
A civil union is a legally recognized arrangement similar to marriage, created primarily as a mean to provide recognition in law for same-sex couples. Civil unions grant some or all of the rights of marriage.

The Civil Partnership Act 2004 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, introduced by the Labour government, which grants civil partnerships in the United Kingdom the rights and responsibilities very similar to those in civil marriage. Initially the Act permitted only same-sex couples to form civil partnerships. This was altered to include opposite-sex couples in 2019. Civil partners are entitled to the same property rights as married couples, the same exemption as married couples regarding social security and pension benefits, and also the ability to exercise parental responsibility for a partner's children, as well as responsibility for reasonable maintenance of one's partner and their children, tenancy rights, full life insurance recognition, next-of-kin rights in hospitals, and others. There is a formal process for dissolving civil partnerships, akin to divorce.
Civil partnership in the United Kingdom is a form of civil union between couples open to both same-sex couples and opposite-sex couples. It was introduced via the Civil Partnership Act 2004 by the Labour government. The Act initially permitted only same-sex couples to form civil partnerships, but the law was expanded to include opposite-sex couples in 2019.
The Christian Democrat Party of New Zealand was a Christian socially conservative political party established in 1995. It contested the 1996 general election as part of the Christian Coalition with the Christian Heritage Party.

Richard Westwood Worth was a New Zealand politician of the New Zealand National Party. He was the Member of Parliament for Epsom from 1999 to 2005 and a list MP from 2005 to 2009.
This article contains a timeline of significant events regarding same-sex marriage and legal recognition of same-sex couples worldwide. It begins with the history of same-sex unions during ancient times, which consisted of unions ranging from informal and temporary relationships to highly ritualized unions, and continues to modern-day state-recognized same-sex marriage. Events concerning same-sex marriages becoming legal in a country or in a country's state are listed in bold.
The Marriage Act 1961(Cth) is an act of the Parliament of Australia which regulates marriage in Australia. Since its passage in 1961, it has been amended on numerous occasions and applies uniformly throughout Australia (including its external territories); and any law made by a state or territory inconsistent with the Act is invalid. The Act was made under the power granted to the federal parliament under section 51(xxi) of the Australian Constitution. Before the passage of the Act, each state and territory had its own marriage laws. The Act only recognises monogamous marriages that comply with the requirements of the Act; other forms of union, including traditional Aboriginal marriages, are not recognised. However, the Family Law Act 1975 treats de facto relationships and polygamous marriages as marriages for the purpose of recognising the rights of parties at a breakup. Since 2009, the Family Law Act 2009 has also recognised the property rights of each partner of de facto relationships on separation.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in New Zealand since 19 August 2013. A bill for legalisation was passed by the House of Representatives on 17 April 2013 by 77 votes to 44 and received royal assent on 19 April. It entered into force on 19 August, to allow time for the Department of Internal Affairs to make the necessary changes for marriage licensing and related documentation. New Zealand was the first country in Oceania, the fourth in the Southern Hemisphere, and the fifteenth in the world to allow same-sex couples to marry. Civil unions have also been available for both same-sex and opposite-sex couples since 2005.

New Zealand lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights are some of the most extensive in the world. The protection of LGBT rights is advanced, relative to other countries in Oceania, and among the most liberal in the world, with the country being the first in the region to legalise same-sex marriage.

The Civil Union Act 2004 is a New Zealand act of parliament legislating civil unions. It was passed into law on Thursday 9 December 2004 by a final vote of 65–55 in the New Zealand Parliament. The act makes it legal for those in same-sex as well as heterosexual relationships to enter into a civil union.

The legal status of same-sex marriage has changed in recent years in numerous jurisdictions around the world. The current trends and consensus of political authorities and religions throughout the world are summarized in this article.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Australia since 9 December 2017. Legislation to allow it, the Marriage Amendment Act 2017, passed the Parliament of Australia on 7 December 2017 and received royal assent from Governor-General Peter Cosgrove the following day. The law came into effect on 9 December, immediately recognising overseas same-sex marriages. The first same-sex wedding under Australian law was held on 15 December 2017. The passage of the law followed a voluntary postal survey of all Australians, in which 61.6% of respondents supported legalisation of same-sex marriage.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Queensland have advanced significantly from the late 20th century onwards, in line with progress on LGBTQ rights in Australia nationally. 2019 polling on gay rights consistently showed that even in regional areas, Queensland is no more conservative about the subject than any other states.
Same-sex marriage is legal in the Australian Capital Territory, and in the rest of Australia, after the Federal Parliament legalised same-sex marriage in December 2017.

This article details the history of the LGBTQ rights movement in Australia, from the colonial era to the present day.

Marriage in New Zealand is governed by an Act of Parliament. The minimum marriage age is 18 years, or 16 years with consent of the Family Court. Polygamous marriages are not permitted in New Zealand. There are prohibitions of marriages between some relatives and some who are already in a civil union.

The Marriage Act 2013 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which introduced same-sex marriage in England and Wales.

The Marriage Amendment Act 2013 is an Act of Parliament in New Zealand, which since 19 August 2013, allows same-sex couples to legally marry.
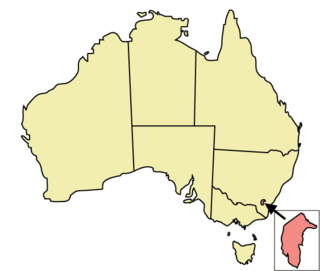
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT) is one of Australia's leading jurisdictions with respect to the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people. The ACT has made a number of reforms to territory law designed to prevent discrimination of LGBTQ people; it was the only state or territory jurisdiction in Australia to pass a law for same-sex marriage, which was later overturned by the High Court of Australia. The Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, Queensland and both South Australia and New South Wales representing a population of 85% on Australia – explicitly ban conversion therapy practices within their jurisdictions by recent legislation enacted. The ACT's laws also apply to the smaller Jervis Bay Territory.
The history of same-sex marriage in Australia includes its express prohibition by the Howard government in 2004 and its eventual legalisation by the Parliament in December 2017. Although a same-sex marriage law was passed by the Australian Capital Territory in 2013, it was struck down by the High Court on the basis of inconsistency with federal law. The Court's decision closed the possibility of concurrent state or territory laws that would allow same-sex marriage where federal law did not. A law legalising same-sex marriage passed the Parliament on 7 December 2017 and received royal assent the following day.











