Related Research Articles

The Lumière brothers, Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas Lumière and Louis Jean Lumière, were manufacturers of photography equipment, best known for their Cinématographe motion picture system and the short films they produced between 1895 and 1905 which places them among the earliest filmmakers.

The National Science and Media Museum, located in Bradford, West Yorkshire, is part of the national Science Museum Group in the UK. The museum has seven floors of galleries with permanent exhibitions focusing on photography, television, animation, videogaming, the Internet and the scientific principles behind light and colour. It also hosts temporary exhibitions and maintains a collection of 3.5 million pieces in its research facility.

Imperial War Museums (IWM) is a British national museum organisation with branches at five locations in England, three of which are in London. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, the museum was intended to record the civil and military war effort and sacrifice of Britain and its Empire during the First World War. The museum's remit has since expanded to include all conflicts in which British or Commonwealth forces have been involved since 1914. As of 2012, the museum aims "to provide for, and to encourage, the study and understanding of the history of modern war and 'wartime experience'."

Film preservation, or film restoration, describes a series of ongoing efforts among film historians, archivists, museums, cinematheques, and non-profit organizations to rescue decaying film stock and preserve the images they contain. In the widest sense, preservation assures that a movie will continue to exist in as close to its original form as possible.

William Gerald Forbes Douglas was a Scottish film director best known for the trilogy of films about his early life.
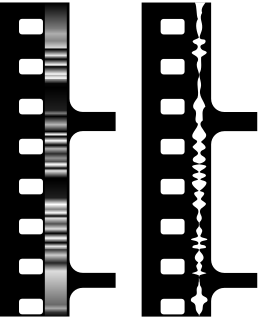
The Movietone sound system is an optical sound-on-film method of recording sound for motion pictures that guarantees synchronization between sound and picture. It achieves this by recording the sound as a variable-density optical track on the same strip of film that records the pictures. The initial version was capable of a frequency response of 8500 Hz. Although sound films today use variable-area tracks, any modern motion picture theater can play a Movietone film without modification to the projector. Movietone was one of four motion picture sound systems under development in the U.S. during the 1920s, the others being DeForest Phonofilm, Warner Brothers' Vitaphone, and RCA Photophone, though Phonofilm was primarily an early version of Movietone.

The Irish Film Institute, formerly the Irish Film Centre, is both an arthouse cinema and a national body that supports Irish Film heritage. The IFI presents film festivals, retrospectives and curated seasons, along with independent, Irish and foreign language films overlooked by commercial multiplexes at its cinemas in the Temple Bar quarter of Dublin. It maintains an archive of Irish films and provides education in film culture.

The George Eastman Museum, the world's oldest museum dedicated to photography and one of the world's oldest film archives, opened to the public in 1949 in Rochester, New York.

The Type Archive is a collection of artefacts representing the legacy of type founding in England, whose famous type foundries and composing systems supplied the world with type in over 300 languages. The Archive was founded in 1992 by Susan Shaw in Stockwell, South London.

The National Film and Sound Archive of Australia (NFSA), known as ScreenSound Australia from 1999 to 2004, is Australia's audiovisual archive, responsible for developing, preserving, maintaining, promoting and providing access to a national collection of film, television, sound, radio, video games, new media, and related documents and artefacts. The collection ranges from works created in the late nineteenth century when the recorded sound and film industries were in their infancy, to those made in the present day.

The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts, Dorothy and Lewis B. Cullman Center, at 40 Lincoln Center Plaza, is located in Manhattan, New York City, at the Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts on the Upper West Side, between the Metropolitan Opera House and the Vivian Beaumont Theater. It houses one of the world's largest collections of materials relating to the performing arts. It is one of the four research centers of the New York Public Library's Research library system, and it is also one of the branch libraries.

Eye Film Institute Netherlands is a film archive, museum, and cinema in Amsterdam that preserves and presents both Dutch and foreign films screened in the Netherlands.

The Cinema Museum is a museum in Kennington, London, and a charitable organisation. Its collection was founded in 1986 by Ronald Grant and Martin Humphries, from their own private collection of cinema history and memorabilia. Its current building was once a workhouse where Charlie Chaplin lived as a child.
The Steven Spielberg Jewish Film Archive is dedicated to the preservation and research of Jewish documentary films. The archive is jointly administered by the Abraham Harman Institute of Contemporary Jewry at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and the Central Zionist Archives of the World Zionist Organization (WZO).

The Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research (WCFTR) is a major archive of motion picture, television, radio, and theater research materials. Located in the headquarters building of the Wisconsin Historical Society in Madison, Wisconsin, the WCFTR holds over three hundred collections from motion picture, television, and theater writers, producers, actors, designers, directors, and production companies. These collections include business records, personal papers, scripts, photographs, promotional graphics, and some twenty thousand films and videotapes of motion picture and television productions.

The Munich Film Archive, in the Munich Stadtmuseum, is one of six film museums in Germany. It has no showrooms and is limited to screening the films in a single cinema with 165 seats, as well as collecting, archiving, and restoring film copies. All analog and digital formats can be shown.

The Film Reference Library (FRL) is Canada’s film research collection located on the 4th floor of TIFF Bell Lightbox, a cultural centre in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The library is a free resource for students, filmmakers, scholars, and journalists. The library is affiliated to International Federation of Film Archives (FIAF), to promote Canadian and global film scholarship by collecting, preserving, and providing access to a comprehensive collection of film prints, and film-related reference resources including books, periodicals, scripts, research files, movies, press kits.
The Yale Film Archive is a film archive located in Sterling Memorial Library at Yale University, and is part of the Yale University Library. The film collection consists of more than 7,000 35mm, 16mm, 8mm, and Super 8mm prints and the video collection includes more than 50,000 items on DVD, Blu-ray, LaserDisc, and VHS. The Film Archive engages in the conservation, preservation, presentation, and circulation of moving image materials. The Yale Film Archive is an Associate of the International Federation of Film Archives.

Gosfilmofond is a state film archive in Russia. It is the main film archive of the Russian Federation and a member of the International Federation of Film Archives (FIAF). It is a state cultural institution — curator of films collection and other materials, engaged in collecting, creative production, cultural and educational, research, methodological and informational activities in the field of cinematography. The collection includes some historic American films. The Director-General is Nikolay Malakov.

African American cinema, also known as Black film, is loosely classified as films made by, for, or about Black Americans. Historically, African American films have been made with African-American casts and marketed to African-American audiences. The production team and director were sometimes also African American. More recently, Black films featuring multicultural casts aimed at multicultural audiences have also included American Blackness as an essential aspect of the storyline.
References
- ↑ Vowles, Charlotte (10 July 2021). "Exeter's hidden gem is a film fan's dreamland". DevonLive. Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- ↑ "Home". www.bdcmuseum.org.uk. The Bill Douglas Cinema Museum. Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- ↑ "Unique collection of silent movie artefacts donated to cinema museum". independent. Retrieved 4 October 2021.
