The Department of Internal Affairs (DIA) is the public service department of New Zealand charged with issuing passports; administering applications for citizenship and lottery grants; enforcing censorship and gambling laws; registering births, deaths, marriages and civil unions; supplying support services to ministers; and advising the government on a range of relevant policies and issues.

The Gender Recognition Act 2004 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that allows adults in the United Kingdom who have gender dysphoria to change their legal gender. It came into effect on 4 April 2005.

The Civil Partnership Act 2004 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, introduced by the Labour government, which grants civil partnerships in the United Kingdom the rights and responsibilities very similar to those in civil marriage. Initially the Act permitted only same-sex couples to form civil partnerships. This was altered to include opposite-sex couples in 2019. Civil partners are entitled to the same property rights as married couples, the same exemption as married couples regarding social security and pension benefits, and also the ability to exercise parental responsibility for a partner's children, as well as responsibility for reasonable maintenance of one's partner and their children, tenancy rights, full life insurance recognition, next-of-kin rights in hospitals, and others. There is a formal process for dissolving civil partnerships, akin to divorce.
Civil partnership in the United Kingdom is a form of civil union between couples open to both same-sex couples and opposite-sex couples. It was introduced via the Civil Partnership Act 2004 by the Labour government. The Act initially permitted only same-sex couples to form civil partnerships, but the law was expanded to include opposite-sex couples in 2019.
Civil union has been legal in New Zealand since 26 April 2005. The Civil Union Act 2004 to establish the institution of civil union for same-sex and opposite-sex couples was passed by the Parliament on 9 December 2004. The Act has been described as very similar to the Marriage Act 1955 with references to "marriage" replaced by "civil union". A companion bill, the Relationships Act, was passed shortly thereafter on 15 March 2005, to remove discriminatory provisions on the basis of relationship status from a range of statutes and regulations. As a result of these bills, all couples in New Zealand, whether married, in a civil union, or in a de facto partnership, now generally enjoy the same rights and undertake the same obligations. These rights extend to immigration, next-of-kin status, social welfare, matrimonial property and other areas. Non-married couples are not however permitted to adopt children, although people in non-marital relationships can adopt as individuals.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in New Zealand since 19 August 2013. A bill for legalisation was passed by the House of Representatives on 17 April 2013 by 77 votes to 44 and received royal assent on 19 April. It entered into force on 19 August, to allow time for the Department of Internal Affairs to make the necessary changes for marriage licensing and related documentation. New Zealand was the first country in Oceania, the fourth in the Southern Hemisphere, and the fifteenth overall to allow same-sex couples to marry. Civil unions have also been available for both same-sex and opposite-sex couples since 2005.

New Zealand lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights are some of the most extensive in the world. The protection of LGBT rights is advanced, relative to other countries in Oceania, and among the most liberal in the world, with the country being the first in the region to legalise same-sex marriage.

Miriam Bridelia Soljak was a pioneering New Zealand feminist, communist, unemployed rights activist and supporter of family planning efforts. Born in Thames, New Zealand, she was raised as a Catholic and studied to be a teacher. From 1898 to 1912, she taught in native schools, learning about Māori culture and becoming fluent in the language. In 1908, she married Peter Soljak, an immigrant from Dalmatia, now part of Croatia, but at the time part of the Austrian Empire. In 1919, because of war legislation, she was denaturalised and forced to register as an enemy alien, because of her marriage. Despite their divorce in 1939, Soljak was unable to recover her British nationality.

Family First New Zealand is a conservative Christian lobby group in New Zealand. It was founded in March 2006 by former Radio Rhema talkback radio host and South Auckland social-worker Bob McCoskrie who continues to be its National Director. Its 2006 stated objectives were to "seek to influence public policy affecting the rights and protection of families and promote a culture that values the family". In 2009 Victoria University religious studies professor Paul Morris said Family First was "successfully broadening the Christian agenda in New Zealand politics in a way never seen before". In 2020 Family First was described as "New Zealand's most formidable conservative campaigners". Family First was established by a trust deed under the Charitable Trusts Act 1957 in 2006, was registered as a charity in 2007 and deregistered in 2022.

Oceania is, like other regions, quite diverse in its laws regarding LGBT rights. This ranges from significant rights, including same-sex marriage – granted to the LGBT+ community in New Zealand, Australia, Guam, Hawaii, Easter Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Wallis and Futuna, New Caledonia, French Polynesia and the Pitcairn Islands – to remaining criminal penalties for homosexual activity in six countries and one territory. Although acceptance is growing across the Pacific, violence and social stigma remain issues for LGBT+ communities. This also leads to problems with healthcare, including access to HIV treatment in countries such as Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands where homosexuality is criminalised.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Australian state of New South Wales have most of the same rights and responsibilities as non-LGBT people.
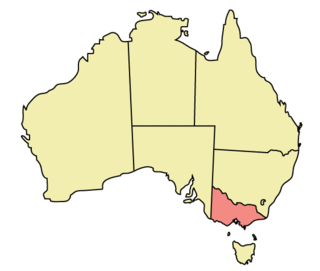
The Australian state of Victoria is regarded as one of the country's most progressive jurisdictions with respect to the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people. Victoria is the only state in Australia, that has implemented a LGBTIQA+ Commissioner.
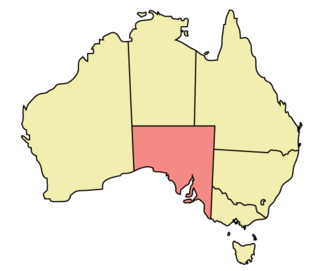
The rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Australian state of South Australia are advanced and well-established. South Australia has had a chequered history with respect to the rights of LGBT people. Initially, the state was a national pioneer of LGBT rights in Australia, being the first in the country to decriminalise homosexuality and to introduce a non-discriminatory age of consent for all sexual activity. Subsequently, the state fell behind other Australian jurisdictions in areas including relationship recognition and parenting, with the most recent law reforms regarding the recognition of same-sex relationships, LGBT adoption and strengthened anti-discrimination laws passed in 2016 and went into effect in 2017.

Marriage in New Zealand is governed by an Act of Parliament. The minimum marriage age is 18 years, or 16 years with consent of the Family Court. Polygamous marriages are not permitted in New Zealand. There are prohibitions of marriages between some relatives and some who are already in a civil union.

The Marriage Amendment Act 2013 is an Act of Parliament in New Zealand, which since 19 August 2013, allows same-sex couples to legally marry.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Australian state of Tasmania have the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. Tasmania has a transformative history with respect to the rights of LGBT people. Initially dubbed "Bigots' Island" by international media due to intense social and political hostility to LGBT rights up until the late 1990s, the state has subsequently been recognised for LGBT law reforms that have been described by activists such as Rodney Croome as among the most extensive and noteworthy in the world. Tasmania's criminal penalties for homosexual activity were the harshest in the Western world when they were repealed in 1997. It was the last Australian jurisdiction to decriminalise homosexuality after a United Nations Human Rights Committee ruling, the passage of federal sexual privacy legislation and a High Court challenge to the state's anti-homosexuality laws. Following decriminalisation, social and political attitudes in the state rapidly shifted in favour of LGBT rights ahead of national trends with strong anti-LGBT discrimination laws passed in 1999, and the first state relationship registration scheme to include same-sex couples introduced in 2003. In 2019, Tasmania passed and implemented the world's most progressive gender-optional birth certificate laws. In July 2023, the Tasmanian government officially included and also added "asexual or asexuality".

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Australia's Northern Territory have the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. The liberalisation of the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Australia's Northern Territory has been a gradual process. Homosexual activity was legalised in 1983, with an equal age of consent since 2003. Same-sex couples are recognised as de facto relationships. There was no local civil union or domestic partnership registration scheme before the introduction of nationwide same-sex marriage in December 2017, following the passage of the Marriage Amendment Act 2017 by the Australian Parliament. The 2017 Australian Marriage Law Postal Survey, designed to gauge public support for same-sex marriage in Australia, returned a 60.6% "Yes" response in the territory. LGBT people are protected from discrimination by both territory and federal law, though the territory's hate crime law does not cover sexual orientation or gender identity. The territory was the last jurisdiction in Australia to legally allow same-sex couples to adopt children.
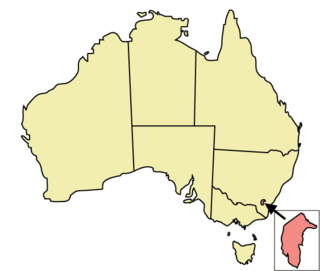
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT) is one of Australia's leading jurisdictions with respect to the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people. The ACT has made a number of reforms to territory law designed to prevent discrimination of LGBTQ people; it was the only state or territory jurisdiction in Australia to pass a law for same-sex marriage, which was later overturned by the High Court of Australia. The Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, New South Wales and Queensland are the only jurisdictions within Australia to legally ban conversion therapy on children. The ACT's laws also apply to the smaller Jervis Bay Territory.
Transgender rights in Australia have legal protection under federal and state/territory laws, but the requirements for gender recognition vary depending on the jurisdiction. For example, birth certificates, recognised details certificates, and driver licences are regulated by the states and territories, while Medicare and passports are matters for the Commonwealth.

Transgender and non-binary people in New Zealand face discrimination in several aspects of their lives. The law is unclear on the legal status of discrimination based on gender identity, and also for intersex people.















