
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancreatitis.

In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats.

A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts.
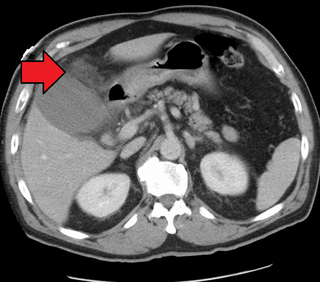
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include right upper abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks precede acute cholecystitis. The pain lasts longer in cholecystitis than in a typical gallbladder attack. Without appropriate treatment, recurrent episodes of cholecystitis are common. Complications of acute cholecystitis include gallstone pancreatitis, common bile duct stones, or inflammation of the common bile duct.

In medicine, a stent is a tube usually constructed of a metallic alloy or a polymer. It is inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open. Stenting refers to the placement of a stent. The word "stent" is also used as a verb to describe the placement of such a device, particularly when a disease such as atherosclerosis has pathologically narrowed a structure such as an artery.

Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique.

Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skilled and specialty trained gastroenterologists. Through the endoscope, the physician can see the inside of the stomach and duodenum, and inject a contrast medium into the ducts in the biliary tree and pancreas so they can be seen on radiographs.
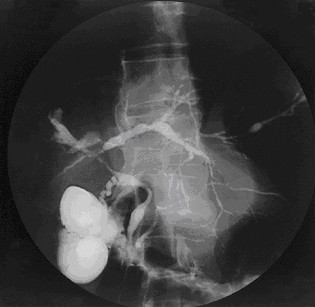
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may have no symptoms or may experience signs and symptoms of liver disease, such as yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes, itching, and abdominal pain.

Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes, in order of frequency, include: a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; heavy alcohol use; systemic disease; trauma; and, in children, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis and/or pancreatic failure.

Common bile duct stone, also known as choledocholithiasis, is the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD). This condition can cause jaundice and liver cell damage. Treatments include choledocholithotomy and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).

Ascending cholangitis, also known as acute cholangitis or simply cholangitis, is inflammation of the bile duct, usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum. It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome (PCS) describes the presence of abdominal symptoms after a cholecystectomy.
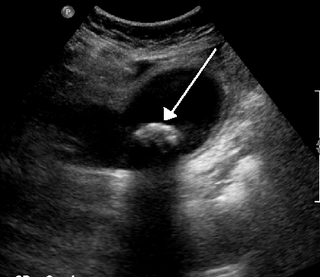
Biliary colic, also known as symptomatic cholelithiasis, a gallbladder attack or gallstone attack, is when a colic occurs due to a gallstone temporarily blocking the cystic duct. Typically, the pain is in the right upper part of the abdomen, and can be severe. Pain usually lasts from 15 minutes to a few hours. Often, it occurs after eating a heavy meal, or during the night. Repeated attacks are common. Cholecystokinin - a gastrointestinal hormone - plays a role in the colic, as following the consumption of fatty meals, the hormone triggers the gallbladder to contract, which may expel stones into the duct and temporarily block it until being successfully passed.
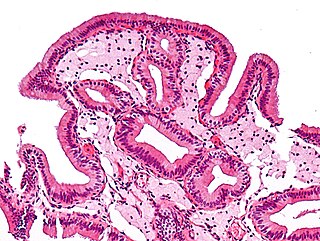
Gallbladder diseases are diseases involving the gallbladder and is closely linked to biliary disease, with the most common cause being gallstones (cholelithiasis).
Cholecystostomy or (cholecystotomy) is a medical procedure used to drain the gallbladder through either a percutaneous or endoscopic approach. The procedure involves creating a stoma in the gallbladder, which can facilitate placement of a tube or stent for drainage, first performed by American surgeon, Dr. John Stough Bobbs, in 1867. It is sometimes used in cases of cholecystitis or other gallbladder disease where the person is ill, and there is a need to delay or defer cholecystectomy. The first endoscopic cholecystostomy was performed by Drs. Todd Baron and Mark Topazian in 2007 using ultrasound guidance to puncture the stomach wall and place a plastic biliary catheter for gallbladder drainage.

Biliary pseudolithiasis is an unusual complication of ceftriaxone where the drug complexes with calcium and mimics gallstones. It is reversed when ceftriaxone administration is stopped. It was first described in 1988 by Schaad et al. as "reversible ceftriaxone-associated biliary pseudolithiasis". Ceftriaxone has been frequently associated with biliary sludge or biliary pseudolithiasis in subsequent reports. Ceftriaxone is excreted primarily through the urine, but also through the bile, up to 40% of its excretion, with concentrations in the bile 20-150 times higher than in the serum. It forms a calcium salt in the gallbladder, which can exceed its solubility and create precipitates that resemble gallstones on ultrasonography. The incidence of pseudolithiasis in children treated with ceftriaxone is up to 25%, but most patients are asymptomatic. Risk factors for biliary pseudolithiasis include age greater than 24 months, gram-negative sepsis, high doses of ceftriaxone, hypercalcemia, surgery, and decreased bile flow/increased ceftriaxone excretion in bile. Conservative management with serial ultrasounds is recommended until the "stones" completely resolve. If associated with ceftriaxone, it resolves on average about 2 weeks after the ceftriaxone is stopped.

A biloma is a circumscribed abdominal collection of bile outside the biliary tree. It occurs when there is excess bile in the abdominal cavity. It can occur during or after a bile leak. There is an increased chance of a person developing biloma after having a gallbladder removal surgery, known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy. This procedure can be complicated by biloma with incidence of 0.3–2%. Other causes are liver biopsy, abdominal trauma, and, rarely, spontaneous perforation. The formation of biloma does not occur frequently. Biliary fistulas are also caused by injury to the bile duct and can result in the formation of bile leaks. Biliary fistulas are abnormal communications between organs and the biliary tract. Once diagnosed, they usually require drainage. The term "biloma" was first coined in 1979 by Gould and Patel. They discovered it in a case with extrahepatic bile leakage. The cause of this was trauma to the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. Originally, biloma was described as an "encapsulated collection" of extrahepatic bile. Biloma is now described as extrabiliary collections of bile that can be either intrahepatic or extrahepatic. The most common cause of biloma is trauma to the liver. There are other causes such as abdominal surgery, endoscopic surgery and percutaneous catheter drainage. Injury and abdominal trauma can cause damage to the biliary tree. The biliary tree is a system of vessels that direct secreations from the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas through a series of ducts into the duodenum. This can result in a bile leak which is a common cause of the formation of biloma. It is possible for biloma to be associated with mortality, though it is not common. Bile leaks occur in about one percent of causes.
Canine gallbladder mucocele (GBM) is an emerging biliary disease in dogs described as the excessive and abnormal accumulation of thick, gelatinous mucus in the lumen, which results in an enlarged gallbladder. GBMs have been diagnosed more frequently in comparison to prior to the 2000s when it was considered rare. The mucus is usually pale yellow to dark green in appearance.

Choledochoduodenostomy (CDD) is a surgical procedure to create an anastomosis, a surgical connection, between the common bile duct (CBD) and an alternative portion of the duodenum. In healthy individuals, the CBD meets the pancreatic duct at the ampulla of Vater, which drains via the major duodenal papilla to the second part of duodenum. In cases of benign conditions such as narrowing of the distal CBD or recurrent CBD stones, performing a CDD provides the diseased patient with CBD drainage and decompression. A side-to-side anastomosis is usually performed.

Biliary endoscopic sphincterotomy is a procedure where the sphincter of Oddi and the segment of the common bile duct where it enters the duodenum are cannulated and then cut with a sphincterotome, a device that includes a wire which cuts with an electric current (electrocautery).

















