
Schleswig-Holstein is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg.

Schleswig is a town in the northeastern part of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the capital of the Kreis (district) Schleswig-Flensburg. It has a population of about 27,000, the main industries being leather and food processing. It takes its name from the Schlei, an inlet of the Baltic sea at the end of which it sits, and vik or vig which means "bay" in Old Norse and Danish. Schleswig or Slesvig therefore means "bay of the Schlei".

Sylt is a former island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, and well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian Islands and is the largest island in North Frisia. The northernmost island of Germany, it is known for its tourist resorts, notably Westerland, Kampen and Wenningstedt-Braderup, as well as for its 40-kilometre-long (25-mile) sandy beach. It is frequently covered by the media in connection with its exposed situation in the North Sea and its ongoing loss of land during storm tides. Since 1927, Sylt has been connected to the mainland by the Hindenburgdamm causeway. In later years, it has been a resort for the German jet set and tourists in search of occasional celebrity sightings.

Nordfriesland, also known as North Frisia, is the northernmost district of Germany, part of the state of Schleswig-Holstein. It includes almost all of traditional North Frisia, as well as adjacent parts of the Schleswig Geest to the east and Stapelholm to the south, and is bounded by the districts of Schleswig-Flensburg and Dithmarschen, the North Sea and the Danish county of South Jutland. The district is called Kreis Nordfriesland in German, Kreis Noordfreesland in Low German, Kris Nordfraschlönj in Mooring North Frisian, Kreis Nuurdfresklun in Fering North Frisian and Nordfrislands amt in Danish.
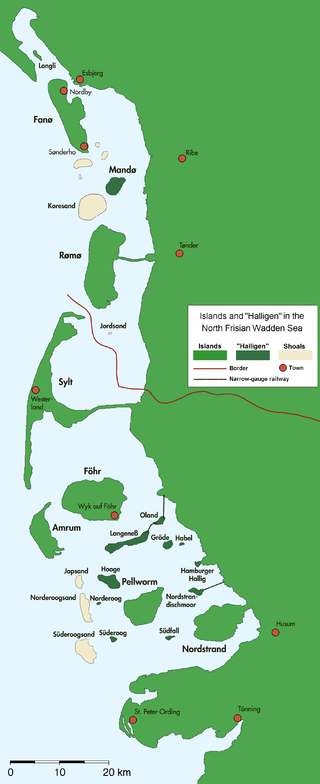
The North Frisian Islands are the Frisian Islands off the coast of North Frisia.

Husum is the capital of the Kreis (district) Nordfriesland in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town was the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Storm, who coined the epithet "the grey town by the sea". It is also the home of the annual international piano festival Raritäten der Klaviermusik founded in 1986.

Dithmarschen is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Nordfriesland, Schleswig-Flensburg, Rendsburg-Eckernförde, and Steinburg, by the state of Lower Saxony, and by the North Sea. From the 13th century up to 1559 Dithmarschen was an independent peasant republic within the Holy Roman Empire and a member of the Hanseatic League.

The Wadden Sea National Parks in Denmark, Germany and the Netherlands are located along the German Bight of the North Sea. In Germany and Denmark they also mark the area of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of the Wadden Sea. Divided from each other by administrative borders, they form a single ecological entity. The purpose of the national parks is the protection of the Wadden Sea ecoregion.

The Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park is a national park in the Schleswig-Holstein area of the German Wadden Sea. It was founded by the Parliament of Schleswig-Holstein on 1 October 1985 by the National Park Act of 22 July 1985 and expanded significantly in 1999. Together with the Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park, the Hamburg Wadden Sea National Park and those parts of Elbe estuary which are not nature reserves, it forms the German part of the Wadden Sea.

The German Bight is the southeastern bight of the North Sea bounded by the Netherlands and Germany to the south, and Denmark and Germany to the east. To the north and west it is limited by the Dogger Bank. The Bight contains the Frisian and Danish Islands. The Wadden Sea is approximately ten to twelve kilometres wide at the location of the German Bight. The Frisian islands and the nearby coastal areas are collectively known as Frisia. The southern portion of the bight is also known as the Heligoland Bight. Between 1949 and 1956 the BBC Sea Area Forecast used "Heligoland" as the designation for the area now referred to as German Bight.

The Heligoland Bight, also known as Helgoland Bight, is a bay which forms the southern part of the German Bight, itself a bay of the North Sea, located at the mouth of the Elbe river. The Heligoland Bight extends from the mouth of the Elbe to the islands of Heligoland and lies between the East Frisian island of Wangerooge and the North Frisian peninsula of Eiderstedt.

Eiderstedt is a peninsula in the district of Nordfriesland in the German federal state of Schleswig-Holstein.

Sankt Peter-Ording is a popular German seaside spa and a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the only German seaside resort that has a sulphur spring and thus terms itself "North Sea spa and sulphur spring". By overnight stays, St. Peter-Ording is the largest seaside resort and has the most overnight stays in the state of Schleswig-Holstein.
M/V Pallas, callsign C6LO9, IMO number 7039206, was a 147-metre (482 ft) cargo ship built in 1971. On 25 October 1998, her cargo of lumber caught fire while traveling the North Sea off the west coast of Jutland. The ship ran aground on 29 October off the German island of Amrum, in the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park. Around 200–300 tons of fuel oil was lost overboard and caused Germany's most notable maritime environmental disaster.

The Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park was established in 1986 and embraces the East Frisian Islands, mudflats and salt marshes between the Bay of Dollart on the border with the Netherlands in the west and Cuxhaven as far as the Outer Elbe shipping channel in the east. The national park has an area of about 345,800 hectares (1,335 sq mi). The National Park organisation is located in Wilhelmshaven. In June 2009, the National Park became a UNESCO World Heritage Site along with the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea and the Dutch Wadden Sea, highlighting its unique intertidal ecosystem and high biodiversity.

The Katinger Watt is an area near Kating in the south of the Eiderstedt peninsula in the north German state of Schleswig-Holstein which is partly maintained by the German Nature and Biodiversity Conservation Union, NABU. The Katinger Watt is part of two larger protected areas, of the Ramsar site Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea and adjacent areas and of a similarly named SPA.

The Bay of Meldorf also called Meldorf Bay, is a bay on the coast of the North German state of Schleswig-Holstein, which forms part of the Heligoland Bight.

Tourism is an important economic factor for Germany's northernmost state of Schleswig-Holstein.

The Hütten Hills are an area of upland, up to 105.8 m above sea level (NHN), roughly west of the town of Eckernförde in the county of Rendsburg-Eckernförde in the North German state of Schleswig-Holstein. They lie within the Hütten Hills Nature Park.
The Königshafen is the northernmost bight of the North Frisian island of Sylt in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein and thus also the northernmost bay in Germany. The bay gets its name from its use as a natural harbour and its legal status as part of the Royal Danish enclave of Listland. The harbour was used until at least the 18th century and was later abandoned as it silted up.
















