
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator, was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was censor in 230 BC. His agnomen, Cunctator, usually translated as "the delayer", refers to the strategy that he employed against Hannibal's forces during the Second Punic War. Facing an outstanding commander with superior numbers, he pursued a then-novel strategy of targeting the enemy's supply lines, and accepting only smaller engagements on favourable ground, rather than risking his entire army on direct confrontation with Hannibal himself. As a result, he is regarded as the originator of many tactics used in guerrilla warfare.

Hannibal was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
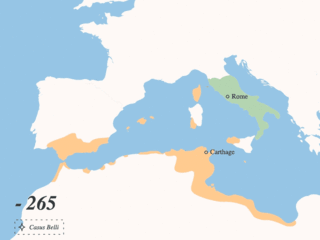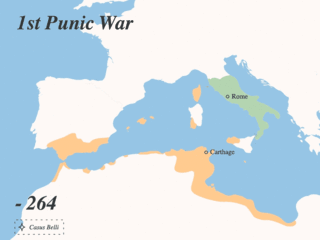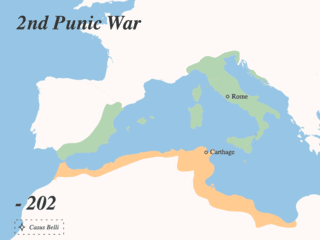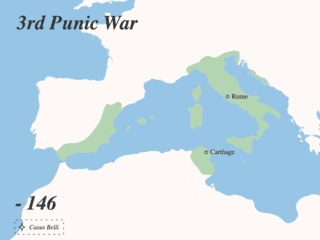
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage. Three wars took place, on both land and sea, across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.

The Second Punic War was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.

Marcus Claudius Marcellus was a Roman general and politician during the 3rd century BC. Five times elected as consul of the Roman Republic. Marcellus gained the most prestigious award a Roman general could earn, the spolia opima, for killing the Gallic king Viridomarus in single combat in 222 BC at the Battle of Clastidium. Furthermore, he is noted for having conquered the fortified city of Syracuse in a protracted siege during which Archimedes, the famous mathematician, scientist, and inventor, was killed, despite Marcellus ordering the soldiers under his command not to harm him. Marcus Claudius Marcellus died in battle in 208 BC, leaving behind a legacy of military conquests and a reinvigorated Roman legend of the spolia opima.

The Battle of Cannae was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by Hannibal, surrounded and practically annihilated a larger Roman and Italian army under the consuls Lucius Aemilius Paullus and Gaius Terentius Varro. It is regarded as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history and one of the worst defeats in Roman history, and it cemented Hannibal's reputation as one of antiquity's greatest tacticians.

Titus Quinctius Flamininus was a Roman politician and general instrumental in the Roman conquest of Greece.
Aulus Atilius Caiatinus was a Roman general and statesman who achieved prominence for his military activities during the First Punic War against Carthage. As consul in 258 BC, he enjoyed several successes in Sicily, for which he later celebrated a triumph. He undertook further campaigning in Sicily both at sea and on land during a second consulship and then as dictator, becoming the first Roman dictator to lead an army outside mainland Italy.
The Fabian strategy is a military strategy where pitched battles and frontal assaults are avoided in favor of wearing down an opponent through a war of attrition and indirection. While avoiding decisive battles, the side employing this strategy harasses its enemy through skirmishes to cause attrition, disrupt supply and affect morale. Employment of this strategy implies that the side adopting this strategy believes time is on its side, usually because the side employing the strategy is fighting in, or close to, their homeland and the enemy is far from home and by necessity has long and costly supply lines. It may also be adopted when no feasible alternative strategy can be devised.
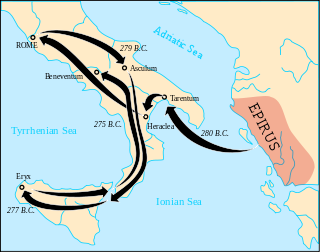
The Pyrrhic War was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans.
The Battle of Pandosia was fought in 331 BC between a Greek force led by Alexander I of Epirus against the Lucanians and Bruttians, two southern Italic tribes. The Italic army soundly defeated the invading Greeks and killed Alexander I of Epirus during the battle.
Carthalo was an officer in Hannibal's army during the Second Punic War.

The Battle of Tarentum in March 212 BC was a military engagement in the Second Punic War.
The Battle of Ager Falernus was a skirmish during the Second Punic War between the armies of Rome and Carthage. After winning the Battle of Lake Trasimene in Italy in 217 BC, the army commanded by Hannibal marched south and reached Campania. The Carthaginians ultimately moved into the district of Falernum, a fertile river valley surrounded by mountains.

The Battle of Beneventum was fought in 214 BC near modern Benevento during the Second Punic War. Roman legions under Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus defeated Hanno's Carthaginian forces, denying Hannibal reinforcements. Livy gives a brief description of the battle, which was part of the Roman campaign to subdue the southern Italian city-states that had joined Hannibal after the Battle of Cannae.

The Battle of Canusium also known as the Battle of Asculum was a three-day engagement between the forces of Rome and Carthage. It took place in Apulia during the spring of 209 BC, the tenth year of the Second Punic War. A larger Roman offensive, of which it was a part, aimed to subjugate and to punish cities and tribes that had abandoned the alliance with Rome after the Battle of Cannae, and to narrow the base of the Carthaginian leader, Hannibal, in southern Italy.
Marcus Minucius Rufus was a Roman consul in 221 BC. He was also Magister Equitum during the dictatorship of Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus known as Cunctator.

Quintus Fabius Maximus was a consul of the Roman Republic in 213 BC. He was the son of Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, the famous dictator who invented Fabian strategy, and served with his father during the Second Punic War.














