
The South East Central Railway is one of the 19 Railway Zones in India. The Zone Office is headquartered at Bilaspur and comprises the Bilaspur, Nagpur and Raipur Division.

Gondia is a city and municipal council in the Indian state of Maharashtra which serves the administrative headquarters of the eponymous administrative district. Gondia is also known as Rice City due to the abundance of rice mills in the area. Gondia Airport is the only airport in the district.
National Highway 6 & Economic Corridor 1 (EC1), was a National Highway in India that has been separately designated under the new national highway numbering system. It was officially listed as running over 1,949 km (1,211 mi) from Surat to Kolkata. The route was also known as Asian Highway 46 (AH46) & Mumbai - Kolkata Highway and Great Eastern Highway.

Itarsi Junction railway station is a junction railway station in Hoshangabad district in Madhya Pradesh from which more than 420 trains pass every day. It is the 8th busiest railway junction in India. It falls under the West Central Railway zone of Indian Railways network. It is located 18 kilometres (11 mi) away from Hoshangabad by train, and by road it is 20 kilometers. It is one of the most important junction stations, behind Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Junction and Nagpur Junction. In 2015 the signal control system was gutted in a fire incident resulting in hundreds of trains being cancelled for over 30 days till normality was restored.

Asansol Junction is a railway station of Eastern Railway in Asansol of Paschim Bardhaman district in the Indian state of West Bengal. The station is on the Howrah–Delhi main line. It is the 8th busiest railway station in India in terms of frequency of trains after Kanpur Central, Vijayawada Junction, Delhi Junction, New Delhi, Ambala Cant, Howrah and Patna Junction. Around 171 trains pass through the station daily. It serves Asansol and the surrounding areas.

The Asansol–Gaya section is a railway line connecting Asansol and Gaya in India. This 267-kilometre long (166 mi) track is part of the Grand Chord, Howrah–Gaya–Delhi line and Howrah–Allahabad–Mumbai line. This section includes the NSC Bose Gomoh–Barkakana line. It is under the jurisdiction of Eastern Railway and East Central Railway. The section links to South Eastern Railway through Bokaro Steel City and Adra.
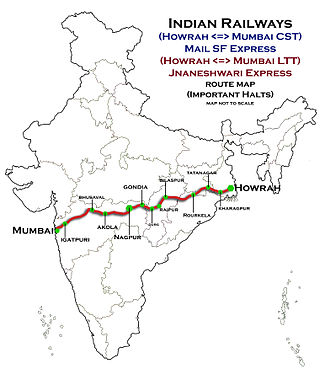
The Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line is a railway line in India connecting Kolkata and Mumbai via Nagpur. The 1,968-kilometre-long (1,223 mi) railway line was opened to traffic in 1900.

Rourkela Junction railway station is a railway junction located in the north-western part of the Indian state of Odisha and serves Rourkela in Sundergarh district. Rourkela is the third-largest urban agglomeration in Odisha.

The Bilaspur–Nagpur section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects Bilaspur in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and Nagpur in Maharashtra. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through a forested plateau region interspersed with fertile valleys.
Gondia Junction serves Gondia in Gondia district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is one of the important railway stations in India of South East central railways zone railways. This station is India's third and first in Vidarbha to get mist cooling system.Its falls under nagpur division

Raipur Junction is the main railway station serving the city of Raipur. It is only few of the railway stations in India which has been given the grade 'A-1' by the Indian Railways and is one of the highest-revenue-earning railway stations in India. This station is one of the prominent stations on the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line. It is also the originating point of the Raipur–Vizianagarm branch line route. Raipur is the busiest railway station in South Eastern Central Railway zone.

Durg Junction Railway Station, is a junction station located in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. It serves Durg, Bhilai city and the adjoining areas of it. Durg Junction is the part of South East Central Railway. It is one of the largest railway junctions of Chhattisgarh in terms of network. It is also one of the most prominent and important station in Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line. It is an 'A' grade station of Indian Railways in terms of passenger services.

The Nagpur–Bhusawal section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects Nagpur and Bhusawal both in the Indian state of Maharashtra. This section also has a number of branch lines. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, Nagpur–Bhusawal section passes through a section of the Deccan Plateau. The main line crosses Nagpur, Wardha, Amravati, Akola, and Buldhana districts of Vidarbha region and Jalgaon district of Khandesh region.

The Howrah–Kharagpur line is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line, Howrah–Chennai main line and Kolkata Suburban Railway.

The Jabalpur–Bhusaval section is a railway line connecting Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh and Bhusaval, Maharashtra. This 552 km (343 mi) track is part of the Howrah–Allahabad–Mumbai line, one of the busiest railways in India. The line is under the jurisdiction of West Central Railway and Central Railway.

The Netaji S.C.Bose Gomoh–Hatia line is a railway line connecting NSC Bose Gomoh and Hatia in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It is under the jurisdiction of East Central Railway and South Eastern Railway.

Tumsar Road Junction railway station serves Tumsar City and the surrounding area in Bhandara district in Maharashtra, India. The station consists of five platforms. The platforms are not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation.

Dongargarh Railway Station(DGG) is a busy railway station in Mumbai–Howrah rail zone in SECR. It is situated in Dongargarh town in Rajnandgaon district of Chhattisgarh state. It is a very important railway junction near Rajnandgaon railway station. It is midway between Jatkanhar and Paniajob. DGG is main station to reach Bambleshwari Temple.

The Barkakana–Netaji S.C.Bose Gomoh line is a railway line connecting Barkakana and Gomoh in India. This 105-kilometre long (65 mi) track is under the jurisdiction of East Central Railway. The section links to South Eastern Railway through Bokaro Steel City and Adra.

Electric Loco Shed, Asansol is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at Asansol of the Eastern Railway zone in West Bengal, India. It is one of the two electric locomotive sheds of the Eastern Railway, the others being at Howrah (HWH). As of November,2022, there are 142 locomotives in the shed.




















