Related Research Articles

The First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated and Rome gained territory from Carthage.
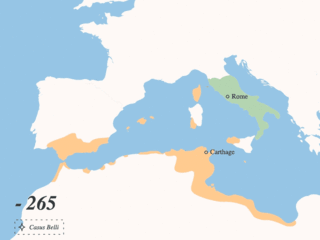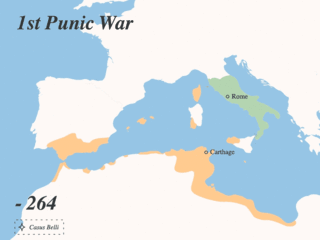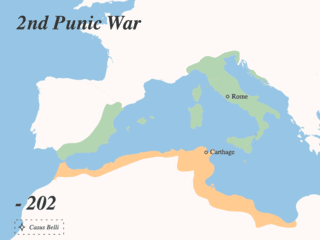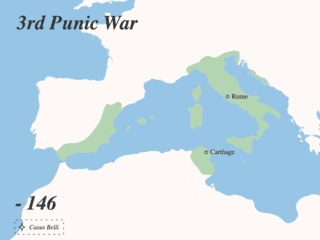
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage. Three wars took place, on both land and sea, across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.

The Second Punic War was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war.
Year 256 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Longus and Caedicius/Regulus. The denomination 256 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 259 BC – 250 BC.
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair.
The Battle of Zama was fought in 202 BC in what is now Tunisia between a Roman army commanded by Scipio Africanus and a Carthaginian army commanded by Hannibal. The battle was part of the Second Punic War and resulted in such a severe defeat for the Carthaginians that they capitulated, while Hannibal was forced into exile. The Roman army of approximately 30,000 men was outnumbered by the Carthaginians who fielded either 40,000 or 50,000; the Romans were stronger in cavalry, but the Carthaginians had 80 war elephants.

The siege of Carthage was the main engagement of the Third Punic War fought between Carthage and Rome. It consisted of the nearly-three-year siege of the Carthaginian capital, Carthage. In 149 BC, a large Roman army landed at Utica in North Africa. The Carthaginians hoped to appease the Romans, but despite the Carthaginians surrendering all of their weapons, the Romans pressed on to besiege the city of Carthage. The Roman campaign suffered repeated setbacks through 149 BC, only alleviated by Scipio Aemilianus, a middle-ranking officer, distinguishing himself several times. A new Roman commander took over in 148 BC, and fared equally badly. At the annual election of Roman magistrates in early 147 BC, the public support for Scipio was so great that the usual age restrictions were lifted to allow him to be appointed commander in Africa.

The Battle of Agrigentum was the first pitched battle of the First Punic War and the first large-scale military confrontation between Carthage and the Roman Republic. The battle was fought after a long siege which started in 262 BC and resulted both in a Roman victory and the beginning of Roman control of Sicily.

The Battle of Cape Ecnomus or Eknomos was a naval battle, fought off southern Sicily, in 256 BC, between the fleets of Carthage and the Roman Republic, during the First Punic War. The Carthaginian fleet was commanded by Hanno and Hamilcar; the Roman fleet jointly by the consuls for the year, Marcus Atilius Regulus and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus. It resulted in a clear victory for the Romans.
Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus was a Roman general and statesman, who served as consul of the Roman Republic in 256 and 250 BC. He is remembered for his military successes; his military achievements, especially the Battle of Cape Ecnomus, significantly contributed to the victory of the Romans in the First Punic War.

The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264–241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian control. It lasted from 241 to late 238 or early 237 BC and ended with Carthage suppressing both the mutiny and the revolt.
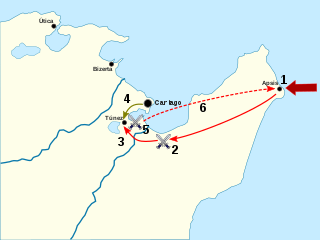
The Battle of the Bagradas River, also known as the Battle of Tunis, was a victory by a Carthaginian army led by Xanthippus over a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus in the spring of 255 BC, nine years into the First Punic War. The previous year, the newly constructed Roman navy established naval superiority over Carthage. The Romans used this advantage to invade Carthage's homeland, which roughly aligned with modern-day Tunisia in North Africa. After landing on the Cape Bon Peninsula and conducting a successful campaign, the fleet returned to Sicily, leaving Regulus with 15,500 men to hold the lodgement in Africa over the winter.

The battle of Adys took place in late 256 BC during the First Punic War between a Carthaginian army jointly commanded by Bostar, Hamilcar and Hasdrubal and a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus. Earlier in the year, the new Roman navy had established naval superiority and used this advantage to invade the Carthaginian homeland, which roughly aligned with modern Tunisia in North Africa. After landing on the Cape Bon Peninsula and conducting a successful campaign, the fleet returned to Sicily, leaving Regulus with 15,500 men to hold the lodgement in Africa over the winter.
The Battle of Panormus was fought in Sicily in 250 BC during the First Punic War between a Roman army led by Lucius Caecilius Metellus and a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal, son of Hanno. The Roman force of two Roman and two allied legions defending the city of Panormus defeated the much larger Carthaginian army of 30,000 men and between 60 and 142 war elephants.

Marcus Atilius Regulus was a Roman statesman and general who was a consul of the Roman Republic in 267 BC and 256 BC. Much of his career was spent fighting the Carthaginians during the first Punic War. In 256 BC, he and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus defeated the Carthaginians at the naval battle off Cape Ecnomus; afterwards he led the Roman expedition to Africa but was defeated at the Bagradas River in spring of 255 BC. He was captured and then probably died of natural causes.
The military of Carthage was one of the largest military forces in the ancient world. Although Carthage's navy was always its main military force, the army acquired a key role in the spread of Carthaginian power over the native peoples of northern Africa and southern Iberian Peninsula from the 6th century BC and the 3rd century BC. Carthage's military also allowed it to expand into Sardinia and the Balearic Islands. This expansion transformed the military from a body of citizen-soldiers into a multinational force composed of a combination of allies, citizens and foreign mercenary units.
The siege of Lilybaeum lasted for nine years, from 250 to 241 BC, as the Roman army laid siege to the Carthaginian-held Sicilian city of Lilybaeum during the First Punic War. Rome and Carthage had been at war since 264 BC, fighting mostly on the island of Sicily or in the waters around it, and the Romans were slowly pushing the Carthaginians back. By 250 BC, the Carthaginians held only the cities of Lilybaeum and Drepana; these were well-fortified and situated on the west coast, where they could be supplied and reinforced by sea without the Romans being able to use their superior army to interfere.
The Roman withdrawal from Africa was the attempt by the Roman Republic in 255 BC to rescue the survivors of their defeated expeditionary force to Carthaginian Africa during the First Punic War. A large fleet commanded by Servius Fulvius Paetinus Nobilior and Marcus Aemilius Paullus successfully evacuated the survivors after defeating an intercepting Carthaginian fleet, but was struck by a storm while returning, losing most of its ships.
Hasdrubal was a Carthaginian general who served during the middle years of the First Punic War, fought between Carthage and Rome, and took a leading part in three of the four major field battles of the war. He was a citizen of the city state of Carthage, which was in what is now Tunisia. His date of birth and age at death are both unknown, as are his activities prior to his coming to prominence in 255 BC. Modern historians distinguish him from other Carthaginians named Hasdrubal by the cognomen "son of Hanno".
References
- ↑ Polybius. The Histories, I.28.
- ↑ Polybius. The Histories, I.29.
- 1 2 Siege of Aspis, 256 B.C. Rickard, J (10 May 2007), Siege of Aspis, 256 BC. Retrieved on December 13, 2008.
- ↑ "Roman invasion of Africa". The History of Rome. London: Carey, Lea & Blanchard. 1837. pp. 109 . Retrieved December 14, 2008.
siege of aspis.
- ↑ James Hampton, ed. (1823). "The General History of Polybius - Chapter III". The General History of Polybius. Vol. I (5th ed.). London: W. Baxter. p. 35. Retrieved December 14, 2008.
