
The sitar is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in medieval India and flourished in the 16th and 17th centuries and arrived at its present form in 18th-century India.
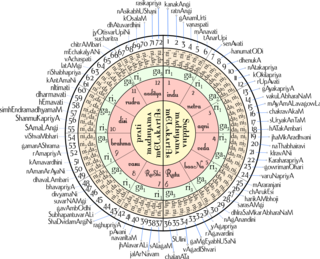
A raga or raag is a melodic framework for improvisation akin to a melodic mode in Indian classical music. The rāga is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a result has no direct translation to concepts in classical European music. Each rāga is an array of melodic structures with musical motifs, considered in the Indian tradition to have the ability to "colour the mind" and affect the emotions of the audience.

Indian classical music is the classical music of the Indian subcontinent. It has two major traditions: the North Indian classical music tradition is called Hindustani, while the South Indian expression is called Carnatic. These traditions were not distinct until about the 15th century. During the period of Mughal rule of the Indian subcontinent, the traditions separated and evolved into distinct forms. Hindustani music emphasizes improvisation and exploration of all aspects of a raga, while Carnatic performances tend to be short composition-based. However, the two systems continue to have more common features than differences.

The sarod is a stringed instrument, used mainly in Hindustani music on the Indian subcontinent. Along with the sitar, it is among the most popular and prominent instruments. It is known for a deep, weighty, introspective sound, in contrast with the sweet, overtone-rich texture of the sitar, with sympathetic strings that give it a resonant, reverberant quality. A fretless instrument, it can produce the continuous slides between notes known as meend (glissandi), which are important in Indian music.

The Rudra veena —also called Bīn in North India—is a large plucked string instrument used in Hindustani classical music, especially dhrupad. It is one of the major types of veena played in Indian classical music, notable for its deep bass resonance.

The vichitra veena (Sanskrit: विचित्र वीणा is a stick zither, a plucked string instrument used in Hindustani music. Similar to the Carnatic gottuvadhyam it has no frets and is played with a slide.

The Sarasvati vīṇa is an Indian plucked veena. It is named after the Hindu goddess Saraswati, who is usually depicted holding or playing the instrument. Also known as raghunatha veena is used mostly in Carnatic Indian classical music. There are several variations of the veena, which in its South Indian form is a member of the lute family. One who plays the veena is referred to as a vainika.
Lalmani Misra was an eminent Indian classical musician known as much for his art as for his scholarship.
Gopal Shankar Mishra was an Indian musician and music teacher, who played the vichitra veena.

The Jal Tarang is a melodic percussion instrument that originates from the Indian subcontinent. It consists of a set of ceramic or metal bowls filled with water. The bowls are played by striking the edge with beaters, one in each hand.
The Maihar Band is an instrumental musical group in the Indian city of Maihar that performs both Indian and western music. After an epidemic orphaned many children, Allauddin Khan, a musician of the Maihar court who was moved by the tragedy, taught them how to play music and formed an orchestral group later known as the Maihar Band. The ruling prince, Braj Nath Singh, cooperated and helped Allauddin Khan in procuring and preparing required instruments.
Mushtaq Ali Khan and was an Indian classical sitar, surbahar player.

Asad Ali Khan was an Indian musician who played the plucked string instrument rudra veena. Khan performed in the style dhrupad and was described as the best living rudra veena player in India by The Hindu. He was awarded the Indian civilian honor Padma Bhushan in 2008.

Pandit Gopal Krishan Sharma (1926-2004) was an exponent of Vichitra Veena, an ancient Indian musical instrument.

The veena, also spelled vina, comprises a family of chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent. Ancient musical instruments evolved into many variations, such as lutes, zithers and arched harps. The many regional designs have different names such as the Rudra veena, the Saraswati veena, the Vichitra veena and others.

Ragini Trivedi is an Indian classical musician performing on vichitra veena, sitar and jal tarang. Daughter of the vichitra veena player and musicologist Lalmani Misra, she is an exponent of Misrabani and is the creator of a digital music notation system called Ome Swarlipi.
Bindu Madhav Pathak was an exponent of rudra veena and Sitar. He played Khayal style of music on been. He was an 'A' grade artist of All India Radio. Some of his famous students are Hindraj Divekar, Shrikant Pathak, Ramchandra V Hegde and Jyoti Hegde. He was a recipient of several awards and titles, including the Karnataka Kala Tilak Award, Sri Kanak Purandhar Prashasti, Arya Bhata Award, and "Vidyaparipoorna" title. Pathak retired as the Head of the Department of Music of Karnatak University. He died at 68 on 4 February 2004.

Brahm Sarup Singh was a renowned player of vichitra veena. He was born in the city of Amritsar, India to the Late Shri Harnam Singh who was a disciple of Ustad Abdul Aziz Khan.
Wahid Khan, more commonly known as Wahid Khan Beenkar or Indorewale Wahid Khan, was an Indian classical rudra veena player and, along with his younger brother Ghagge Nazir Khan, founded the Mewati gharana, later popularized by Pandit Jasraj and Rais Khan.

The eka-tantrī vīṇā was a medieval tube-zither veena in India, with a single string and one or more gourd resonators. The instrument became prominent in Indian music in about the 10th century C.E. as instruments of court music. Alongside the alapini vina and kinnari vina it replaced the harp-style veenas and lute-style veenas in sculpture. It was possibly a forerunner of the rudra vina. It shares its name with the modern single-string drone lute, the ektara.













