
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen ion, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula CH3. In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond, it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion, methylium cation or methyl radical. The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed.

Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds such as barbiturates, artificial flavourings, vitamin B1, and vitamin B6.

Catechol, also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is a toxic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4(OH)2. It is the ortho isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances.

An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the parent acid is a carboxylic acid, the formula of the anhydride being (RC(O))2O. Symmetrical acid anhydrides of this type are named by replacing the word acid in the name of the parent carboxylic acid by the word anhydride. Thus, (CH3CO)2O is called acetic anhydride. Mixed (or unsymmetrical) acid anhydrides, such as acetic formic anhydride (see below), are known, whereby reaction occurs between two different carboxylic acids. Nomenclature of unsymmetrical acid anhydrides list the names of both of the reacted carboxylic acids before the word "anhydride" (for example, the dehydration reaction between benzoic acid and propanoic acid would yield "benzoic propanoic anhydride").
The Cannizzaro reaction, named after its discoverer Stanislao Cannizzaro, is a chemical reaction which involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen, who first published his work on the reaction in 1887.
Squaric acid, also called quadratic acid because its four carbon atoms approximately form a square, is a diprotic organic acid with the chemical formula C4O2(OH)2.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

In chemistry, an oxocarbon or oxide of carbon is a chemical compound consisting only of carbon and oxygen. The simplest and most common oxocarbons are carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide. Many other stable or metastable oxides of carbon are known, but they are rarely encountered, such as carbon suboxide and mellitic anhydride.

Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, also called tetrahydroxy-p-benzoquinone, tetrahydroxybenzoquinone, or tetrahydroxyquinone, is an organic compound with formula C6O2(OH)4. Its molecular structure consists of a cyclohexadiene ring with four hydroxyl groups and two ketone groups in opposite (para) positions.

Acetylenediol, or ethynediol, is a chemical substance with formula HO−C≡C−OH (an ynol). It is the diol of acetylene. Acetylenediol is unstable in the condensed phase, although its tautomer glyoxal (CHO)2 is well known.

Acetylenedicarboxylic acid or butynedioic acid is an organic compound (a dicarboxylic acid) with the formula C4H2O4 or HO2CC≡CCO2H. It is a crystalline solid that is soluble in diethyl ether.

Dioxosuccinic acid or dioxobutanedioic acid is an organic compound with formula C4H2O6 or HO−(C=O)4−OH.
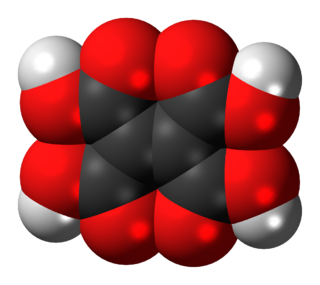
Ethylenetetracarboxylic acid is an organic compound with formula C
6H
4O
8, or (HO(OC)-)2C=C(-(CO)OH)2.
2,5-Dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone or 2,5-dihydroxy-para-benzoquinone is an organic compound with formula C
6H
4O
4, formally derived from 1,4-benzoquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms with hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is one of seven dihydroxybenzoquinone isomers. It is a yellow solid with planar molecules that exhibits ferroelectric properties.

In chemistry, furantetracarboxylic acid is an organic compound with formula C
8H
4O
9, or (C4O)(-(CO)OH)4, which can be viewed as deriving from furan C
4H
4O through replacement of the four hydrogen atoms by carboxyl functional groups -(CO)OH.

Benzoquinonetetracarboxylic dianhydride is an organic compound with formula C
10O
8 which can be seen as the result of removing two molecules of water H
2O from benzoquinonetetracarboxylic acid.

Hydromelonic acid, is an elusive chemical compound with formula C
9H
3N
13 or (HNCN)
3(C
6N
7), whose molecule would consist of a heptazine H3(C
6N
7) molecule, with three cyanamido groups H–N=C=N– or N≡C–NH– substituted for the hydrogen atoms.
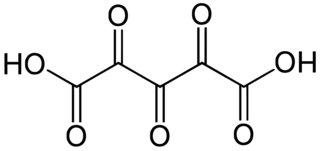
Trioxoglutaric acid or trioxopentanedioic acid is a hypothetical chemical compound with formula C5H2O7 or HO−(C=O)5−OH. It can be seen as a derivative of glutaric acid, hence its common name. It would be the next member of the series of fully oxidized straight-chain dicarboxylic acids, that starts with the oxalic, oxomalonic, and dioxosuccinic acids.















