and Pavia, but lacked any geographic or cultural cohesion, which prevented it from surviving and forming a nucleus of a larger state, as was the case with West Francia and East Francia.

Liutgard of Saxony was Queen of East Francia from 876 until 882 by her marriage with King Louis the Younger.
Wilbert was the archbishop of Cologne from 870 until his death.

Louis the Younger, sometimes called Louis the Saxon or Louis III, was the second eldest of the three sons of Louis the German and Hemma. He succeeded his father as the King of Eastern Francia on 28 August 876 and his elder brother Carloman as King of Bavaria from 879 to 882. He died in 882 and was succeeded in all his territories, which encompassed most of East Francia, by his younger brother, Charles the Fat, already king of Italy and emperor.

The Treaty of Prüm, concluded on 19 September 855, was the second of the partition treaties of the Carolingian Empire. As Emperor Lothair I was approaching death, he divided his realm of Middle Francia among his three sons.
Raganar , Frankish Count, was a vassal of Charles the Bald and fought in many of Charles' campaigns. The precise counties that Raganar ruled are uncertain but are known to have been south of Thérouanne.


















