Customer relationship management (CRM) is a process in which a business or another organization administers its interactions with customers, typically using data analysis to study large amounts of information.
Marketing research is the systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of qualitative and quantitative data about issues relating to marketing products and services. The goal is to identify and assess how changing elements of the marketing mix impacts customer behavior.
Personalized marketing, also known as one-to-one marketing or individual marketing, is a marketing strategy by which companies use data analysis and digital technology to show adverts to individuals based on their perceived characteristics and interests. Marketers use methods from data collection, analytics, digital electronics, and digital economics then use technology to analyze it and show personalized ads based on algorithms that attempt to deduce people’s interests.

Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data science. Analytics also entails applying data patterns toward effective decision-making. It can be valuable in areas rich with recorded information; analytics relies on the simultaneous application of statistics, computer programming, and operations research to quantify performance.

Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource, it is the practice of managing an organization's data so it can be analyzed for decision making.
Personalization consists of tailoring a service or product to accommodate specific individuals. It is sometimes tied to groups or segments of individuals. Personalization involves collecting data on individuals, including web browsing history, web cookies, and location. Various organizations use personalization to improve customer satisfaction, digital sales conversion, marketing results, branding, and improved website metrics as well as for advertising. Personalization acts as a key element in social media and recommender systems. Personalization influences every sector of society — be it work, leisure, or citizenship.
Cohort analysis is a kind of behavioral analytics that breaks the data in a data set into related groups before analysis. These groups, or cohorts, usually share common characteristics or experiences within a defined time-span. Cohort analysis allows a company to "see patterns clearly across the life-cycle of a customer, rather than slicing across all customers blindly without accounting for the natural cycle that a customer undergoes." By seeing these patterns of time, a company can adapt and tailor its service to those specific cohorts. While cohort analysis is sometimes associated with a cohort study, they are different and should not be viewed as one and the same. Cohort analysis is specifically the analysis of cohorts in regards to big data and business analytics, while in cohort study, data is broken down into similar groups.
Predictive analytics, or predictive AI, encompasses a variety of statistical techniques from data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events.
Path analysis is the analysis of a path, which is a portrayal of a chain of consecutive events that a given user or cohort performs during a set period of time while using a website, online game, or eCommerce platform. As a subset of behavioral analytics, path analysis is a way to understand user behavior in order to gain actionable insights into the data. Path analysis provides a visual portrayal of every event a user or cohort performs as part of a path during a set period of time.

Digital marketing is the component of marketing that uses the Internet and online-based digital technologies such as desktop computers, mobile phones, and other digital media and platforms to promote products and services.
Business analytics (BA) refers to the skills, technologies, and practices for iterative exploration and investigation of past business performance to gain insight and drive business planning. Business analytics focuses on developing new insights and understanding of business performance based on data and statistical methods. In contrast, business intelligence traditionally focuses on using a consistent set metrics to both measure past performance and guide business planning. In other words, business intelligence focusses on description, while business analytics focusses on prediction and prescription.
Customer analytics is a process by which data from customer behavior is used to help make key business decisions via market segmentation and predictive analytics. This information is used by businesses for direct marketing, site selection, and customer relationship management. Marketing provides services to satisfy customers. With that in mind, the productive system is considered from its beginning at the production level, to the end of the cycle at the consumer. Customer analytics plays an important role in the prediction of customer behavior.
Artificial intelligence marketing (AIM) is a form of marketing that uses artificial intelligence concepts and models such as machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision to achieve marketing goals. The main difference between AIM and traditional forms of marketing resides in the reasoning, which is performed by a computer algorithm rather than a human.
Social media measurement, also called social media controlling, is the management practice of evaluating successful social media communications of brands, companies, or other organizations.
Trade Promotion Management (TPM) is a software application that assist companies in managing their trade promotion activity.
Fashion forecasting began in France during the reign of Louis XIV. It started as a way of communicating about fashion and slowly transformed into a way to become ahead of the times in the fashion industry. Fashion forecasting predicts the moods of society and consumers, along with their behavior and buying habits and bases what they may release in the coming future off of the forecast. Fashion trends tend to repeat themselves every 20 years, and fashion forecasting predicts what other trends might begin with the rotation of fashion as well. Fashion forecasting can be used for many different reasons, the main reason being staying on top of current trends and knowing what your consumer is going to want in the future. This method helps fashion brands know what to expect and what to begin producing ahead of time. Top name brands and high end companies such as Vogue and Gucci even use this method to help their designers become even more informed on what is to come in the fashion industry.
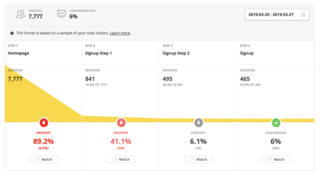
Funnel analysis involves mapping and analyzing a series of events that lead towards a defined goal, like an advertisement-to-purchase journey in online advertising, or the flow that starts with user engagement in a mobile app and ends in a sale on an eCommerce platform. Funnel analyses "are an effective way to calculate conversion rates on specific user behaviors". This can be in the form of a sale, registration, or other intended action from an audience.
In the fields of Information Technology (IT) and Systems Management, IT operations analytics (ITOA) is an approach or method to retrieve, analyze, and report data for IT operations. ITOA may apply big data analytics to large datasets to produce business insights. In 2014, Gartner predicted its use might increase revenue or reduce costs. By 2017, it predicted that 15% of enterprises will use IT operations analytics technologies.

Social media analytics or social media monitoring is the process of gathering and analyzing data from social networks such as Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, or Twitter. A part of social media analytics is called social media monitoring or social listening. It is commonly used by marketers to track online conversations about products and companies. One author defined it as "the art and science of extracting valuable hidden insights from vast amounts of semi-structured and unstructured social media data to enable informed and insightful decision-making."
Guided analytics is a sub-field at the interface of visual analytics and predictive analytics focused on the development of interactive visual interfaces for business intelligence applications. Such interactive applications serve the analyst to take important decisions by easily extracting information from the data.





