
3C-E is a psychedelic of the amphetamine class. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, Shulgin lists the dosage range as 30 to 60 mg, consumed orally. The duration of action was stated to be 8–12 hours.

Escaline (3,5-methoxy-4-ethoxyphenethylamine) is a psychedelic drug and entheogen of the phenethylamine class of compounds. Escaline was first synthesized and reported in the scientific literature by Benington, et al., in 1954, but was later re-examined in the laboratory of David E. Nichols, who prepared a series of mescaline analogues that included escaline, proscaline, and isoproscaline. The effects of this and related mescaline analogues in humans were first described by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , Shulgin lists the dosage range as 40 to 60 mg, consumed orally. The duration of action was stated to be 8–12 hours.
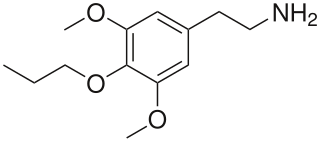
Proscaline (4-propoxy-3,5-DMPEA) is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug. It has structural properties similar to the drugs mescaline, isoproscaline, and escaline. In PiHKAL, Alexander Shulgin reports that a dose of 30–60 mg produces effects lasting 8–12 hours.

2C-T is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug of the 2C family. It is used by some as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs mescaline and 2C-T-2.
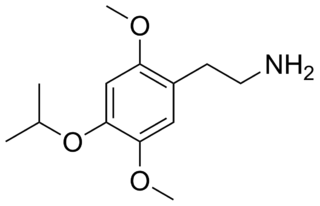
2C-O-4 (4-isopropoxy-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a phenethylamine of the 2C family. It is also a positional isomer of isoproscaline and was probably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. It produces hallucinogenic, psychedelic, and entheogenic effects. Because of the low potency of 2C-O-4, and the inactivity of 2C-O, Shulgin felt that the 2C-O series would not be an exciting area for research, and did not pursue any further analogues.

Isoproscaline or 4-isopropoxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine is an analog of mescaline. It is closely related to proscaline and was first synthesized by David E. Nichols. It produces hallucinogenic, psychedelic, and entheogenic effects.

4-Desoxymescaline, or 4-methyl-3,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine, is a mescaline analogue related to other psychedelic phenethylamines. It is commonly referred to as DESOXY. DESOXY was discovered by Alexander Shulgin and published in his book PiHKAL.

2C-F (4-fluoro-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 250 mg. 2C-F may be found as a brownish freebase oil, or as a white crystalline hydrochloride salt.

Aleph is a psychedelic hallucinogenic drug and a substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine class of compounds, which can be used as an entheogen. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, Shulgin lists the dosage range as 5–10 mg. According to Shulgin, the effects of aleph typically last for 6 to 8 hours.
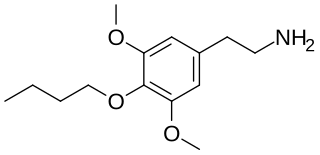
Buscaline (3,5-dimethoxy-4-butoxyphenethylamine) is a chemical compound prepared as a possible psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. Buscaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 150 mg, and the duration is "several hours". Buscaline produces no psychedelic or psychoactive effects, but causes heart arrythmia and light diarrhea. It does not cause any visuals or insights. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of buscaline.

Phenescaline, or 3,5-dimethoxy-4-phenylethoxyphenethylamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. Phenescaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the minimum dosage is listed as 150 mg, and the duration is unknown. Phenescaline produces a threshold effect. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of phenescaline.
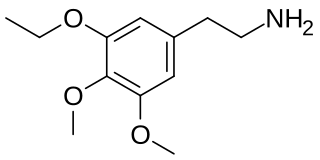
Metaescaline (3,4-dimethoxy-5-ethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. Metaescaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 200–350 mg, and the duration listed as 8–12 hours. Metaescaline produces mental insights, entactogenic, MDMA-like effects, and TOMSO-like activation. Little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of metaescaline, though it has been studied to a limited extent in comparison with other related compounds.

AEM is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. AEM was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 220 mg, and the duration unknown. AEM produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of AEM.

BOD (4-methyl-2,5,β-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the beta-methoxy analog of 2C-D. BOD was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 15–25 mg, and the duration listed as 8–16 hours. BOD produces strongly distorted open-eye visuals, and some closed-eye visuals. It also has an entheogenic effect and produces humor. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of BOD.

BOM (3,4,5,beta-tetramethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the beta-methoxy derivative of mescaline. BOM was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 200 mg, and the duration unknown. BOM produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about its pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity.

4-D (3,5-methoxy-4-trideuteromethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known recreational psychedelic drug. It is one of the few drugs that bears deuterium. It is a deuterated analog of mescaline. It may be prepared either as a sulfate salt or a hydrochloride salt. 4-D was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage is listed as approximately 200–400 mg for the sulfate salt, and 178–356 mg for the hydrochloride salt. 4-D lasts for approximately 12 hours. It causes closed-eye visuals, mild open-eye visuals, color distortion, and mydriasis. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 4-D.
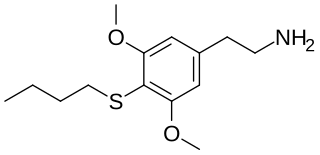
Thiobuscaline, or 3,5-dimethoxy-4-butylthiophenethylamine]], is a lesser-known psychedelic drug.
Thiomescaline (TM) is a pair of lesser-known psychedelic drugs with the molecular formula C11H17NO2S. 3-TM and 4-TM are analogs of mescaline in which an oxygen atom has been replaced with a sulfur atom. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and described in his book PiHKAL. Very little data exists on the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of thiomescaline.

Thioproscaline, or 3,5-dimethoxy-4-propylthiophenethylamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the 4-propylthio analog of mescaline. Thioproscaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the dosage range is listed as 20–25 mg, and the duration listed as 10–15 hours. Thioproscaline causes closed-eye visuals, slight open-eye visuals, and a body load. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of thioproscaline.

2C-Se is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It was originally named by Alexander Shulgin as described in his book PiHKAL. Shulgin considered 2C-Se to be around three times the potency of mescaline, but was too concerned about toxicity to test it extensively, though he considered it noteworthy as the only psychedelic drug to contain a selenium atom.




















