
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances.

Bioremediation is a process used to treat contaminated media, including water, soil and subsurface material, by altering environmental conditions to stimulate growth of microorganisms that degrade the target pollutants. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic activities, such as industrialization and agricultural processes. Bioremediation could prove less expensive and more sustainable than other remediation alternatives.

Geobacter is a genus of bacteria. Geobacter species are anaerobic respiration bacterial species which have capabilities that make them useful in bioremediation. Geobacter was found to be the first organism with the ability to oxidize organic compounds and metals, including iron, radioactive metals, and petroleum compounds into environmentally benign carbon dioxide while using iron oxide or other available metals as electron acceptors. Geobacter species are also found to be able to respire upon a graphite electrode. They have been found in anaerobic conditions in soils and aquatic sediment.
Biodegradability prediction is biologically inspired computing and attempts to predict biodegradability of anthropogenic materials in the environment. Demand for biodegradability prediction is expected to increase with governments stepping up environmental regulations.
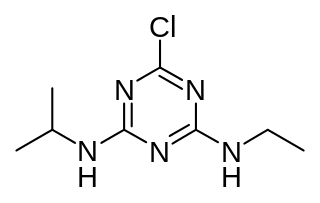
Atrazine is a herbicide of the triazine class. It is used to prevent pre-emergence broadleaf weeds in crops such as maize (corn) and sugarcane and on turf, such as golf courses and residential lawns. Atrazine's primary manufacturer is Syngenta and it is one of the most widely used herbicides in the United States and Australian agriculture.

Biodegradable plastics are plastics that can be decomposed by the action of living organisms, usually microbes, into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. Biodegradable plastics are commonly produced with renewable raw materials, micro-organisms, petrochemicals, or combinations of all three.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Society for Microbiology. It was established in 1953 as Applied Microbiology and obtained its current name in 1975. Articles older than six months are available free of cost from the website, however, the newly published articles within six months are available to subscribers only. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 4.792. The journal has been ranked as one of the top 100 journals over the past 100 years in the fields of biology and medicine. The current editor-in-chief is Gemma Reguera.
Microbial biodegradation is the use of bioremediation and biotransformation methods to harness the naturally occurring ability of microbial xenobiotic metabolism to degrade, transform or accumulate environmental pollutants, including hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), heterocyclic compounds, pharmaceutical substances, radionuclides and metals.
The Institute of Microbial Technology (IMTECH), based in Chandigarh, India, is one of the constituent establishments of the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR). It was established in 1984.
OXO-degradation is the degradation of polymers such as plastic by an oxidative process. Such degradation breaks down plastic into small pieces that are easier to biodegrade. When biodegradation does happen fast enough, either simultaneously or successively, the combined process becomes OXO-biodegradation and would break the polymer down to simple molecules.

Microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular, multicellular, or acellular. Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology and parasitology.
S-200 is a bioremediation product used to clean up oil spills. It is an oleophilic nitrogen-phosphorus nutrient that promotes the growth of micro-organisms that degrade hydrocarbons. S-200 bonds to the hydrocarbon to eliminate the need to reapply in tidal or rain events. S-200 is identified as a bioremediation accelerator and as such, does not contain bacterial cultures, but rather contributes to the establishment of a robust microbial population. In the laboratory, considerable biodegradation to alkanes was seen over the course of treatment. Field trials have yielded inconsistent results.

Hydroxyquinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The compound is a colorless solid that is soluble in water. It reacts with air to give a black insoluble solid.
A microbial consortium or microbial community, is two or more bacterial or microbial groups living symbiotically. Consortiums can be endosymbiotic or ectosymbiotic, or occasionally may be both. The protist Mixotricha paradoxa, itself an endosymbiont of the Mastotermes darwiniensis termite, is always found as a consortium of at least one endosymbiotic coccus, multiple ectosymbiotic species of flagellate or ciliate bacteria, and at least one species of helical Treponema bacteria that forms the basis of Mixotricha protists' locomotion.
Biodegradable additives are additives that enhance the biodegradation of polymers by allowing microorganisms to utilize the carbon within the polymer chain as a source of energy. Biodegradable additives attract microorganisms to the polymer through quorum sensing after biofilm creation on the plastic product. Additives are generally in masterbatch formation that use carrier resins such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS) or polyethylene terephthalate (PET).

The Plastisphere is a term used to refer to ecosystems that have evolved to live in human-made plastic environments. All the plastic that is accumulating in marine ecosystems serve as a habitat for various types of microorganisms, which is where scientists coined the term Plastisphere. The use of plastic has increased twenty-fold since 1964, and it is expected to double by 2035. Despite efforts to implement recycling programs, recycling rates tend to be quite low. For instance, in the EU, only 29% of the plastic consumed is recycled. The plastic that does not reach a recycling facility or landfill, will most likely end up in our oceans due to accidental dumping of the waste, losses during transport, or direct disposal from boats. In 2010, it was estimated that 4 to 12 million metric tons (Mt) of plastic waste entered into marine ecosystems.
The Marine Unsaturated Model is a two-dimensional finite element model capable of simulating the migration of water and solutes in saturated-unsaturated porous media while accounting for the impact of solute concentration on water density and viscosity, as saltwater is heaving and more viscous than freshwater. The detailed formulation of the MARUN model is found in and. The model was used to investigate seepage flow in trenches and dams, the migration of brine following evaporation and, submarine groundwater discharge, and beach hydrodynamics to explain the persistence of some of the Exxon Valdez oil in Alaska beaches.

Botanical Studies is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all aspects of botany. It is published by Springer Science+Business Media and affiliated with the Institute of Plant and Microbial Biology. The editors-in-chief is Yu-Ming Ju. The journal was established in 1947 as the Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica, receiving its current title in 2006.

OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of omics and integrative biology published by Mary Ann Liebert. The journal was founded in 1995 as Genome Science and Technology, changing its name to Microbial & Comparative Genomics in 1997, eventually acquiring its current title in 2004. The journal is now edited by Vural Özdemir. Since 2008 the journal has been published online only.

Plastic degradation in marine bacteria describes when certain pelagic bacteria break down polymers and use them as a primary source of carbon for energy. Polymers such as polyethylene(PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are incredibly useful for their durability and relatively low cost of production, however it is their persistence and difficulty to be properly disposed of that is leading to pollution of the environment and disruption of natural processes. It is estimated that each year there are 9-14 million metric tons of plastic that are entering the ocean due to inefficient solutions for their disposal. The biochemical pathways that allow for certain microbes to break down these polymers into less harmful byproducts has been a topic of study to develop a suitable anti-pollutant.










