
The First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated and Rome gained territory from Carthage.
Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus was a Roman general and statesman during the third century BC. He played a major part in the Second Punic War, establishing Roman rule in the east of the Iberian peninsula and tying up several Carthaginian armies to keep them from reinforcing Hannibal.
Mago Barca was a Carthaginian, member of the Barcid family, who played an important role in the Second Punic War, leading forces of Carthage against the Roman Republic in Iberia and northern and central Italy. Mago was the third son of Hamilcar Barca, was the brother of Hannibal and Hasdrubal, and was the brother-in-law of Hasdrubal the Fair.

Syphax was a king of the Masaesyli tribe of western Numidia during the last quarter of the 3rd century BC. His story is told in Livy's Ab Urbe Condita. He ruled over a territory extending from present day Constantine to Fez.

The Battle of Mylae took place in 260 BC during the First Punic War and was the first real naval battle between Carthage and the Roman Republic. This battle was key in the Roman victory of Mylae as well as Sicily itself. It also marked Rome's first naval triumph and also the first use of the corvus in battle.

The Battle of Cape Ecnomus or Eknomos was a naval battle, fought off southern Sicily, in 256 BC, between the fleets of Carthage and the Roman Republic, during the First Punic War. The Carthaginian fleet was commanded by Hanno and Hamilcar; the Roman fleet jointly by the consuls for the year, Marcus Atilius Regulus and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus. It resulted in a clear victory for the Romans.
The Battle of the Aegates was a naval battle fought on 10 March 241 BC between the fleets of Carthage and Rome during the First Punic War. It took place among the Aegates Islands, off the western coast of the island of Sicily. The Carthaginians were commanded by Hanno, and the Romans were under the overall authority of Gaius Lutatius Catulus, but Quintus Valerius Falto commanded during the battle. It was the final and deciding battle of the 23-year-long First Punic War.

Hasdrubal Barca, a latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.
Gaius Laelius was a Roman general and statesman, and a friend of Scipio Africanus, whom he accompanied on his Iberian campaign and his African campaign. His command of the Roman fleet in the attack on New Carthage and command of the Roman cavalry at Zama contributed to Scipio's victories.
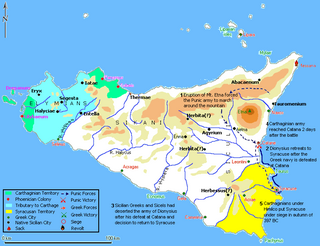
The siege of Syracuse in 397 BC was the first of four unsuccessful sieges Carthaginian forces would undertake against Syracuse from 397 to 278 BC. In retaliation for the siege of Motya by Dionysius of Syracuse, Himilco of the Magonid family of Carthage led a substantial force to Sicily. After retaking Motya and founding Lilybaeum, Himilco sacked Messana, then laid siege to Syracuse in the autumn of 397 BC after the Greek navy was crushed at Catana.

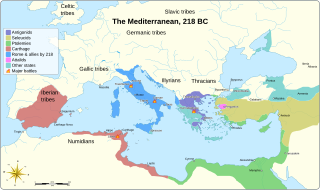
The Battle of Cissa was part of the Second Punic War. It was fought in the fall of 218 BC, near the Celtic town of Tarraco in north-eastern Iberia. A Roman army under Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus defeated an outnumbered Carthaginian army under Hanno, thus gaining control of the territory north of the Ebro River that Hannibal had just subdued a few months prior in the summer of 218 BC. This was the first battle that the Romans had ever fought in Iberia. It allowed the Romans to establish a secure base among friendly Iberian tribes, and due to the eventual success of the Scipio brothers in Spain, Hannibal looked for but never received reinforcements from Spain during the war.

The Battle of Ebro River was a naval battle fought near the mouth of Ebro River in the spring of 217 BC between a Carthaginian fleet of approximately 40 quinqueremes, under the command of Himilco, and a Roman fleet of 35 ships, under Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus. Hasdrubal Barca, the Carthaginian commander in Iberia, had launched a joint expedition to destroy the Roman base north of the Ebro River. The Carthaginian naval contingent was totally defeated after a surprise attack by the Roman ships, losing 29 ships and the control of seas around Iberia. The reputation of the Romans was further enhanced in Iberia after this victory, causing rebellion among some of the Iberian tribes under Carthaginian control.

The Battle of Decimomannu or Caralis took place in Sardinia when a Carthaginian army sailed to the island to support a local revolt against Roman rule. The army, led by Hasdrubal the Bald, fought a similar size Roman army under the Praetor Titus Manlius Torquatus in the Fall of 215 BC somewhere between Sestu and Decimomannu, just north of Caralis. The Romans destroyed the Carthaginian army and then scattered their fleet in a sea battle south of Sardinia.

The Roman Republic conquered and occupied territories in the Iberian Peninsula that were previously under the control of native Celtic, Iberian, Celtiberian and Aquitanian tribes and the Carthaginian Empire. The Carthaginian territories in the south and east of the peninsula were conquered in 206 BC during the Second Punic War. Control was gradually extended over most of the peninsula without annexations. It was completed after the end of the Roman Republic, by Augustus, the first Roman emperor, who annexed the whole of the peninsula to the Roman Empire in 19 BC.

The Battle of Lilybaeum was the first clash between the navies of Carthage and Rome in 218 BC during the Second Punic War. The Carthaginians had sent 35 quinqueremes to raid Sicily, starting with Lilybaeum. The Romans, warned by Hiero of Syracuse of the coming raid, had time to intercept the Carthaginian contingent with a fleet of 20 quinqueremes and managed to capture several Carthaginian ships.
The Battle of Insubria in 203 BC was the culmination of a major war, carried out by the Carthaginian commander Mago, brother of Hannibal Barca, at the end of the Second Punic war between Rome and Carthage in what is now northwestern Italy. Mago had landed at Genoa, Liguria, two years before, in an effort to keep the Romans busy to the North and thus hamper indirectly their plans to invade Carthage's hinterland in Africa. He was quite successful in reigniting the unrest among various peoples against the Roman dominance. Rome was forced to concentrate large forces against him which finally resulted in a battle fought in the land of the Insubres (Lombardy). Mago suffered defeat and had to retreat. The strategy to divert the enemy's forces failed as the Roman general Publius Cornelius Scipio laid waste to Africa and wiped out the Carthaginian armies that were sent to destroy the invader. To counter Scipio, the Carthaginian government recalled Mago from Italy. However, the remnants of the Carthaginian forces in Cisalpine Gaul continued to harass the Romans for several years after the end of the war.

The Battle of Catana took place in the summer of 397 BC. The Greek fleet under Leptines, the brother of Dionysius I of Syracuse, engaged the Carthaginian fleet under Mago near the city of Catana in Sicily. While the Greek army under Dionysius was present near the city of Catana during the battle, the Carthaginian army under Himilco was away in the interior of Sicily, making a detour around the erupting Mount Etna. The Carthaginian fleet crushed the Greek fleet in the battle, leading to the Carthaginian siege of Syracuse later in 397 BC.

The Battle of Carteia, also known by the modern name Battle of the Guadalquivir, took place during the Second Punic War in 206 BC between the forces of Carthage and the Roman Republic. The name "Battle of the Guadalquivir" is anachronistic, since the river's name "el Guadalquivir", from the Arabic al-wadi al-kabir, was not used until the Islamic conquest of Spain over nine hundred years after the battle. The Carthaginian forces were commanded by Hanno and the Romans by Gaius Lucius Marcius Septimus. The battle resulted in a Roman victory.
Adherbal was a Carthaginian noble who served as the governor of Gadir (Cadiz) during the Second Punic War. He was also a Carthaginian military commander in this war under the command of Mago Barca. He was one of the lesser generals of the Punic War and was often trying to prove his worth. He is perhaps best known for his defeat in the naval Battle of Carteia in 206 BC while attempting to leave Carthaginian Spain with valuable prisoners. His fleet was defeated near the ancient city of Carteia by G. Laelius.














