Chhattisgarh is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Pradesh to the northwest, Maharashtra to the southwest, Jharkhand to the northeast, Odisha to the east, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana to the south. Formerly a part of Madhya Pradesh, it was granted statehood on 1 November 2000 with Raipur as the designated state capital.

Indravati River is a tributary of the Godavari River, in central India.

Dantewada District, also known as Dantewara District or Dakshin Bastar District, is a district in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. Dantewada is the district headquarters. The district is part of Bastar Division. Until 1998, Dantewada District was a tehsil of the larger Bastar District.

Jagdalpur is a city located in the southern part of Chhattisgarh state in India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Bastar district and Bastar division. Before the independence of India, it also served as the capital of the erstwhile princely state of Bastar.

Bastar division is an administrative division of Chhattisgarh state in central India. It includes the districts of Bastar, Dantewada, Bijapur, Narayanpur, Sukma, Kondagaon and Kanker.
National Highway 63 is a National Highway in India, total length 961 km (597 mi). It passes through the states of Maharashtra, Telangana, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh & Odisha.
Muppala Lakshmana Rao, commonly known by his nom de guerre Ganapathy or Ganapathi, is the leader of the Indian Maoist movement and former General Secretary of the Communist Party of India (Maoist), a banned Maoist insurgent communist party in India. He resigned from the post in November 2018.

The Naxalite–Maoist insurgency is part of an ongoing conflict between Left-wing extremist groups and the Indian government. The insurgency started after the 1967 Naxalbari uprising and the subsequent split of the Communist Party of India (Marxist) leading to the creation of a Marxist–Leninist faction. The faction splintered into various groups supportive of Maoist ideology, claiming to fight a rural rebellion and people's war against the government.

Bijapur District, formerly known as Birjapur, is one of the 27 districts of the state of Chhattisgarh in central India. It is one of the two new districts created on May 11, 2007. As of 2011 it is the second least populous district of Chhattisgarh, after Narayanpur. It is the second-least literate district in India, with a literacy rate of at 41.58%, according to the 2011 census.

The Chhattisgarh Police is the law enforcement agency for the state of Chhattisgarh in India. The agency is administered by the Department of Home Affairs of the Government of Chhattisgarh. The force has specialized units to fight the Naxalite–Maoist insurgency in some districts of the state.

Shaheed Mahendra Karma Vishwavidyalaya - (SMKV) or Bastar University , is a State university located in Jagdalpur, Chhattisgarh, India. It is a teaching-cum-affiliating university which affiliates 30 college and has 10 University Teaching Departments (UTD). It was established and incorporated by Chhattisgarh Vishwavidyalaya Adhiniyam No. 18 of 2008 on September 2, 2008.
On 25 May 2013, Naxalite insurgents of the Communist Party of India (Maoist) attacked a convoy of Indian National Congress leaders in the Jhiram Ghati, Darbha Valley in the Sukma district of Chhattisgarh, India. The attack caused at least 27 deaths, including that of former state minister Mahendra Karma and Chhattisgarh Congress chief Nand Kumar Patel. Vidya Charan Shukla, a senior Congress leader, succumbed to his injuries on 11 June 2013.
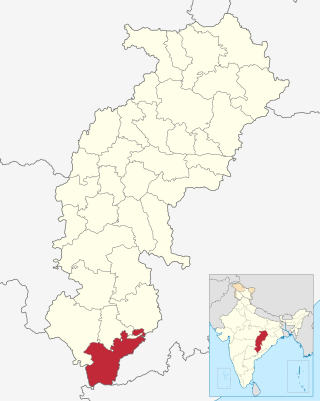
Sukma district is the southernmost district in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. It is located in the Bastar region, known for its tribal culture. Sukma district borders with Odisha, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
Bijapur is a town in Bijapur district, Chhattisgarh, India. It is the seat of the district and one of the 4 taluks in Bijapur district. The Bijapur taluk has an area of 928 km2 and 60,055 inhabitants. It is situated on the National Highway 16 which connects Nizamabad in Telangana with Jagdalpur in southeastern Chhattisgarh.

Abujhmarh is a hilly forest area, spread over 4,000 square kilometres (1,500 sq mi) in Chhattisgarh, covering Narayanpur district, Bijapur district and Dantewada district. It is home to indigenous tribes of India, including Gond, Muria, Abujhmarhia, Madiya, and Halba. It was only in 2009 that the Government of Chhattisgarh lifted the restriction on the entry of common people in the area imposed in the early 1980s. Geographically isolated and largely inaccessible, the area continues to show no physical presence of the civil administration, and is also known as "liberated-zone" as it is an alleged hub of Naxalite-Maoist insurgency, the banned Communist Party of India (Maoist) and its military wing, People's Liberation Guerilla Army (PLGA), who run a parallel government in the area.
National Highway 163 is a National Highway in India that links Kodangal(Ravulapally) in Telangana and Bhopalpatnam road in Chhattisgarh Via major cities like Hyderabad, Uppal, Ghatkesar, Bhuvanagiri, Jangaon, Kazipet, Hanamkonda, Warangal. It was renumbered as NH 163. Currently there was a proposal for extension of NH 163 Pre-starting point to Hyderabad.

Tourism is an important part of the economy of the Indian state of Chhattisgarh, India's tenth largest state. The state has many ancient monuments, rare wildlife, carved temples, Buddhist sites, palaces, water falls, caves, rock paintings and hill plateaus.

The 2018 Chhattisgarh Legislative Assembly election was held to elect members to the Legislative Assembly of the Indian State of Chhattisgarh. The election was held in two phases for a total of 90 seats; the first for 18 seats in South Chhattisgarh was held on 12 November 2018, and the second for the remaining 72 were held on 20 November.

Vivekanand Sinha is the Inspector General of Police of the Durg range of Chhattisgarh. He has previously served as the Inspector General of Police of Bastar region of Chhattisgarh. He has been an IPS since 1996. He was appointed as the head of the Special Investigation Team (SIT) for the investigation of Jhiram Valley Attack by government of Chhattisgarh on 2 January 2019. The Jhiram Valley Attack was a naxal attack which killed top Congress leaders of Chhattisgarh in 2013 during a political rally in Darbha. The new SIT has been formed by the newly elected Congress government of Chhattisgarh to probe into it He has also served as the DIG of Special Protection Group which looks after the security of the Prime Minister of India. During his tenure as IG in Bilaspur, Sinha walked on coal barefoot to convince the locals that there is no magic in walking on coal. This was done to strengthen the human rights of women who were being harassed or boycotted after being labelled as witches.
The 2021 Sukma-Bijapur attack was an ambush carried out by the Naxalite-Maoist militants from the Communist Party of India (Maoist) against Indian security forces on 3 April 2021 at Sukma-Bijapur border near Jonaguda village which falls under Jagargunda police station area in Sukma district of Chhattisgarh, the ensuing gunfight lead to the killing of 22 security personnel as well as 20 Naxalites. The death toll was the worst for Indian security forces fighting the Naxalites since 2017.